It seems like an ethernet connection will always be faster for many people than a wireless connection, and that’s a fair assumption. A wireless connection running on the same network as an ethernet connection will be slower as a wireless connection is subject to more interference than a direct-wired connection.
If your wireless signal is faster than your ethernet, it may be a glitch, or a few different things may be happening to cause it.
Which is Faster: Wi-Fi or Ethernet?
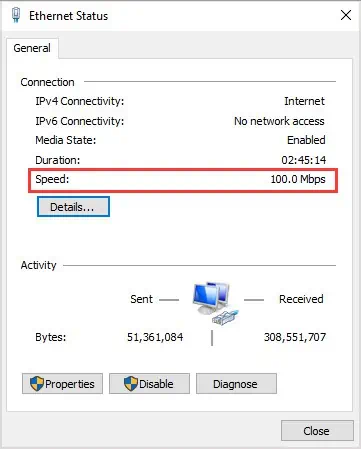
The fastest connection is a connection that has a higher speed cap. For example, I get around 500 Mbps download speed on a wireless network while my best friend gets less than 100 Mbps on ethernet – but we live in two places with two internet plans that have differing speed caps.

Within my household, people who connect directly to the router get faster speeds than those who consistently use wireless.
However, that isn’t the case for everyone. Many factors affect your internet speed, from the equipment you’re running to where certain things are positioned in your house.
For most people, though, ethernet connections are faster than Wi-Fi. If you’re hoping to get the best possible connection to a device, hook it up to a wired connection. Whenethernet isn’t workingin the way you expect, you need to investigate to find out what’s wrong and create a better network connection.
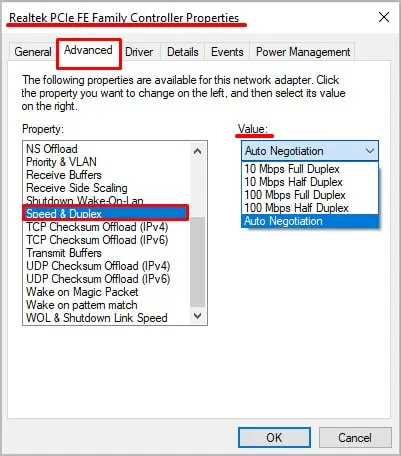
Why is Ethernet Faster?
Ethernet is faster because it’s a direct-wired connection. It isn’t as subject to interference and positioning issues because the signal doesn’t have to transmit through the air.
Why is My Wi-Fi Faster than Ethernet
There are many reasons why your Wi-Fi signal might be faster than your ethernet signal. To figure out which one it is, you may do a few things.
Check Your Ethernet Cables
If your equipment is outdated, you may not be getting your optimal speeds. For example, an old cable or one that has been damaged somehow might not transmit the speed your service is capable of.
For most people, the length of theethernet cableshouldn’t be a significant concern. If you’re using an exceptionally long one, though without the need to do so, consider switching to a shorter cord. Sometimes you may experience data loss and slower speeds as the cable length increases.
A damaged or degraded cable is a much larger concern. Before purchasing a cable, check to see whether it supports your internet speed. If you’re running a connection faster than 1 Gbps, you will want a cord that supports that speed. Look for a cable that’s ratedCat 6 or higher. Some people recommend against using Cat 7 cables, so it might be best to look for 6 or 8.