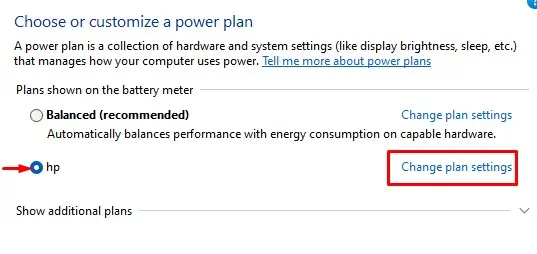
When a system is idle, the configuration in the Operating System can lower system resource consumption, both hardware and software, to reduce power usage. Windows offers you multiple power options that let you lower system performance if it meets certain conditions. One such setting is the Minimum Processor State in Windows.
Minimum Processor State is a power setting that lets you change the minimum processor usage value. You should set the minimum processor state to a lower value so that the processor uses minimum resources when it is performing minimal tasks, inactive or idle. This results in the CPU consuming less power.
However, there is much more to the minimum processor state and how it affects the CPU usage, power consumption, and heat generated. This article addresses a few queries about Windows’s minimum processor state setting and its optimal value.
What Is Minimum Processor State in Windows?
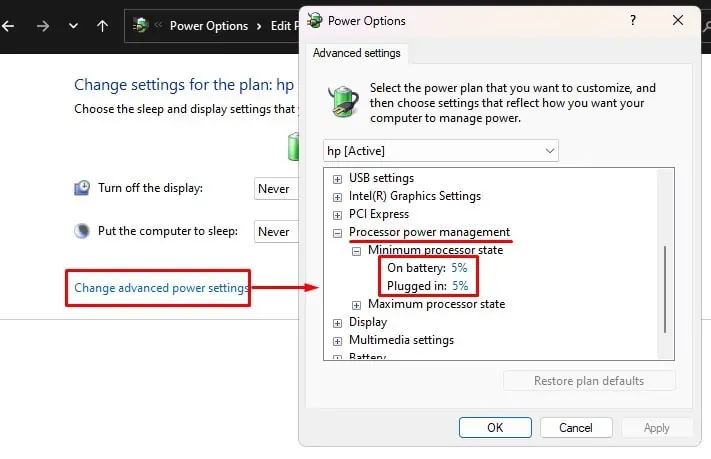
The minimum processor state refers to the amount of processing power a CPU is directed to use when the system is idle or under low stress. The minimum processor state value in power options lets you change the percentage value that determines the minimum operating frequency of the CPU.
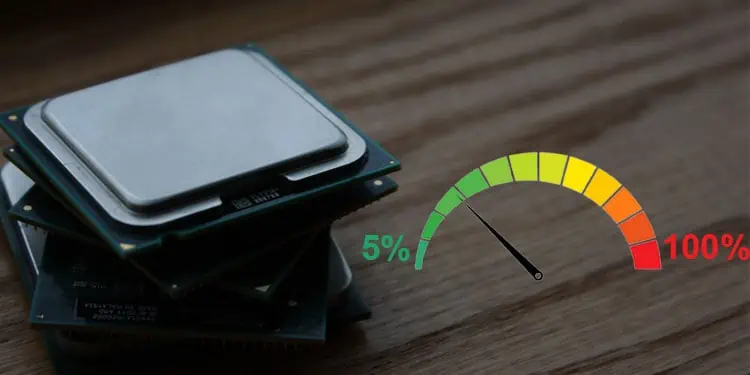
If you set the minimum processor state value to 15%, the CPU will not go below 15% processor usage. But this entirely depends on the device you use.
When you change the minimum processor state value, you may not only control the power consumption, i.e., voltage and current, but also CPU core temperatures and clock speed. You can lower the minimum processor state to lower CPU temperature if you are facinghigher CPU temperature even when idle.
However, if you are running a processor-intensive application, and you see a dip in performance due to processor thermal throttling, increasing the minimum processor state value will bypass the thermal throttling.
Depending on the process you are currently running, you may either increase or decrease the minimum processor state value.
Since minimum and maximum processor state directly contributes to the change in system temperature, setting a lower minimum processor state also lowers the CPU fan’s RPM when idle, and increasing the valueincreases the fan’s RPM.
One disadvantage of lowering the minimum processor state value is that it may decrease system performance. If that’s the case, you may slightly increase the minimum processor state. However, we only recommend setting the value to between 5%-15%.
How Does Minimum Processor State Value Affect Performance?
When you set a lower minimum processor state value, the CPU usage will not go below the set percentage. This is a good configuration if you want to improve your CPU component’s lifespan. However, this can lead your system to have a choppy performance when runningprocessor-intensive application.
When you run an application that uses quite a lot of processor resource, its temperature will increase, resulting in higher CPU fan RPM to cool the processor. But if the CPU starts to thermal throttle and the minimum processor state value is low, the system will use lower processor resource.
This means the low processor resources for the application, which will not perform as efficiently as it used to. This is where increasing the minimum processor state value comes in.