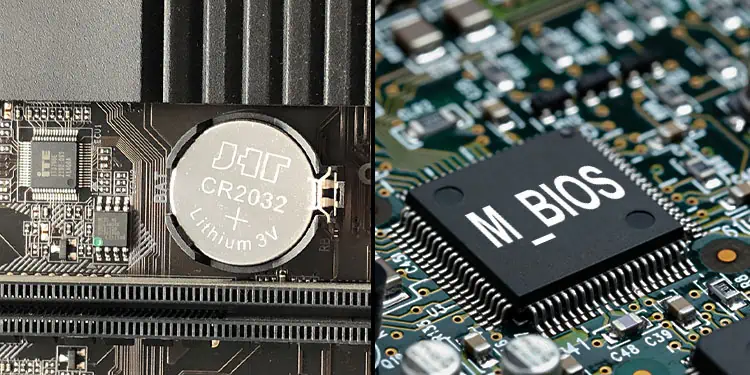
If you have ever examined the motherboard, you may have seen multiple Integrated Circuit (IC) chips soldered onto the motherboard.One of the IC chips contains the lines of code that hold the BIOS.
Just looking at the motherboard, you may not be able to locate the BIOS chip. Depending on the motherboard manufacturer, there could be any markings on the board that indicate the BIOS chip, such as M_BIOS, B_BIOS, UEFI BIOS, etc.
Where Is the BIOS Chip Located?
Two crucial chips are related to the BIOS. One is the CMOS EEPROM chip that holds the BIOS program, and another is the CMOS RAM chip that storesBIOS settings.
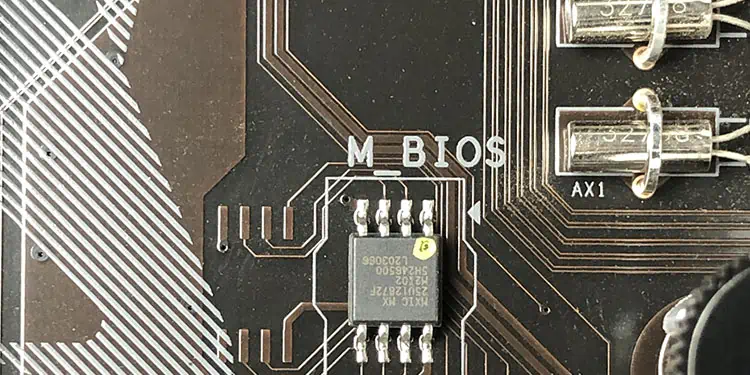
The first one is the CMOS EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) chip that holds the BIOS program. This chip is usually denoted as M_BIOS or B_BIOSon the motherboard. But these notations are not universal.Depending on the motherboardmanufacturer, the notation used to mark the BIOS location could be different.
So we recommend you check your motherboard’s user manual to check the actual notation for your motherboard that indicates the BIOS chip.
The second chip is the CMOS memory chip which holds the BIOS settings. These are volatile memory. Meaning that these chip will remove data inside it once youremove the power supply. So they require a separate power source to store the information once you turn off the system. This is done with the help of a CMOS battery.

The chip that stores the BIOS settings is usually near the CMOS battery.
How Does the BIOS Chip Work?
The IC chip that holds the BIOS is a non-volatile CMOS EEPROM chip. Meaning that the chip won’t lose data stored inside it even when you cut off the power supply. This is why the BIOS does not get deleted even when you remove the CMOS battery and turn off the power supply in your system.
BIOS is the first software the motherboard runs when you turn it on. Your motherboard is programmed such that the BIOS automatically runs as soon as it gets power. Once the BIOS runs, it checks necessary hardware to run the entire system.
When the system starts, the BIOSruns a POST(Power-On Self-Test). During POST, the BIOS checks and verifies all the hardware components connected to the motherboard.
These components include RAM,CPU processor, Input-output Controller Hub, graphics card, keyboard, mouse, etc.If the BIOS fails to detect crucial hardware components, such as the CPU and RAM,themotherboard sends beep codesindicating component detection failure.
Once the BIOS completes POST, it checksstorage devicesfor an Operating System and then loads it into the RAM.

How are BIOS Settings Saved?