Memory Rank refers to thenumber of 64-bit wide bus a single stick of RAM can use at a time. It is solely determined by the number of memory bus a memory module has.
Usually, a higher memory rank also means increased memory capacity in a single stick and lower latency as multiple ranks are accessed concurrently. But it also means complex internal architecture and lower memory bandwidth.
Most users confuse single-sided modules (memory chip on single side) as single rank and double-sided modules (memory chip on double-sided) as dual. But this reasoning is not entirely true.Single rank uses a single 64-bit bus, whereasdual rank module uses two 64-bit buses in interleaved mode.
Both single and dual-rank RAM have their own set of advantages and disadvantages. So let’s further dive into the topic to determinewhich RAM is better for you.
Understanding Single-Rank RAM
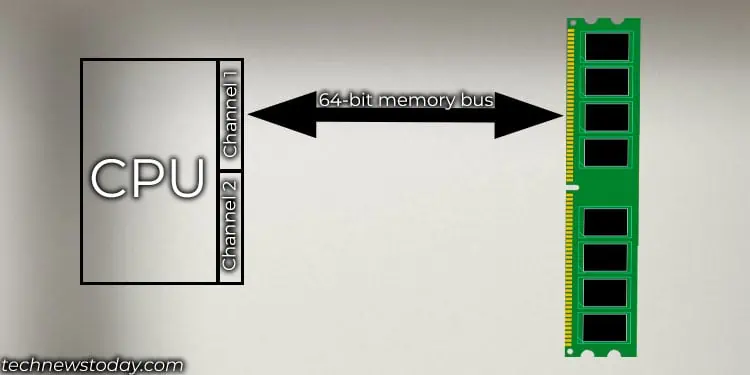
Every CPU connects to the memory using 64-bit wide memory buses (72-bits forECC memory). A CPU may have 2, 4, or 8 of these memory buses. Now, each memory IC chip attached to your RAM communicates to the CPU using an x4, x8, or x16-bit memory bank.
This means the memory chip with an x4 memory bank connects to the CPU using a 4-bit memory bus, the x8 memory chip uses an 8-bit memory bus, and so on.
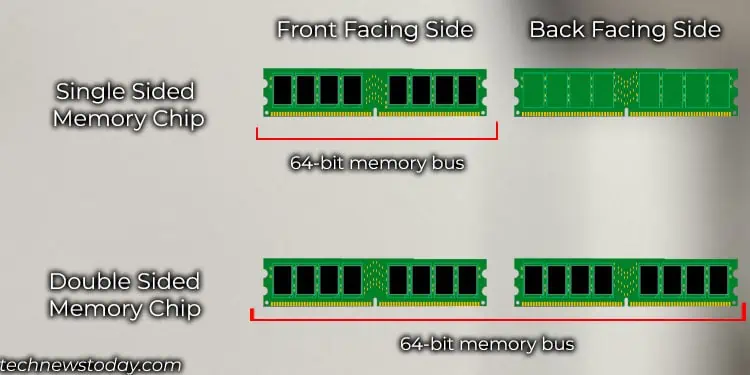
If RAM consists of x8 memory chips, it will require a total of 8 (64-bit memory bus/8 bit bus for single chip) memory chips or 9 in case of ECC memory. In this case, the 8 memory chip acts as a single rank and is usually soldered on one side of the memory stick.
For RAM composed of x16 memory chips, it will need 4 (64/16) memory chips. In this case, the four memory chips are considered one rank, or single rank, and are usually soldered on one side of the memory stick.
Lastly, if a RAM stick consists of memory chips that use x4 memory bank, it will need a total of 16 (64-bit memory bus/4-bit bus for single chip) memory chips. This means the total 16 chips can utilize the total 64-bit memory bus in one single rank.
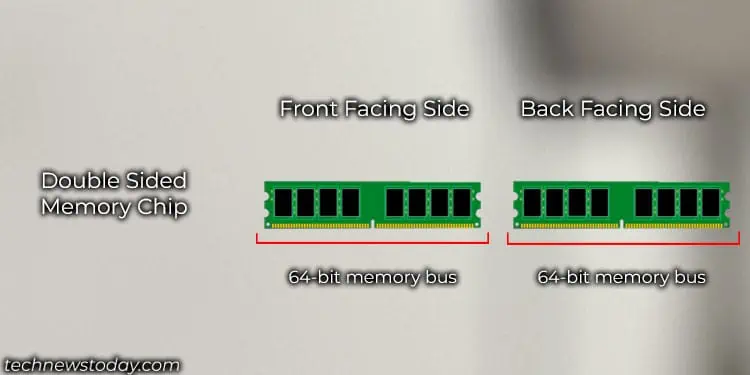
In this case, the total 16 memory chips can be divided into half and soldered on each side of the memory module. For ECC RAM, two separate chip is added on either side (one on each side).
The memory chip on both sides might make it seem like it is dual-rank RAM, but actually, the entire 16-memory chip uses a total of 64-bit memory addresses. So, it is a single-ranked RAM.
A group of memory chips (x4, x8, or x16) that adds up to the total of 64-bit bus width is one rank or single rank.
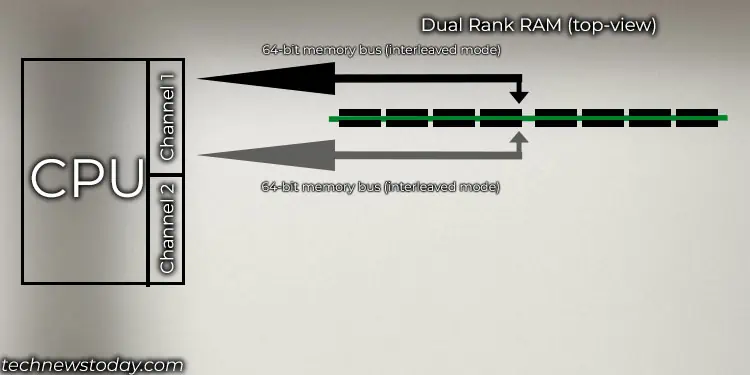
Most overclocking enthusiasts use four single ranks by filling up all four DIMM slots. This makes the RAM’s performance reach close to a dual-rank memory in adual-channel setup.
However, if your system only has two DIMM slots, you would want two dual-rank memory toget the maximum performance.