You’ve probably seen the setting that lets you choose whether to run the device as a bridge or a router while navigating through the network configurations. The purpose for both of these modes is the same, i.e, to offer network connectivity over a larger coverage area.
However, some minor technical intricacies make these two modes totally different in how they operate. In this context, we’ll compare these two networking modes today and recommend the best option to get the most out of your internet experience.
What is a Router Mode?
In router mode, IPs of devices connected are stored in tables and most viable route is selected to transfer data. The IPs can be given dynamically by the device or defined by user.
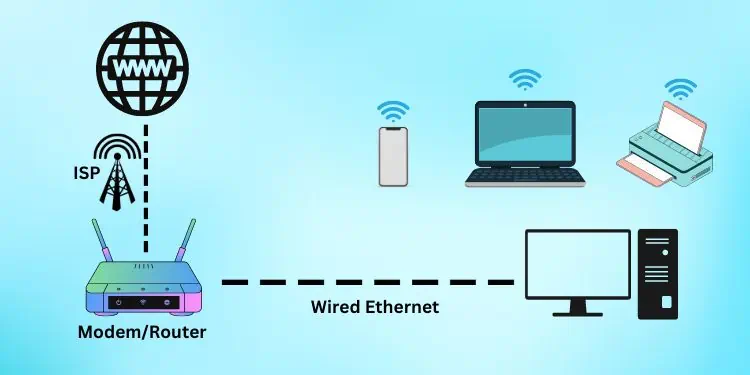
A router is involved in receiving the packets with the destination address attached to them and, forwards the packets to the receiver in the most convenient route.This process of forwarding the data is called dynamic routing.
It connects the LAN with the WAN. The router Converts an IP from one class to another using a process called Network Address Translation (NAT).
Router Mode is just to make the networking device function as a Router. Generally, the Modem/Router combo offered by the ISPs is, by default, set to the Router mode. However, if you use multiple routers for Wi-Fi range expansion, a private set of IPs created by the router generates conflict and can cause issues on the network. This is what is known as theDouble NAT.
The router mode also supports multiple authentication methods, making it a more flexible option while setting up a connection.
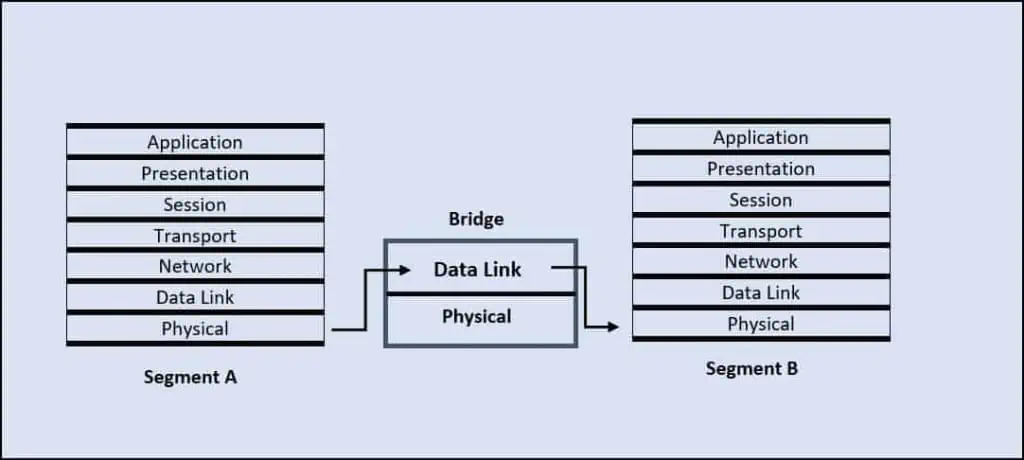
Bridges use source and destination MAC before forwarding packets, contributing to less network congestion. Bridging essentially is the process of connecting two networks and making them function as one.
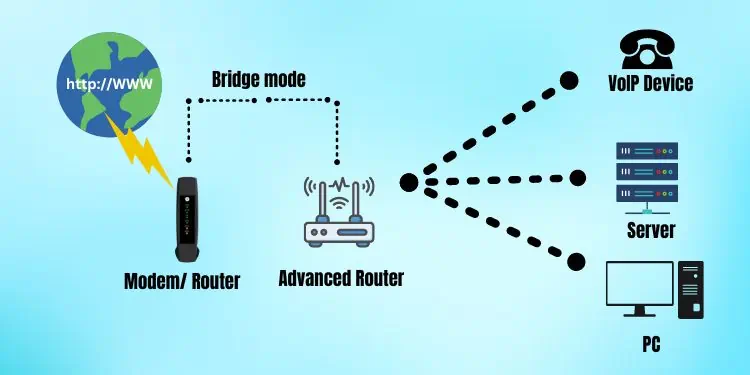
Now,getting into Bridge mode,is a setting that can be configured to make networking devices work simultaneously and extend the port access to a wider area. This configuration will disable the Network Access Translation (NAT) on one of the routers and turn it into a layer 2 device (On OSI) and extends the LAN.
With the IP assigning or NAT turned off, the router will not work as aDHCP server, which reduces the IP address conversion time. This can also be said as the latency of transferring the data between two points is relatively faster because of reduced data hops.
Enabling the bridge mode on a primary networking device will take away the routing capability from the device, if present. Configuring a device to work on the bridge mode renders the WAN port useless since the device is typically non-existent apart from extending the primary connection.
Router Mode Vs Bridge Mode – Major Differences
From anOSI model perspective,the router is a Level three device that performs the routing of traffic in an extended network. Routers are referred to as the network’s gateway as they forward the packets from one network to another. This is the normal modus operandi when a networking device is set to run on a Router mode.
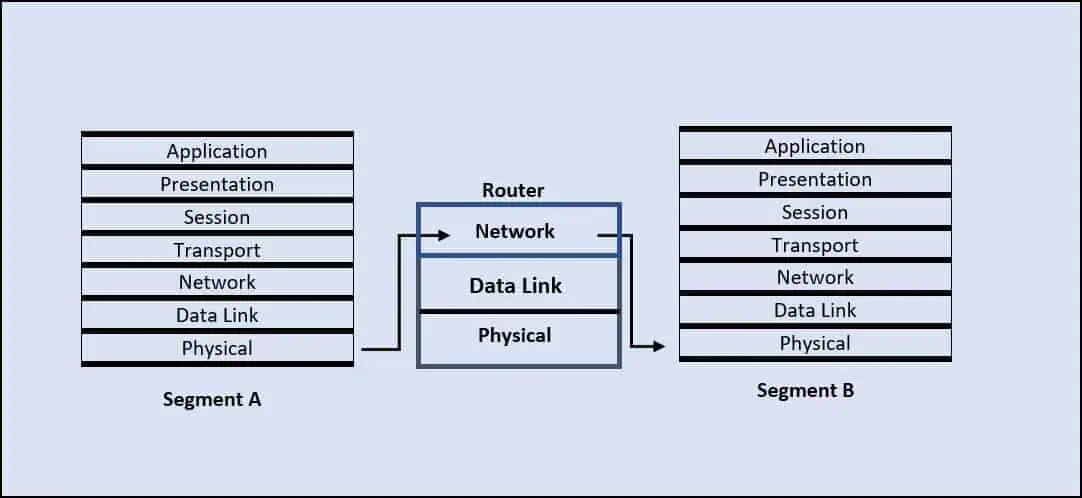
A bridge is a network framework segregating the LAN into segments and dividing the traffic into those segments. On an OSI Model, it works on the Data Link layer. Bridges are used to overcome the limitations of the bus topology by reducing network traffic and limiting bandwidth usage. Thus, enabling the Bridge mode does this function by converting the networking device into a bridge.