Your computer needs to perform multiple functions before it loads up the Operating system. One such function is the Power on Self Test (POST) which tests the components attached to the computer and ensures that they are ready to be used by the system.
Although POST is a common process on many digital electronic devices, it is most often linked with computers. This test is crucial to detect the issues with the components and convey them to the users with error messages.
We will discuss this topic more, giving you a general idea of how POST works on your computer, why is it important, and how to solve the error detected during the POST.
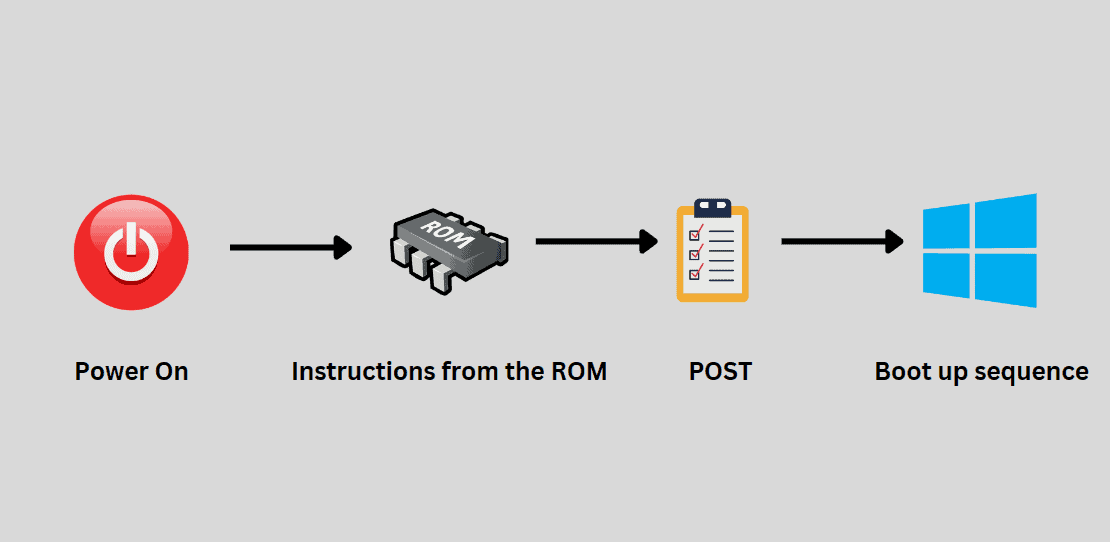
What is Power on Self Test (POST)?
Power on self-test (POST) is a system diagnostic process that is carried out by the BIOS right after you power on the computer. The main function of this test is to see if the components connected to your computer are functioning well.
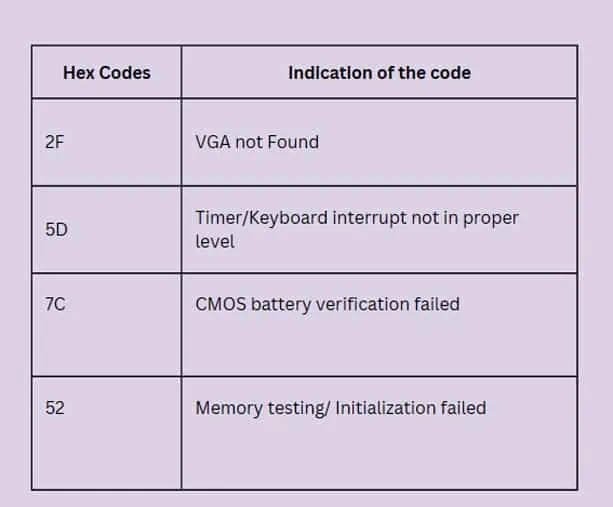
POST checks the hardware components installed on your computers such as the RAM, hard drive, processor, and others, and ensures these are functioning as intended. After the test is completed or if there are some issues detected, the system notifies the user with an error code using beep sounds,LED light flashes, or a hexadecimal POST code.
Once the POST is completed by the BIOS, it passes control to the bootstrap loader function on the system BIOS. Bootstrapping provides a set of instructions for the system to load the Operating system by checking the hard drives and other bootable devices.
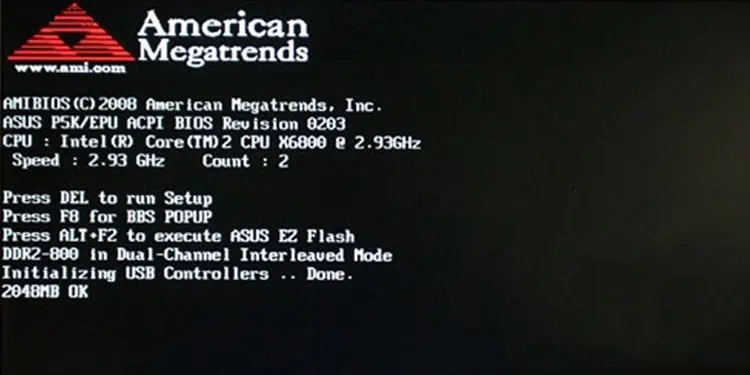
The POST process starts immediately after you turn on the computer by pressing the power button. When the Power button of the computer is pressed the electric current flows all the way through the circuits to different components including the ROM BIOS.
Note: This test starts only if the computer is cold-booted i.e if the computer is powered on after a shutdown. The system will skip the POST if the computer is restarted or warm-booted.
The CPU seeks the first phase of instructions that are required for the startup from the BIOS Chip. BIOS stores a set of guidelines on specific memory addresses to run the Power on Self Test. POST usually follows this sequence while conducting the tests.
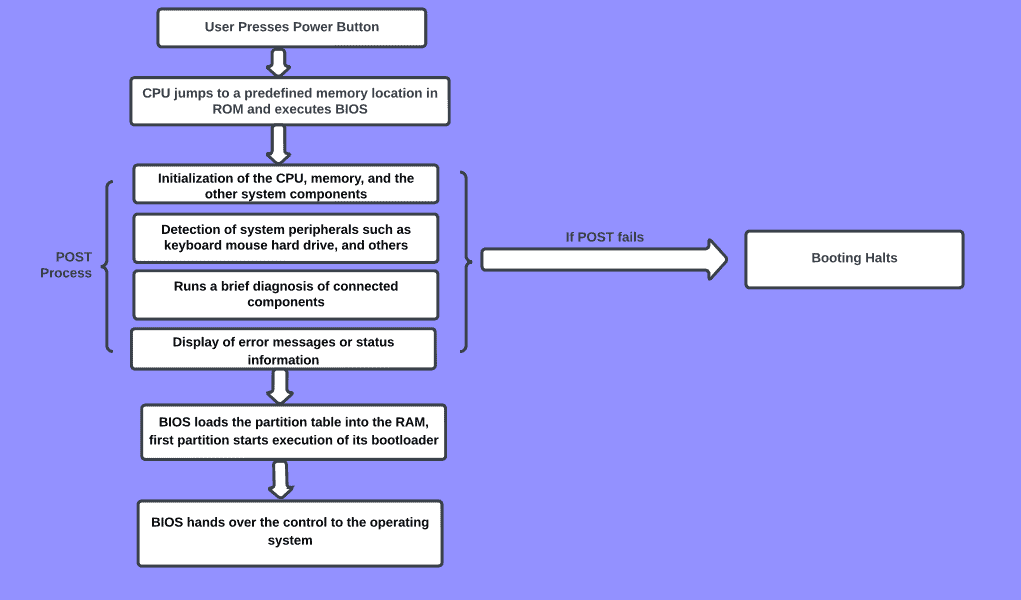
Once these hardware components are checked and initialized, the POST heads toward the test of Nonsystem Hardware components. It initializes the configuration and nonsystem board components in this sequence:
After the POST is complete, the start-up program is ordered to find the Master Boot Record (MBR). This is located in the first sector of your computer’s Hard drive (C drive for instance). The MBR then reads the boot-strap which locates the startup file of the Operating system. The control of the system is then handed over to Windows, Linux, or any other operating system you are using.
Signs that PC has Failed POST
If POST identifies some problem with the hardware components of your computer and fails the test, the system will not boot into the Operating System. It will then notify about the issues in the computer through beep sounds, text messages on the screen, LED light codes, or POST codes. If POST cannot display the error message using the Text codes on the screen, it will utilize the beep sound or the LED flashes.
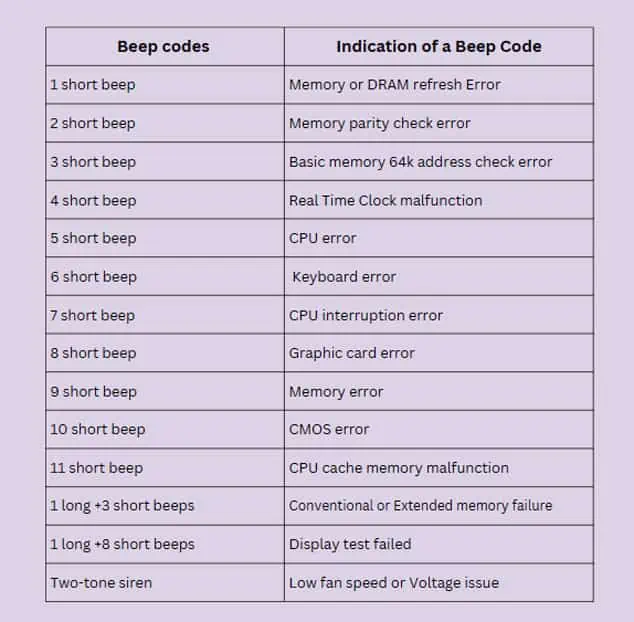
Some system boards also give the error message only using a light code or a beep sound. These error codes are useful to diagnose the problem on your computer and fix them accordingly.