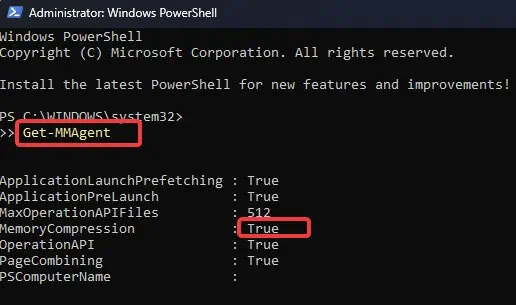
Memory Management is one of the major functions of an Operating system that controls and maintains the memory allocation for each system process. With the introduction of Windows 10 version 1507, Microsoft added Memory compression as the latest addition to its existing Windows Memory Management process.
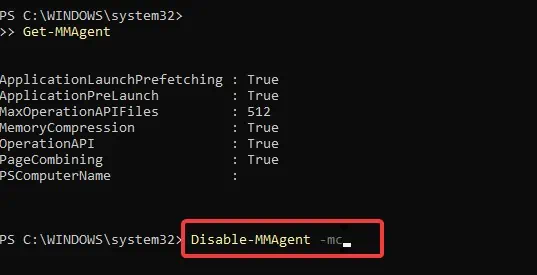
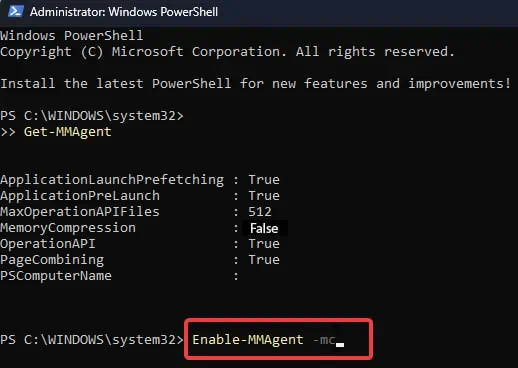
This memory management technique works by reducing memory usage by compressing some information stored in RAM. Although this feature comes enabled by default in Windows 10 and 11 systems, users have the option to disable it anytime.
If you are curious about this feature and wondering whether you should leave it enabled or turn it off, this article can help you decide on that.
What is Memory Compression?
Before we dive into what Memory compression really is, we must have a bit idea about “Paging”. This is a memory management process that uses the secondary memory or the storage drives to reduce the RAM’s workload. When the system detects that theRAM memory is running low, it transfers some sections of system processes, known as Pages, to the hard disk.
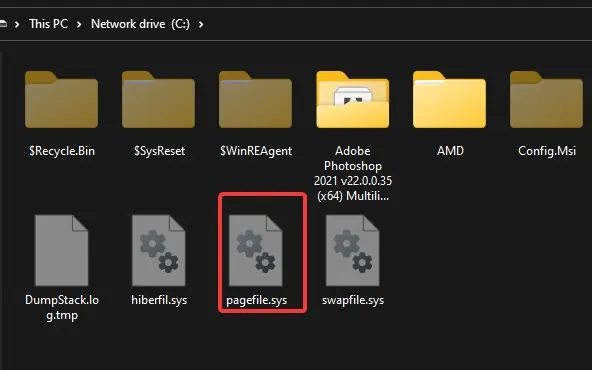
These pages are located in the system volume of Windows (C: drive on most computers) as a file namedpagefile.sys. This file contains information on the processes that are rarely used by the system. The system only retrieves that information from the file when needed. The paging process in this manner saves memory space.
The drawback of paging is that the continuous read-and-write process in the hard drive takes time and causes system slowdowns.
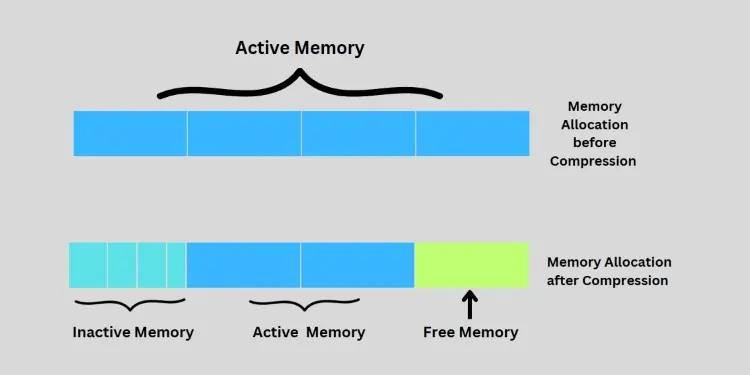
Memory Compressionaddresses this drawback of paging by compressing the infrequently used pages rather than writing them on the disk. This decreases the frequency of reads and writes over the disk and also significantly improves the response time.
Memory compression offers more space for the system processes to be kept in the RAM and allows more tasks to run simultaneously.
How Does Memory Compression Work in Windows?
Microsoft introduced memory compression from Windows 10 version 1507. From Version 1607, memory compression is no longer displayed as a “system and compressed memory” process in Windows and is located under Memory details on the Performance tab.
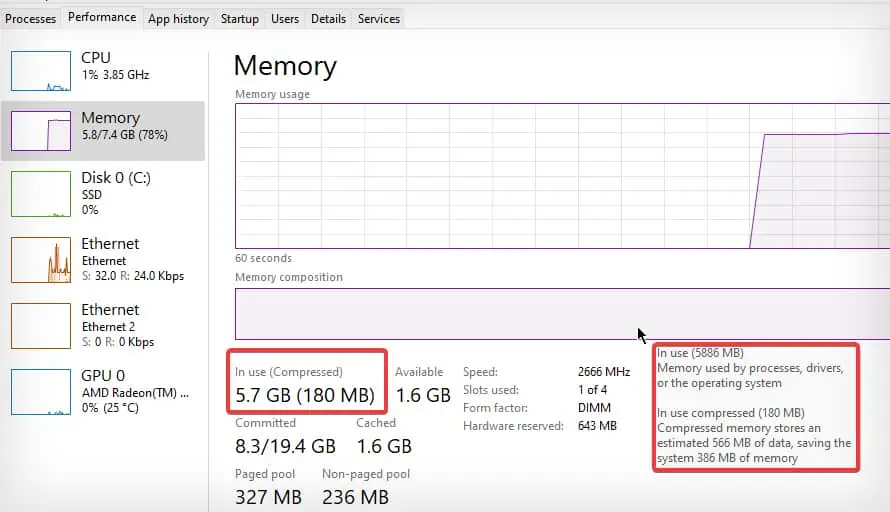
The general concept behind memory compression is to compress the memory pages that are not currently being used by any system processes or application to free up the main memory that can be used by other processes.
This reduces the need for the system to swap memory pages between physical memory and pagefile on disk, which can be a slow and resource-intensive process.
Since accessing the memory is faster than accessing the drives, memory compression can contribute to memory space without significantly reducing the performance. When a page requires to be swapped, it can be first compressed and stored in the memory.
When needed again, the same page is decompressed and returned back. This overall process is way faster than swapping pages to the drives, although a bit slower than accessing the real memory as decompression is required.