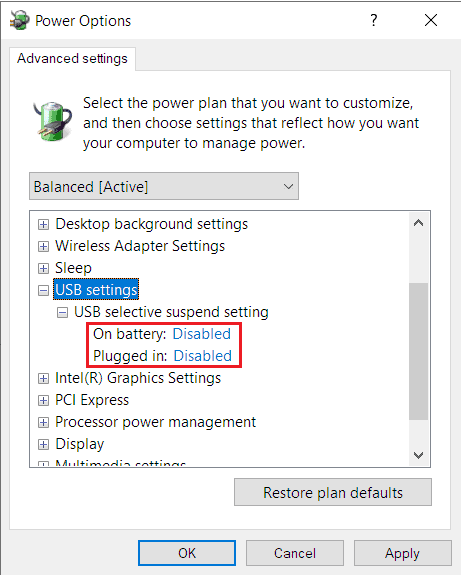
You might have come across the USB Selective Suspend setting while looking through the advanced power plan settings. Many troubleshooting guides also mention that you need to disable this setting to resolve USB problems.
This setting is enabled by default and as such, most users wonder if disabling it causes any issues in their system.
The short answer to this question is that USB Selective Suspend is a power saving feature and whether you may disable it depends on your scenario.
In this article, we have explained this feature in detail to help you decide if you should turn it on or off by yourself.
What is USB Selective Suspend?
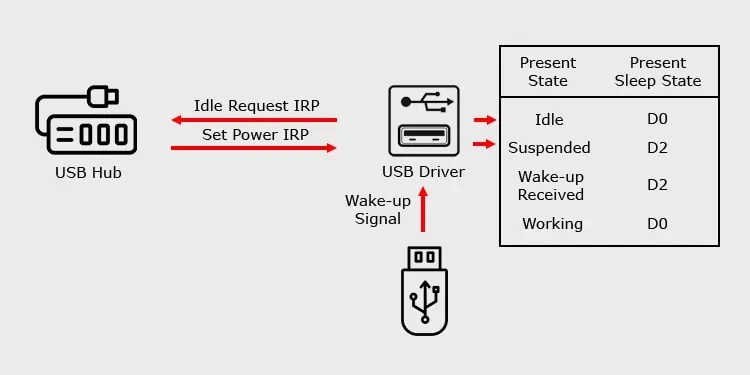
USB selective suspend is a Windows feature that allows the USB hub driver to suspend asingle USB portwithout affecting other ports. This is a power-saving feature that suspends the port when it has been idle for some time.
However, you shouldn’t confuse suspend with disable. The driver doesn’t cut off all power from the ports but powers it down to a low power state.
The suspended USB can respond to the external wake signal if its remote wake-up capacity is enabled. The USB devices produce the wake signals when you insert it to the port.
One thing you should know is that all devices don’t produce wake up signals. Mice, keyboards, modems, external USB hubs, etc., have wake-up capability. However, some devices such as mass storage devices, audio and video device, and so on don’t have such capacity.
To understand the full process for USB Selective Suspend, let’s take a look at the USB power/sleep states and the mechanism behind it.
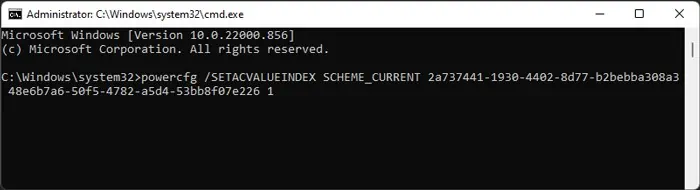
There are many models of USB power states. However, if we want to discuss the selective suspend, we utilize the Windows Driver Model (WDM), which has D0 to D3 power states.
The D-state is different from S-state (system’s power level) andC-state (processor’s power level). So, they can have different values. However, a higher D-state can prevent other states from going to a lower level.
In this power state, all USB ports on the computer have full power and receive requests as soon as you connect a device. So, lowering the power state from D1 to D0 disables the suspension of the ports.
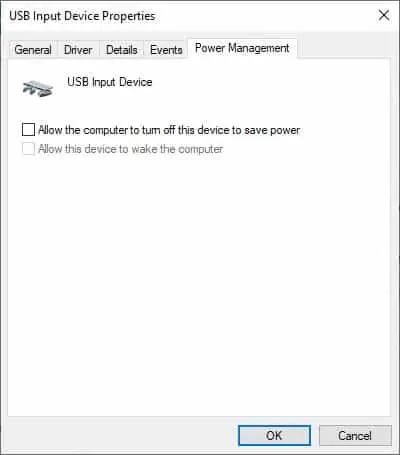
Since there’s no need to remotely wake up the port, the driver also disables the remote wake up feature.
In this power state, the bus driver suspends the USB ports. However, it enables the remote wake feature, allowing the port to respond to external wake signals.