Computer RAM has evolved over the years, whether it’s in terms of architecture or form factor. Narrowing down, they are primarily categorized asSRAM and DRAM.
Further, these can be classified intoSynchronous and Asynchronous, which are both used today but serve different purposes.
Considering SRAM’s high cost, it’s implemented as a cache memory. So, we are rather more familiar with DRAM, and particularly itssynchronous type (SDRAM). All modern-day PCs and laptops are equipped with theDDR SDRAM, which has five generations, DDR5 being the latest.

Well, RAMs are not backward compatible and come in different form factors/packages (DIMM, SODIMM, UDIMM, etc.). So, you need to be extra picky when choosing the correct one for your system. Having said that, most servers and workstations preferECC RAM, which can automatically detect and correct memory errors.
With so many RAM types available, it is obvious to get confused about what RAM your system uses. So, here is a quick read to help you understand better about memory types.
Types of RAM Depending on Internal Architecture
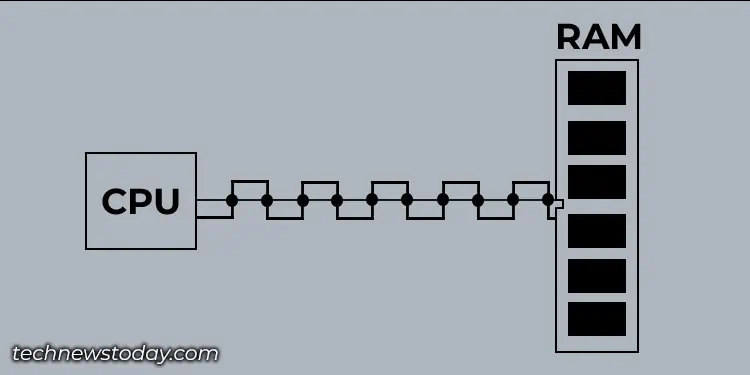
First, depending on internal architecture, you may find two types of RAM:SRAM and DRAM. The main memory you use on your computer is a type of DRAM, while the CPU cache (L1, L2, and L3) is that of SRAM.

Static Random Access Memory (SRAM)
Let’s start with SRAM or Static Random Access Memory. SRAM is primarily used as the CPU’s cache memory. Besides the CPU, SRAM is also used as a buffer on dedicated graphics cards or even in printers.
SRAM is a very high-speed memory, which is faster than DRAM. It is used to store data that needs to be accessed very quickly. This is why modern computers still use SRAM as a CPU cache.
The reason that SRAM is faster is that SRAM is built from transistors and basic flip-flop logic circuits to store data. So, it runs at the same speed as the PC’s circuitry. However, there is a difference in the speed of L1, L2, and L3 caches, although all of them use SRAM technology.
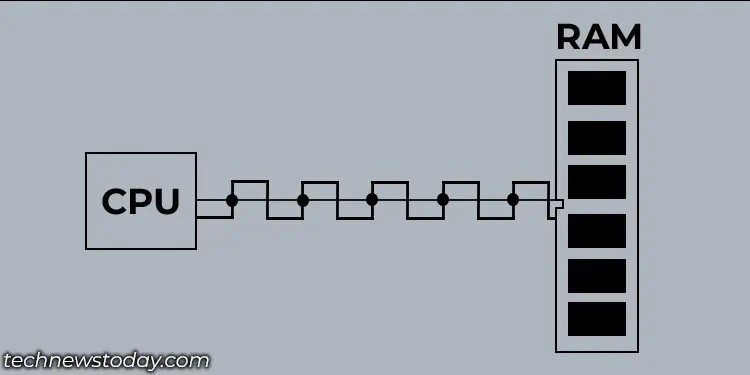
This is also why devices like mobile phones and smart-watches use SRAM technology to store frequently accessed data.
SRAM uses 6 transistors and a complex internal architecture to store a single bit of data. Due to this, SRAMs storage capacity is low and is expensive to manufacture.
Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM)
Unlike SRAM, DRAM stores data in memory cells consisting of simple circuitry with just a capacitor and a transistor. The transistor is like a switch that reads the charge in the capacitor. When a bit is stored, the capacitor is charged.