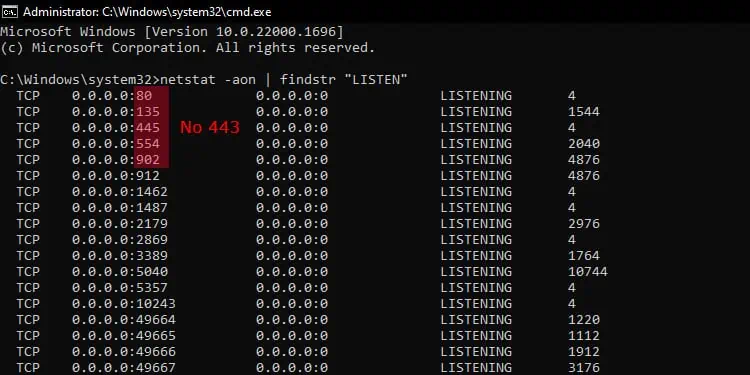
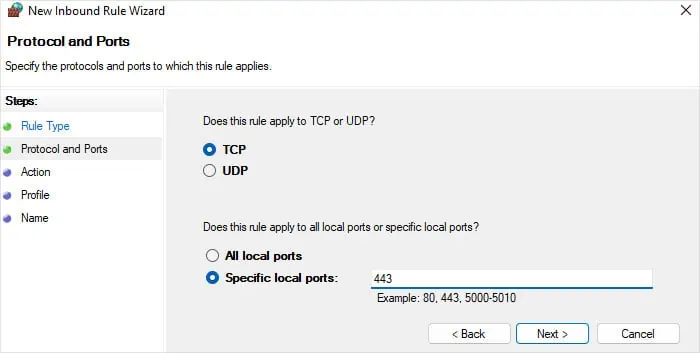
When hosting a web server or a web application, you need to open port 443 (or port 80) on the server so that it can receive a web request. While port 80 relates to HTTP, port 443 corresponds to HTTPS.
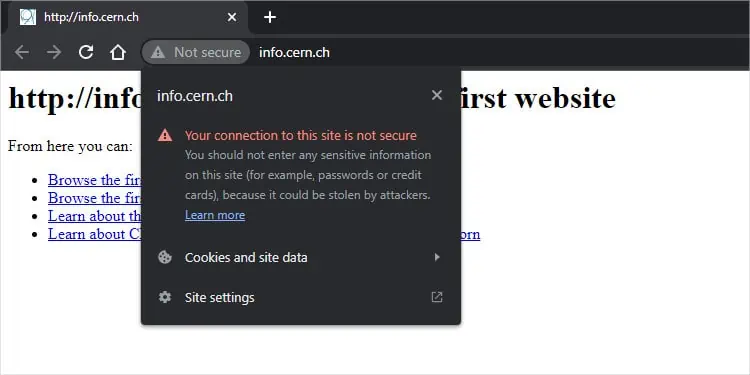
According to Google’s research in 2021, over 95% of websites have been using HTTPS. It offers more secure communication than HTTP and is the de facto standard for modern web security.
If you want to understand more about this port and how it works, you need to know what a port represents first. So, let’s start!
What Exactly is a Port?
In a general sense, a port represents the connection point or interface between external and internal devices. So, in a computer network, it is a unique virtual endpoint where the network connection starts or ends. The ports can allow or restrict outbound, inbound, or both connections, and the firewall is responsible for the corresponding rules.
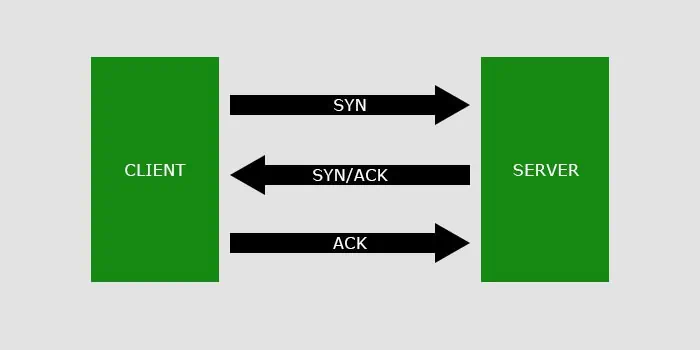
If you attempt to access another device on the network, your device will use certain ports depending on the protocol you are using to establish the connection. The protocol can be the usual communication protocol like Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)/User Datagram Protocol (UDP), data sharing protocol like File Transfer Protocol (FTP), and so on.
The port needs to be opened on the other device to establish the connection. They are associated with different services that help establish and implement the connection based on the communication protocol.
A total of 65536 port numbers are available for the different network protocols. Among them,
What is Port 443 and How Does It Relate to HTTPS?
Many web servers use Transport Layer Security (TLS) certificates to improve their security. If you try accessing such a web server using TCP protocol, the network will use an encrypted channel to send the request to, and receive data from the server. Port 443 is the default virtual endpoint of this secure channel on the web server.
Your web browser will utilize the Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) in the application layer to send requests and receive the data. So, port 443 is directly associated with HTTPS protocol. Some VPN or other services also use this port to bypass firewall restrictions.
TLS is a more recent version of Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), so you might still find SSL used a lot to describe security certificates. But nowadays, SSL is deprecated and only the recent versions of TLS are in use.
Most web servers now use TLS certificates as data security is of utmost concern. This is why you’ll seehttps://instead ofhttp://in almost all URLs.
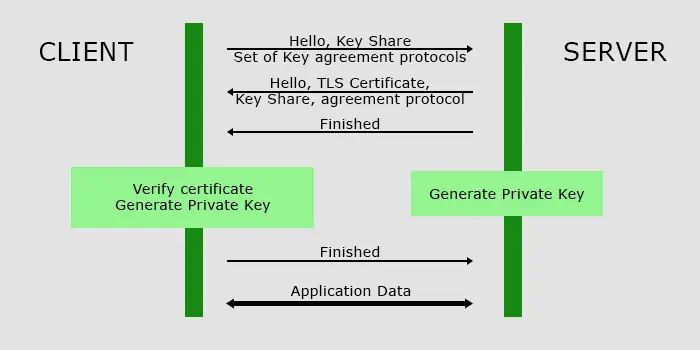
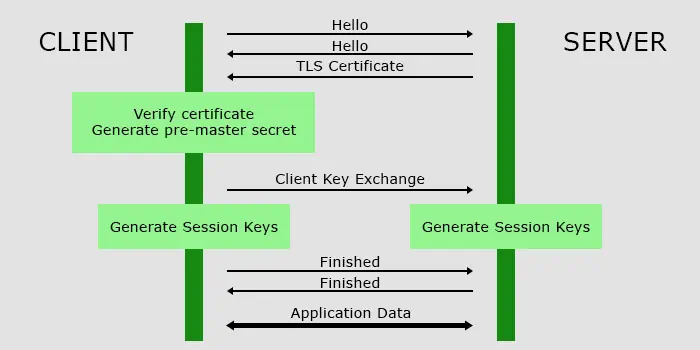
How Does HTTPS and TLS Encryption Work?
TLS technology uses a set of two keys (public and private) for encryption. Only the private key can decode the data that the public key encrypts and vice versa. Here’s the complete process of how HTTPS and TLS encryption work: