When buying a motherboard or a graphics card, have you ever wondered what the PCIe versions represent? Clearly, the higher number is better, but what does it mean to have a PCIe with a higher version?
Today we are here to discuss the difference between PCIe 3.0 and PCIe 2.0. Before we start, let us see what a PCIe is.
PCIe, or the Peripheral Component Interconnect Express, acts as an interface thatconnects various internal PC componentssuch as the graphics card, SSD (Solid State Drive), sound card, NIC (Network Interface Card) card, etc. to the motherboard.

You may wonder why we use PCIe to connect vital computer components. Well, one specific reason is that the PCIe offers high-speed data transfer that components, such as the GPU, require constantly.
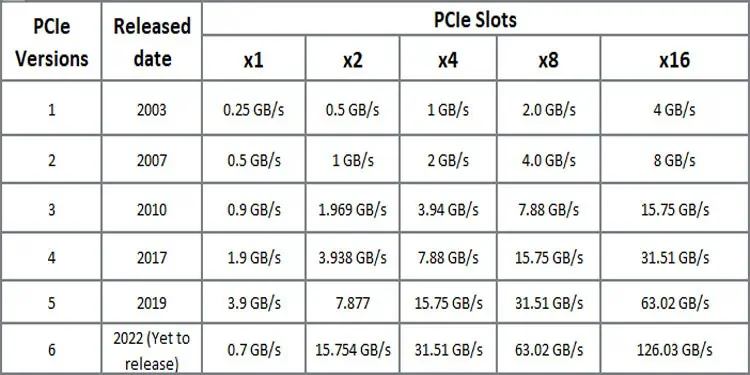
As of date, we have five versions of PCIe, PCIe 1.0 to 5.0. However, the PCIe version is not to be confused with PCIe lanes, which we will discuss later in the article.
Basically, with each generation of PCIe, you will have greater bandwidth, transfer rate, and frequency. For less tech-savvy readers, this means that the internal components connected to their respective PCIe slots will perform a lot better.
Furthermore, when you have a graphics card connected to a higher version of PCIe, your games will also run at higher Frames Per Second (FPS), giving you a smooth experience.
Some may think that PCIe lanes and PCIe slots are the same. However, this is not quite the case. PCIe lanes act as the medium through which PCIe slots transfer data to the motherboard.
There can be four, eight, sixteen, or thirty-two lanes of PCIe on a motherboard. PCIe x4 means this slot uses four lanes to transfer its data. Other PCIe slots utilize the remaining lanes. However, x16 can use either 8 or 16 PCIe lanes.
Depending on the motherboard, you will have multiple PCIe slots. PCIe x1 is the shortest slot with one PCIe lane, whereas PCIe x16 and x8 is the longest slot. PCIe x8 uses eight lanes, whereas x16 can use either eight or sixteen lanes.
For example, consider that your motherboard has 20 total PCIe lanes in total. If x16 uses 16 PCIe lanes, you now only have 4 PCIe lanes left on your motherboard.
PCIe 3.0 Vs PCIe 2.0 – Differences
Now that we know about the PCIe, its lanes, and slots, let us discuss compare PCIe 3.0 and PCIe 2.0 in terms of encoding, bandwidth, transfer speed, and frequency. Furthermore, depending on the slot sizes and version, these terms vary as well.
So without further delay, let us see what PCIe 3.0 brought to the table.
First, let’s look at some key differences between PCIe version 3.0 and 2.0.