You must have noticed Triple Buffering in some games graphic settings. Depending upon the games played, the triple buffering setting may vastly influence your gameplay experience.
Aware of normal YouTube buffering, many do not know how exactly buffering and triple buffering work. This creates a skeptical perspective towards enabling or disabling the feature.
In this article, we’ll attempt to explain triple buffering and address the question of whether you should turn it on or off.

What is Buffering? How Does It Help in Displaying Graphics?
First of all, let’s know how graphics on the computer is displayed. We’ll take a simple analogy of a video game being played on a monitor with a 30Hz refresh rate. The monitor switches 30 still photos or frames in one second to make it look like it’s in motion i.e it takes 33.33 milliseconds to display a single frame. The time gradually decreases as we move to the monitor with a higher refresh rate.
But, those pictures aren’t like usual taken and stored pictures. The pictures/frames in a video game are generated in real time by the graphics processor.
The GPU possesses a certain frame render speed. The monitor also has a definite value regarding how many frames it can show per second, i.e., refresh rate. Generally,refresh rates of Monitorsare lower than the GPUs’ rendering speeds for low-end games.

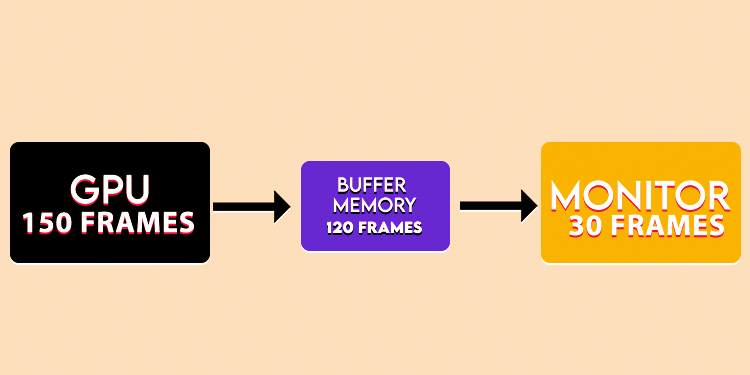
Suppose, for a particular game your GPU has the ability to generate 150 frames in a second. But, a monitor with a 30Hz refresh rate can’t display more than 30 frames per second. The refresh rate threshold of a monitor won’t let the GPUs run at their optimum capacity and cause screen tearing, FPS jumps, etc.
Buffers exist to take advantage of potentially higher render speeds of GPUs. They refer to the temporary spaces in dynamic memory to store data just before it gets fetched. GPUs can store the exceeding amount of generated frames within the buffer memory. So that the pre-rendered frames can be shown on the screen after the current frames are over.
This helps the GPU pre-calculate the required frame and focus on the upcoming frames, which smoothens the real-time experience. It also helps in coping with GPUs’ render speed fluctuations.
What is Multiple Buffering?
Instead of a single buffer, we can use multiple buffers to optimize the rendering process. Double and Triple Buffering are the widely used methods under Multiple Buffering.
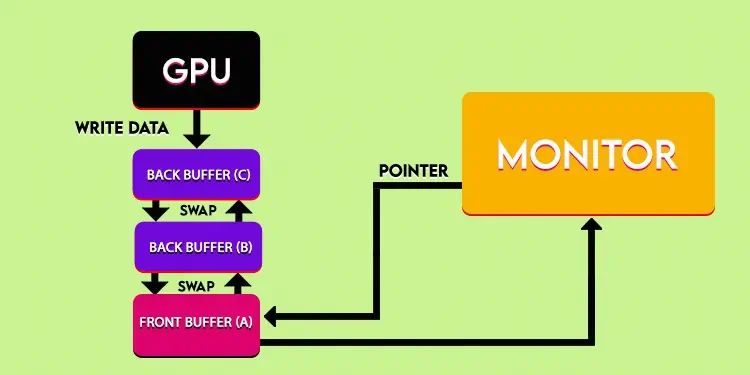
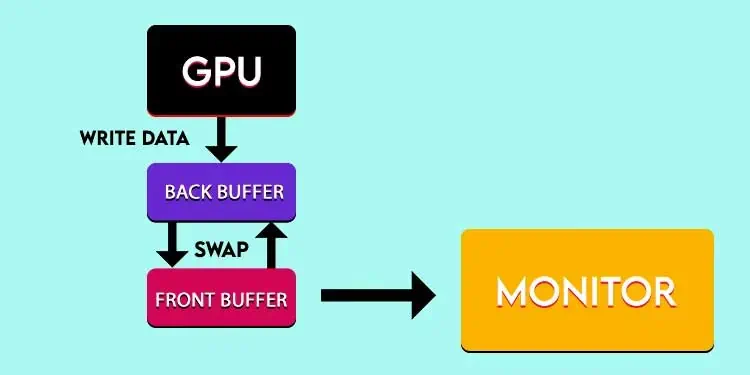
Double buffering offers two buffer spaces for the GPU to store the rendered images. Actually, one buffer(front buffer) itself shows the images on screen while GPU bakes the next frame on another empty buffer(back buffer). After the front buffer is displayed, it flips with the back buffer, which has a pre-rendered frame.
Now, the previous front buffer that switched to be the back buffer is emptied, and the next frame is posed into it. Then, the flipping cycle repeats. It’s faster than single buffering because it flips the display pointer towards a frame-ready buffer, meanwhile letting the GPU render another frame on the recently used buffer.
What is Triple Buffering?