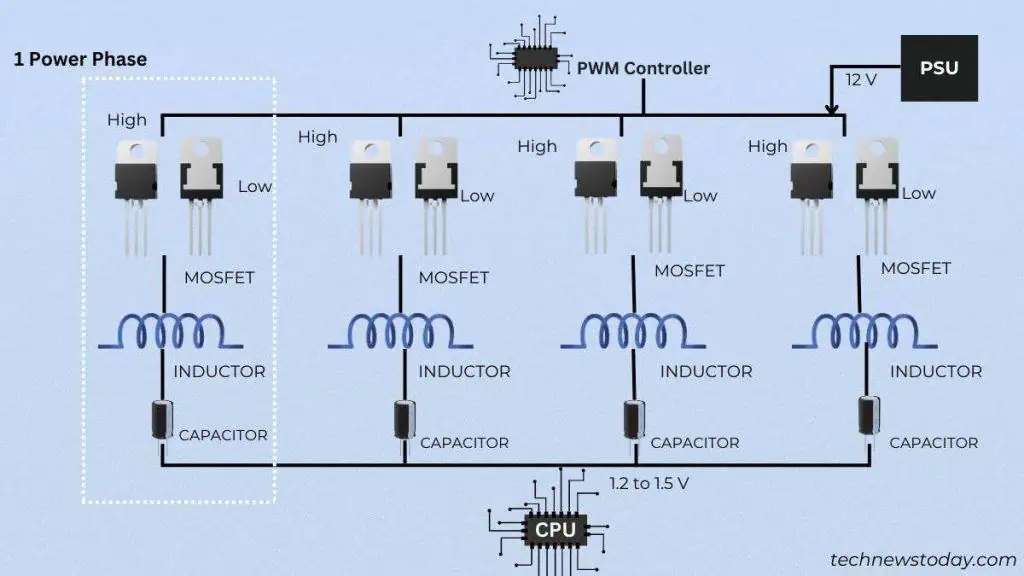
The Voltage Regulatory Module (VRM) section in the motherboardsteps downthe raw12 Vpower supply to1.2to1.45 Vrequired by the processor, RAM, and other components.
While this isn’t the first thing that pops up in our mind when choosing a motherboard, it’s still essential, especially for overclockers.
If you’re seeking higher clock speeds, know that it requiresclean and stable voltage, which is only possible withhigh-quality VRMs.

If your motherboard consists of a low number or poor-quality VRMs, it can significantly impactits lifespan.
It may mess up the power delivery and even lead tofrequent crashing,blue screen errors, andpermanent damage to your PCcomponents.
Buckle up as I’m going to discuss everything you should know about motherboard VRMs in this in-depth guide.

Motherboard VRM Constituents
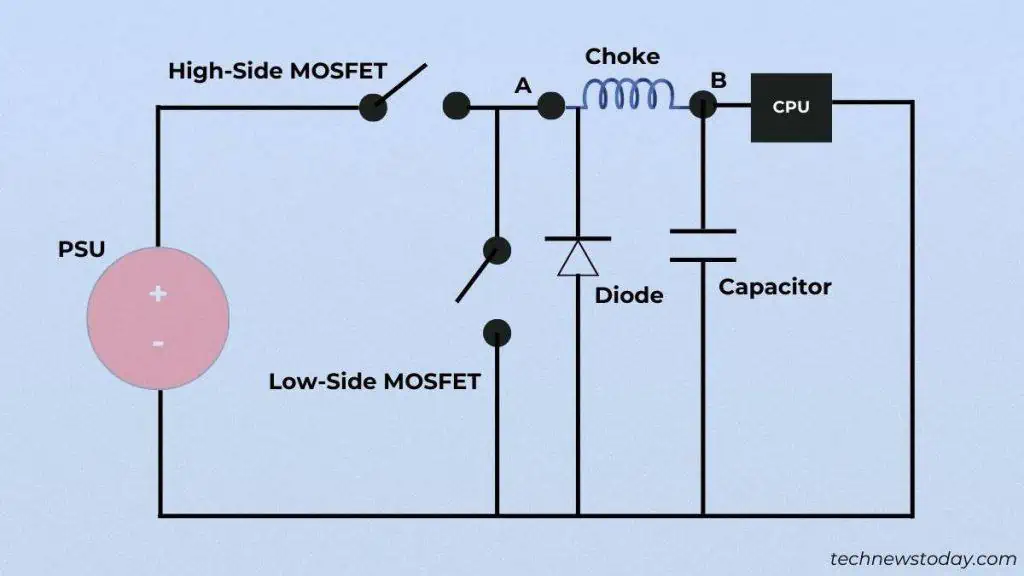
Let me clear this confusion right away – the12 V supplied by the PSUdoesn’t directly reach the processor.
It passes throughdiodes and resistorsbefore landing on the VRM, where the current is stabilized andvoltage is stepped downas per the CPU’s requirement.
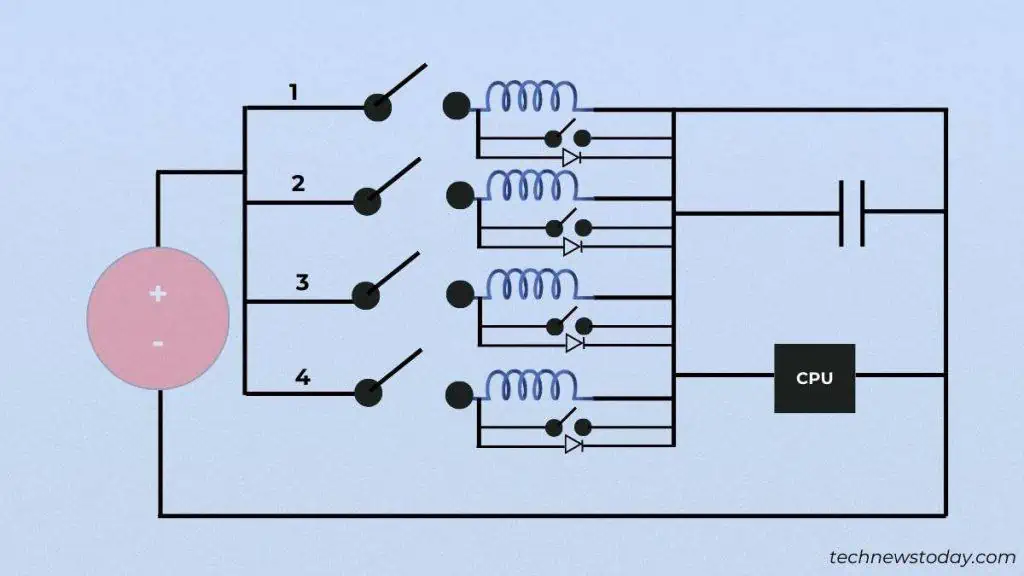
The Voltage Regulatory Module is composed of severalMOSFETs,chokes, andcapacitors. Each of them has a specific function and is essential for proper/clean power delivery.

These components are well scattered around theprocessor socket. Without them,your CPUwould fry out. That said, here are some basic things you should know.
As the name suggests, themetal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistorsare responsible for opening and closing the electronic gates. This means the inductors/chokes are charged onlywhen the switch is closed.
These transistors sit underneath the VRM heatsink. So, it’s pretty easy to guess that these components are the ones thatproduce the most heat. That’s simply because a MOSFET has to open and close thousands of times per second.

While they are designed to withstand temperatures up to 150 degrees,they will eventually dieif overheated. That’s the reason most boards come with a dedicated sensor so you cancheck the MOSFET temperaturefrom time to time.
In the past, motherboards used to come with a set of MOSFET chips –high and low side switches. But in modern models, you’ll only find a single transistor that contains the functionality of both.