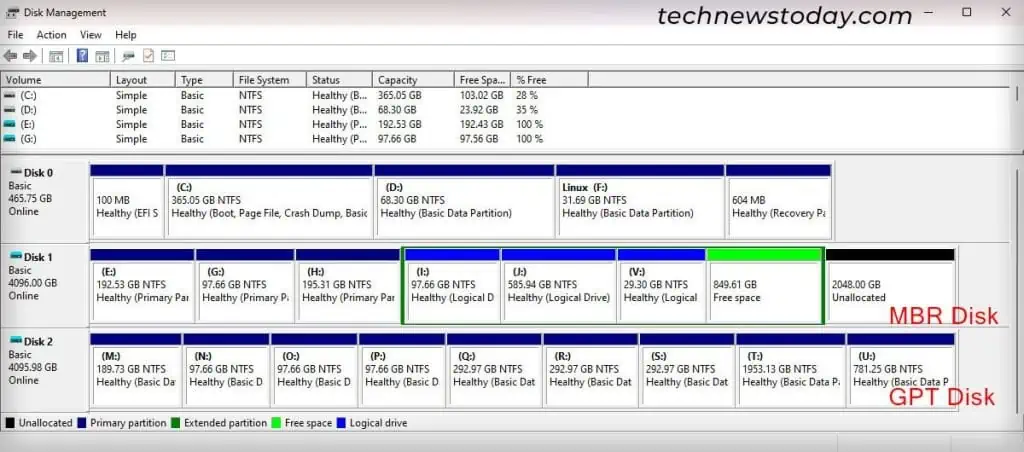
If you try toinitialize a new SSD on Disk Management, it will ask you to choose between the MBR and GPT partition styles. In short, GPT was introduced to overcome the limitations of the MBR partition scheme.
While older and current systems are all compatible with MBR, all newer systems will be GPT-based. So it’s best you always choose MBR unless your computer does not support it.
Let’s get into the details!
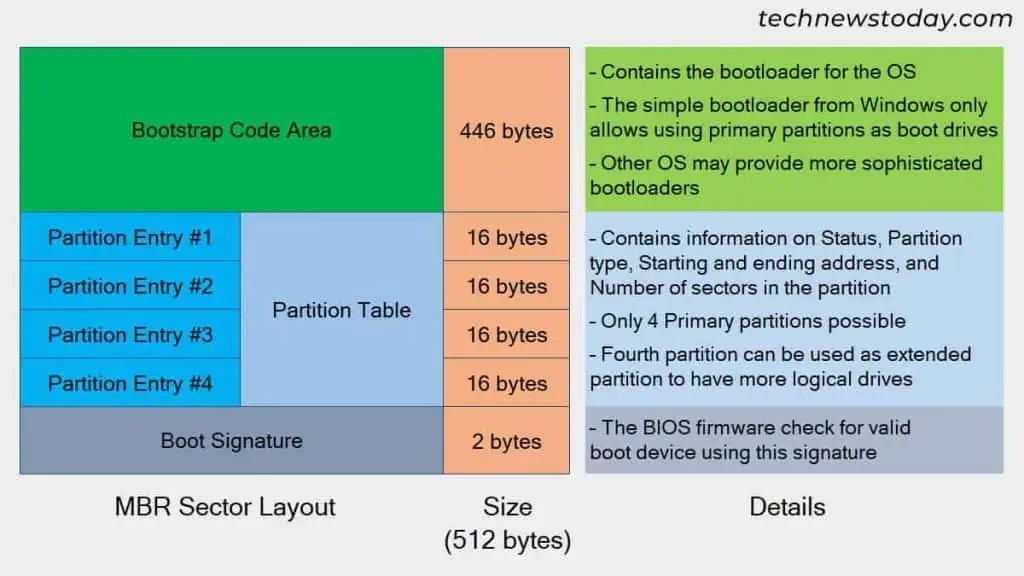
What is a Master Boot Record (MBR)?
Master Boot Record (MBR) is the partitioning scheme used in traditional hard disks. It wasintroduced with PC DOS 2.0in 1983.
In this scheme, the disk uses its first 512-byte sector to store partition and boot information. This sector is called the MBR sector and consists of three main parts,
MBR contains a partition table with four entries that use32-bit logical block addressing. It means that the entries use 32 bits to store the partition addresses and sizes.
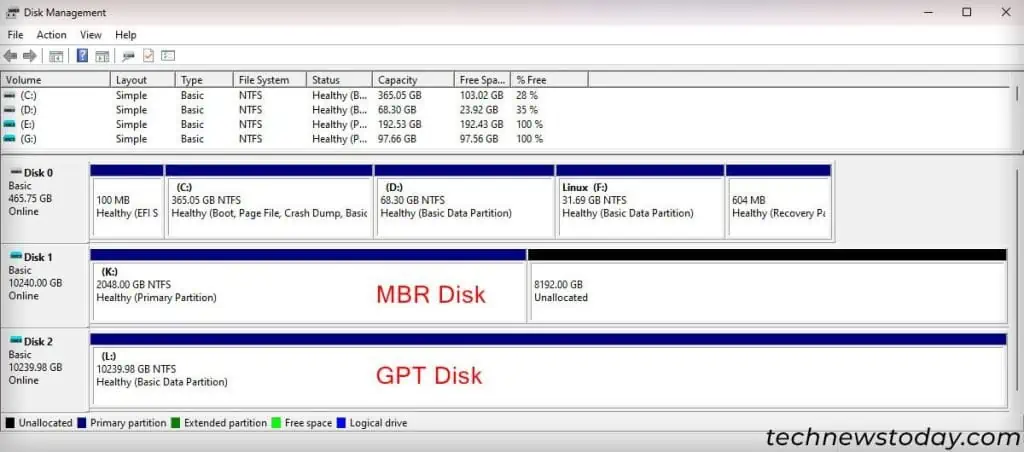
Such addressing affects the maximum possible size for MBR-based partitions. I will discuss this in detail later in the article.
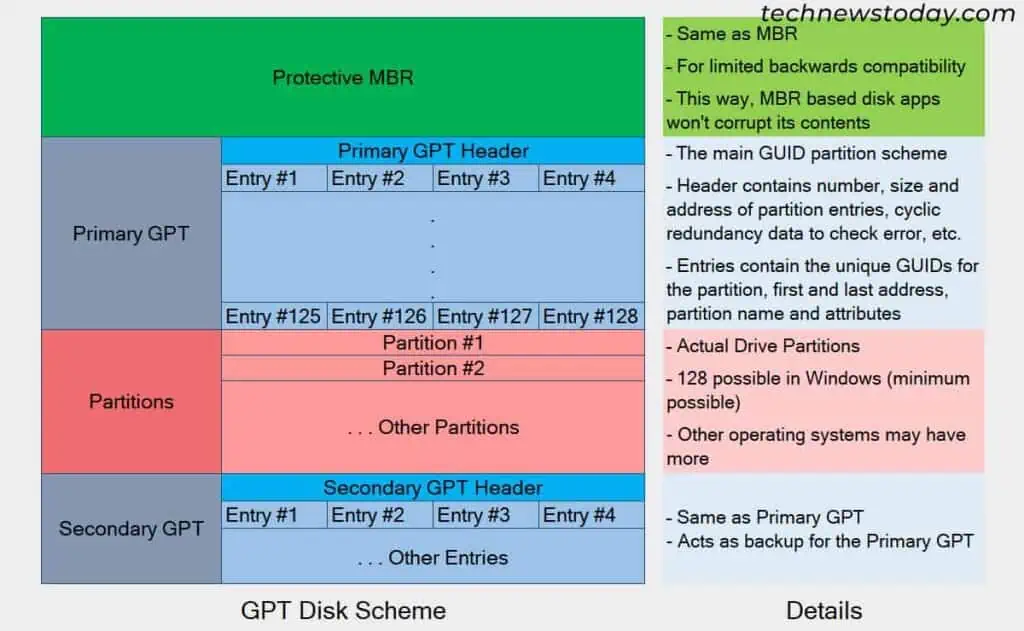
What is a GUID Partition Table (GPT)?
Globally Unique Identifier (GUID) Partition Table (GPT) partition scheme was introduced by Intel in the late 1990s as a part of the EFI, later called the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) specification.
GPT uses 64 bitsfor logical block addressing, so it can support much larger capacity disks compared to MBR. As I’ve shown in the figure above, the complete GPT-based disk consists of four sections:
It is only possible to use a GPT disk as a boot device with UEFI firmware. If you have legacy BIOS systems, it only supports booting from MBR-based disks.
Differences between MBR and GPT
Now that I’ve talked about the basics of MBR and GPT partition schemes, let’s look at the individual differences.
Also, GPT is associated with UEFI, and MBR is associated with legacy BIOS. So, I highly recommend checking out my article onUEFI vs Legacy BIOSas well.