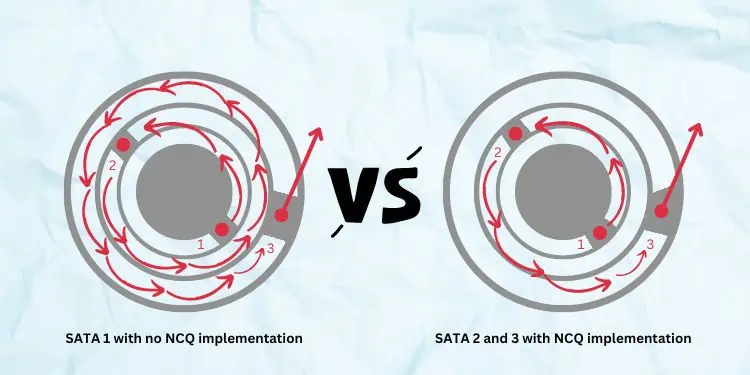
Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA) is an interface that lets you connect your storage devices (HDDs, SSDs, and optical drivers) to the motherboard.
Basically, SATA is the replacement for PATA, which adopted parallel communication (carrying multiple bits of data). Moreover, they have become ade facto standard for both HDDs and SSDstoday.
However, since its introduction, we have encountered several revisions, with the latest one being the SATA 3.5. Regarding the same, this article will guide you through the differences between these versions and whether or not to switch to the latest one.

As the name suggests, theSerial Advanced Technology Attachmentis based on serial communication. This means that data is transferred from the storage devices to the computer motherboard one bit at a time.
This is why data transmission using SATA is less susceptible to any interruptions or damages. Moreover, the higher data transmission rate is another reason why most users prefer them over other storage device interfaces.
In the earlier days, we heavily relied on Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment (PATA), also referred to as IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics). Reportedly, they use a 40-pins configuration with around 40 or 80 conductor ribbon cables.
Apart from the bulky connector with vast sets of pins, their data transfer rate was also relatively low (up to133 MB/s). Also, with the increasing RPM of the hard drives, PATA got out of favor and was eventually replaced by SATA.
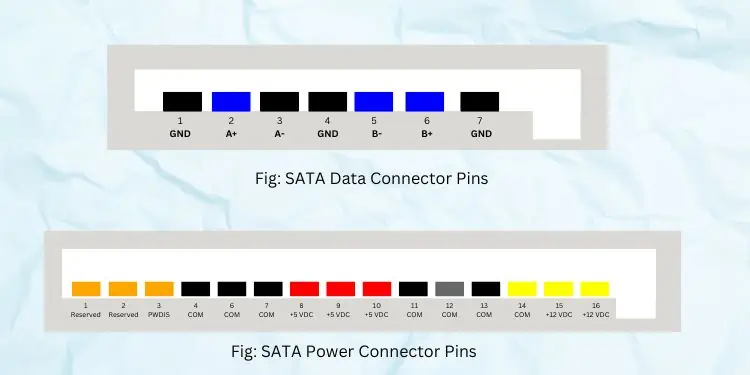
Basically, the newer technology was better in terms of data transfer rate (150 MB/s), and the data corruption rate was also significantly reduced. Moreover, the data connector pins were alsoreduced from 40 to just 7.
Furthermore, SATA replaced the 4-pin Molex power connectors with much more powerful15-pin SATA power connectors. The other improvements include the hot-swapping feature, less power consumption, and low-priced.
Please look at the table below to learn the fundamental differences between PATA and SATA:
Note:SATA and PATA are incompatible but can co-exist on the same machine having both the interfaces. Hence, if you wish to connect your PATA hard drive to a motherboard having only a SATA port, you require a PATA to SATA converter.
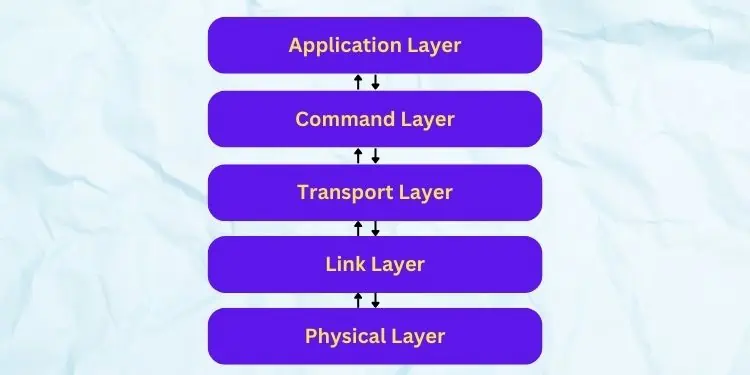
SATA Interface Architecture
Regardless of the SATA bus interface type, the working mechanism remains the same. Well, it has a five-layered architecture – physical, link, transport, command, and application layers.

Well, PATA was extensively used for almost two decades. However, even after SATA replaced them, the data transfer rate wasn’t still high to work best with storage devices having higher RPMs.
Hence, it was evident that users were looking to replace the first version of SATA as soon as possible. Thus, the SATA interface was revised multiple times to fit consumer needs.