PSU restarts are random and unpredictable. Unlike computer restarts that occur under certain circumstances, thesedo not display error messagesor follow any particular sequence. Instead, the system suddenly shuts down and undergoes a reboot—and you might also hear aclicking soundalong with it.
When I got my first PC a decade ago, it kept restarting non-stop from day one. After a bit of exploration, I came to know that there was a manufacturing defect in my PSU. But not all PSUs come with a similar defect.
If your PSU keeps restarting, firstverify if it meets the power requirementof your build. If that is fine, maybe there is a problem in thepower supply connectoror the PSU itself. In such cases, you have totest your PSU for faults.

Calculate the Power Requirement
As a rule of thumb, it is always recommended to get a PSU that can deliver significantly higher power than the actual power demand of your system. In fact, most manufacturers recommend keeping a margin of 25%, and so do I.
If the power requirement of the system nears or exceeds thePSU wattage, you will certainly experience unwanted restarts due to overloading. You might also experiencepower supply overheatingwhen the PSU fails to meet the power demands of the system.
I once happened to installRTX 3080Tiinto my build with a650W PSU. The power requirement of the GPU was so high during the intensive gaming sessions that the PSU could not withstand it and kept restarting. I thenupgraded to a 850W PSUwhich solved all my problems in the blink of an eye.
Having said that, I don’t mean to say you need an upgrade too. Before coming to a conclusion, first use any online power supply calculator like the one from theCooler Masterand check how much power your system actually uses. If it comes to exceed the PSU wattage, considergetting a new one.
Underclock PC Components
If you have overclocked your PC components, likeCPUorGPU, the power draw will be comparatively higher than on the normal conditions. Furthermore, there might be sessions when the power draw of your PC suddenly surpasses the rated output power of the PSU, mostly if you have an underpowered PSU. It can cause instabilities in the PSU, triggering the restart.
Therefore, it is always a better idea to get a PSU with a wattage headroom of about 40% if you are into overclocking.

On the other hand, you may underclock the components or disable overclocking, if you no longer require it. You mayreset the BIOSto do the needful.
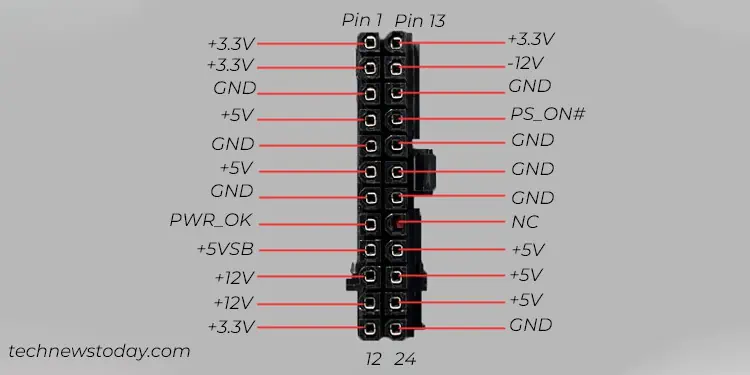
Now that you have verified the power requirement and checked overclocking, let’s test the PSU for faults. Oftentimes, you may determine if thePSU is faultysimply by testing the output voltage levels in the power connectors.
As seen in the image above, each of the voltage pins in the24 pin ATX power connectorshould receive the designated voltage levels at a tolerance limit of ±5%. If there is a huge difference between the expected and actual voltage levels, you may confirm that your PSU has faults.

You will basically need a multimeter to test your PSU for faults. Along with the 24 pin connector, you should also test the CPU,SATA, PCIe, and Molex connectors too, if applicable. you may go through this comprehensive guide tosafely test your PSU.