Most motherboards include a Real Time Clock (RTC) module that keeps track of your system date and time also known as the BIOS Time.
It’s saved in the CMOS chip and you may set up it from the BIOS/UEFI interface.
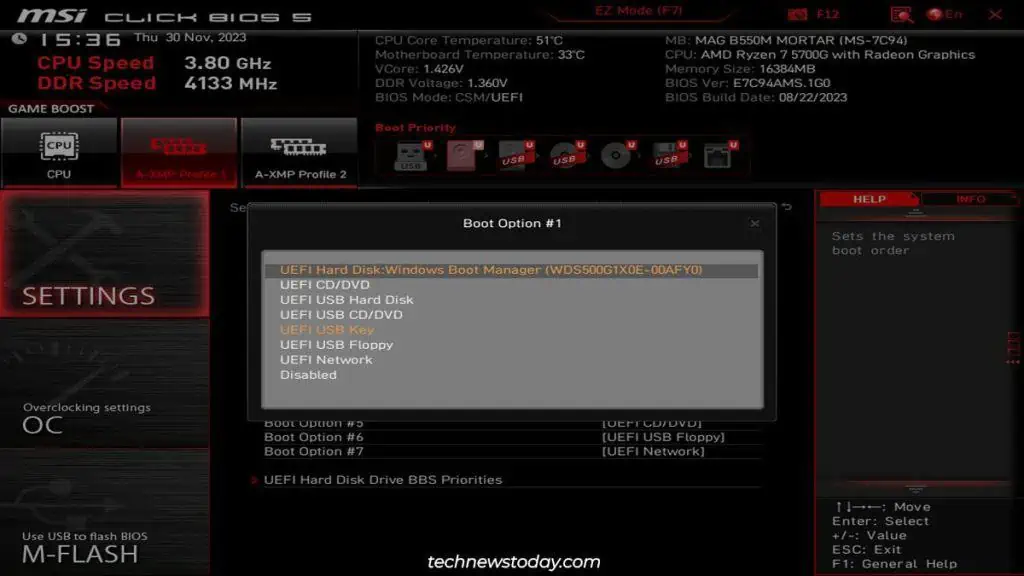
To change the BIOS time,access your BIOS/UEFI interfaceand go to theSystemtab. You’ll be able toset the BIOS date and timethere.
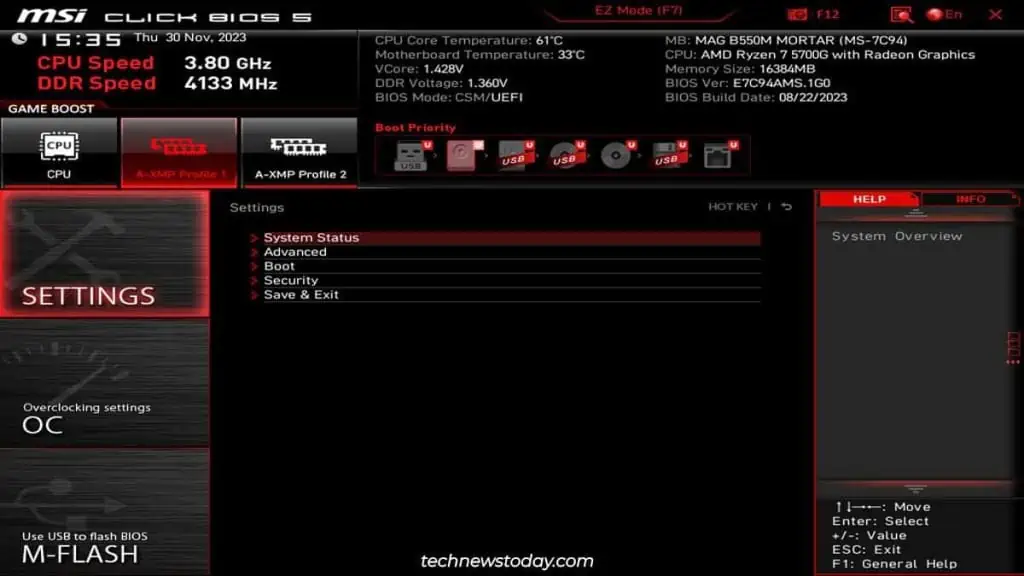
You may be wondering, why is this even necessary ? Doesn’t Windowsautomatically set the correct timefor you? I’ll start by answering all such common queries.
How To Set the BIOS Time
Wheninstalling Windowson a new system, an invalid BIOS time can cause the installation to fail.
After the installation, it’s mainly used for features likeResume by RTC Alarmor network operations like Kerberos authentication.
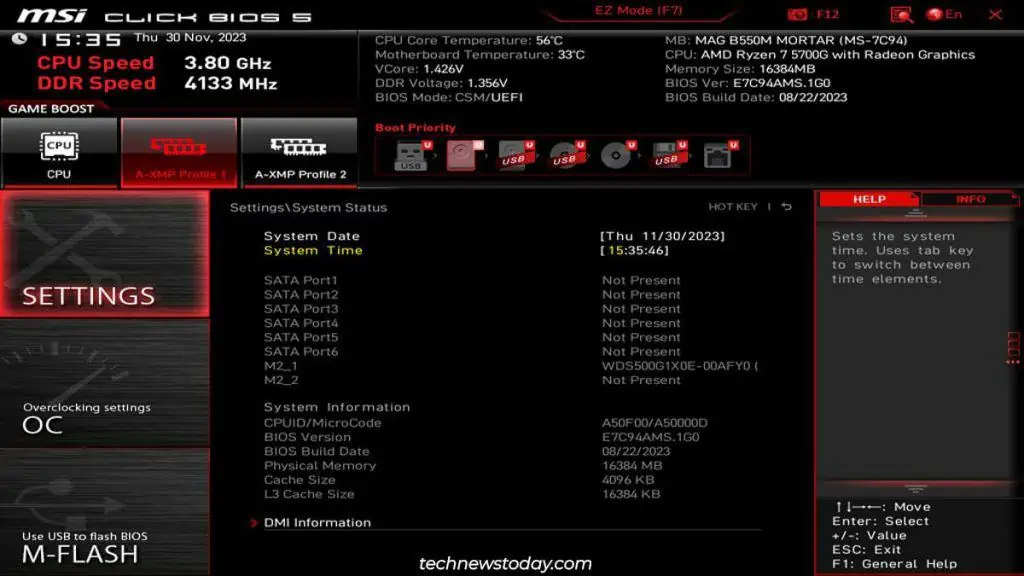
Depending on your setup and needs, you may need toset the BIOS time correctly.
How To Reduce the Last BIOS Time
TheLast BIOS Timestat in the Task Manager is completely unrelated to the system time that we just set in the BIOS.
After you press the power button, the BIOS performs thePower-OnSelf-Test (POST). This mainly involves detecting and initializing the system buses, chipset, and devices.
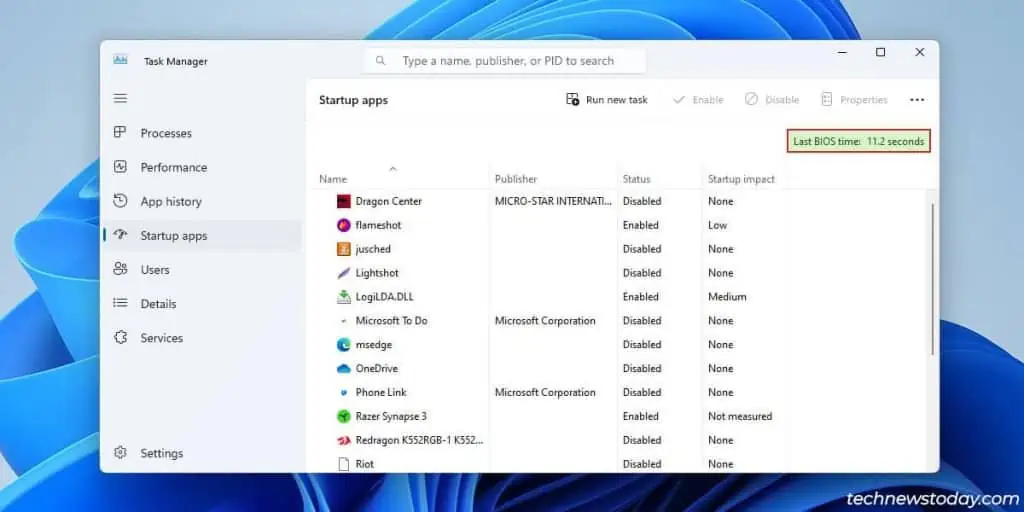
The Last BIOS Time shows how many seconds it takes the BIOS to complete the POST andstart loading the OS.
Onmost modern systems, you may expect the BIOS time to beclose to 10 seconds. Some variation is natural, and not something you need to stress about.
For instance, my PC’s last BIOS time was11.2 seconds. you may check yours from theStartuptab in theTask Manager.
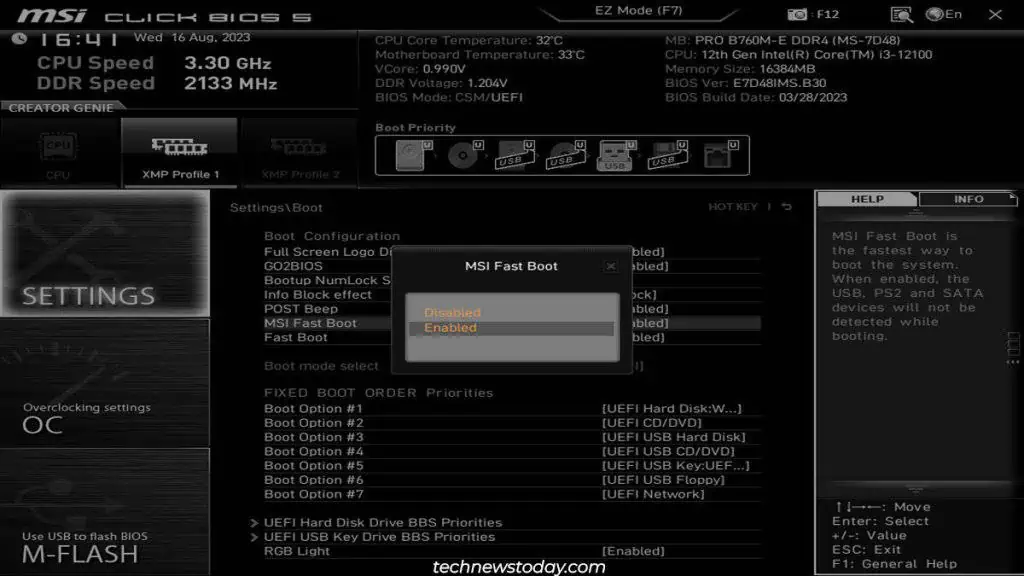
Sometimes, this will be upwards of 20 seconds. If the system boots after exiting the BIOS, this will report the time spent in the BIOS. So, high values (e.g., 217 seconds) are normal.