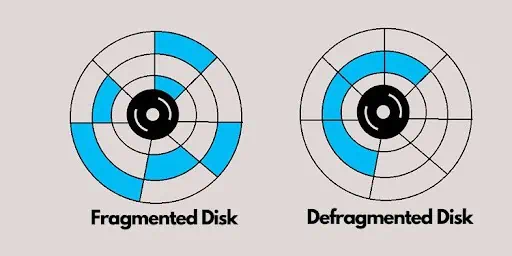
Defragment is a popular utility used to boost the performance of our computers. It is widely known that defragging hard drives works well to make our devices faster.
But do they work on the SSDs?
SSDs are a great find in the storage device segment, with features such as highread/write speeds, low power consumption, and much more. A common notion is that defragging SSDs can amplify these features.
Contrary to what is believed, defragging the SSD won’t give you the expected results and can even severely affect the drive’s performance in the long run.
In this article, we’ll look at how defragmentation works on SSDs and whether it’s necessary.
How does the Defragment Work?
Before diving into how the defragment works, it’s a good idea to understand how a hard disk functions. A hard disk has a cluster of spaces known as the sectors. A hard disk contains many sectors, each of which stores some amount of data. These sectors are located on the platter where the data are stored magnetically.
For instance, if a sector’s size is 1 byte, it can hold up an equivalent amount of data in it. The actuator arm of the disk positions the read/write head over the spinning platter to access the storage spaces of the HDD.
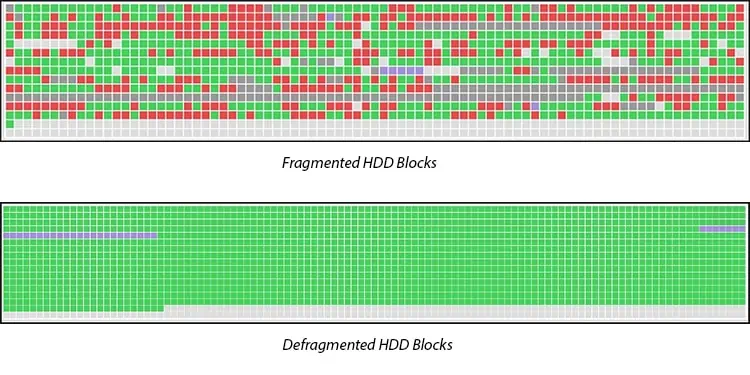
The data on the disk is divided into different pieces or fragments that are read by the computer by putting these pieces together. These fragmented data are accessed by the read/write head, and thus higher data fragmentation leads to longer access times, reducing hard disk performance.
Simply put, fragmentation is the situation in which the pieces of data stored are scattered. When the disk is defragmented, these pieces are placed in proximity to each other, which reduces the access time.
Defragging HDD vs. Defragging SDD
As discussed earlier, the files stored on the HDD are scattered into pieces and stored all over the disk. Continuous writing, deletion, and modification of the file make fragmentation obvious. This reduces performance by increasing read and write time, eventually slowing down the computer.
Defragmenting a hard drive places the chunks of large files that were previously scattered into a single contiguous block. This decreases the rotational latency and head seeking of HDD, which means lesser time taken to assemble the pieces of the file.
SDD, on the other hand, does not have any moving parts with it.SSDs use integrated circuits to store data, most commonly the NAND flash. Unlike the HDD, the SSD does not store on sectors, rather, these data get stored on pages and blocks.
Data is arranged in these blocks through the floating gate transistors that hold the electrical charge. The data available on each block can be accessed at the same speed. This reduces the read and write latency, which sets the SSDs performance apart from the HDD. And this is also the reason that fragmentation holds little or no effect on the performance of SSDs.
