A thermal pad’s job is to fill in the large gap between the heat sink and certain computer parts to maintain proper heat dissipation. You need to consider its thickness, hardness, orientation, and so on while choosing a thermal pad.
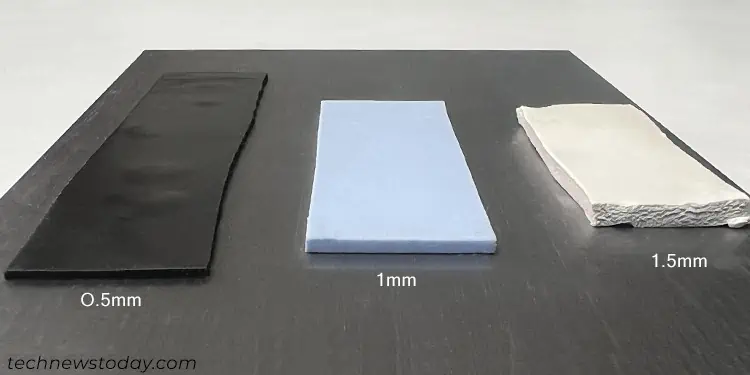
As far as thickness is concerned, I recommend using1mm and 1.5mm padin most cases. But you may need to usemore than one type of padon your device, especially if it’s a graphics card. Also, different devices may require different sizes of thermal pads for the most efficient cooling.
Does Thermal Pad Thickness Matter?
Most thermal pads have 0.5mm, 1mm and 1.5mm thickness since these are suitable formost GPUsandNVMe solid state drives (SSDs)out there. But you’ll also find devices that need much thicker pads.
The thickness of the thermal paste affects its thermal conductivity and the contact between the device and the heatsink. All these factors impact the heat dissipation, process and, consequently the cooling system. Let’s discuss them in more detail.
Contact between Heat Sink and Device Components
Devices like the graphics card and NVMe SSDs have components with different heights which also depends on the manufacturer. So they normally use thermal pads as a thermal interface between the device and the heat sink.
The pad’s job is to bridge the gap between the components and the heatsink and provide a large contact area for proper heat dissipation. If you use athin thermal pad, it may not contact all the components or the heat sink.
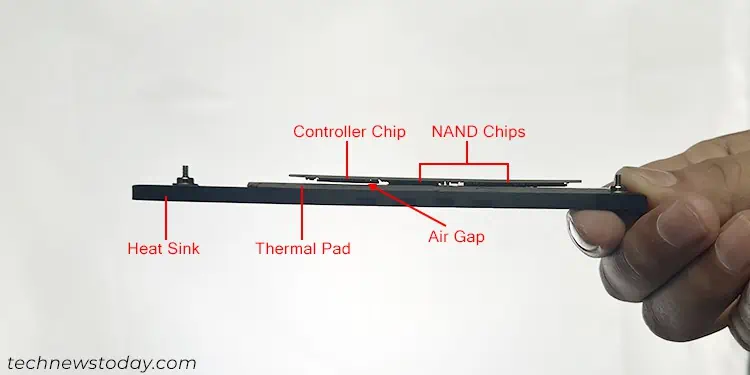
So you need a minimum thickness for the pad depending on the type and design of the device.
While thermal pads serve to provide better contact between the device components and the heatsink, its thermal conductivity is not that much high. So if you use athicker pad, it will decrease the rate of heat dissipationand affect the cooling process.
You need to utilize the thinnest possible heatsink while maintaining proper contact to effectively maintain your NVMe orGPU temperature.
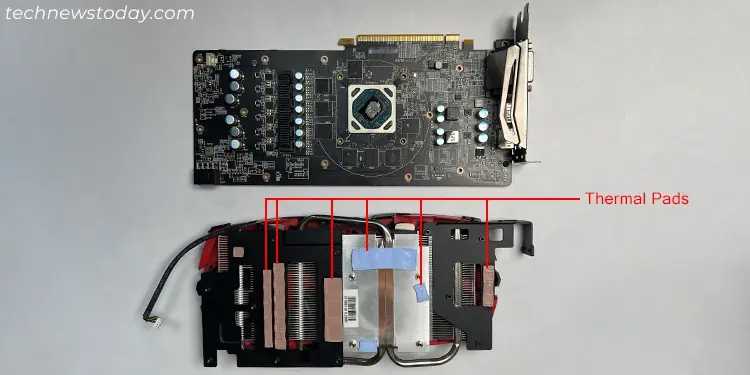
Note: Apart from the thickness of the pad, its hardness also matters while determining the most effective cooling solution.
In general, you want to use softer pads that compress easily and maintain contact over all the components. A hard thermal pad may also smush and damage the components. However, it can’t be so soft that the pad deforms easily.
Thermal Pad Thickness for NVMe
Generally, most NVMe or M.2 heat sinks come with1mm or 1.5mm thermal padsand that’s the size you would want. I don’t recommend using 0.5mm heat sinks at all as they may be too thin to maintain proper contact with the NVMe’s components.