Running an executable (.exe) file is simply a matter of opening it in general cases like installing or opening an application. But, if you are a network/system administrator and want to create a script for automating various tasks, you will likely reach a point where you need to run an executable file.
Well, for Windows users, you already have abuilt-in toolcalled Windows PowerShell to do just that. Using it, you may run powerful commands and even build applications with efficient scripts.
In this article, we have compiled a list of various ways you may utilize the PowerShell tool to run an.exefile.
How to Run Exe in Powershell?
While running the commands in the methods below, replace the items like filename or path appropriately. Also, exclude the angle brackets and include spaces as is while writing the commands.
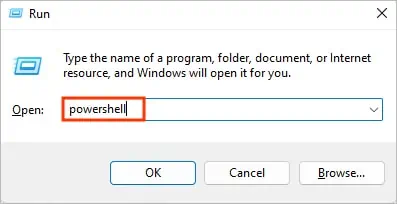
Run Directly without Parameters Using the & Operator
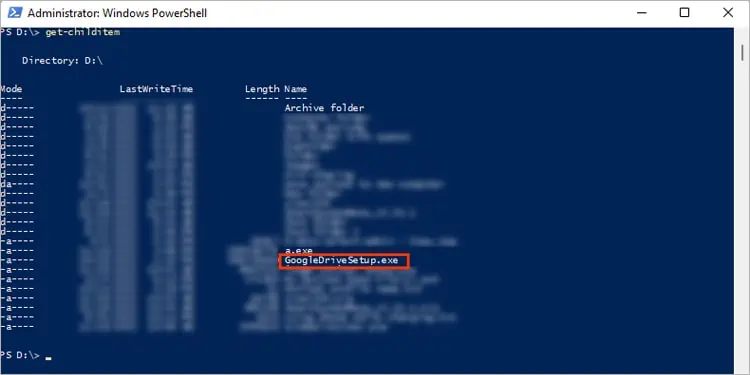
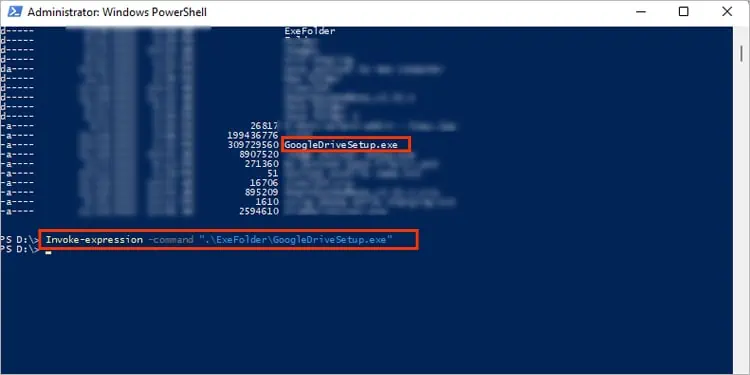
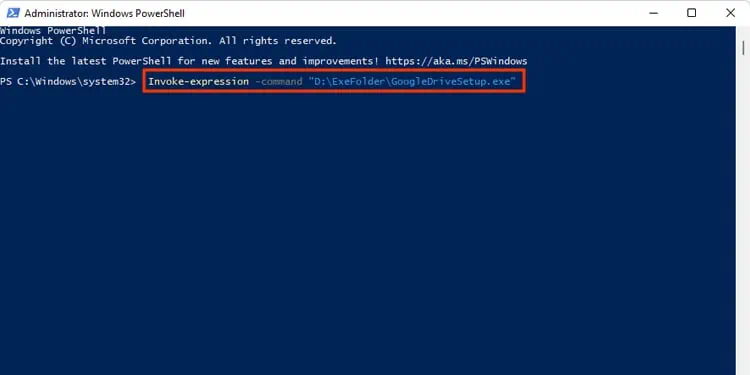
With PowerShell, you may directly run an executable file with the” &” operator (also known as the call operator). You can browse to the file location or provide the full address path in the command. Then you can execute the command.
If you are wondering what’s happening here, well, by typing the ampersand (&) symbol, PowerShell understands that it needs to run the program. Otherwise, PowerShell will treat the command as a string and won’t invoke the.exefile.
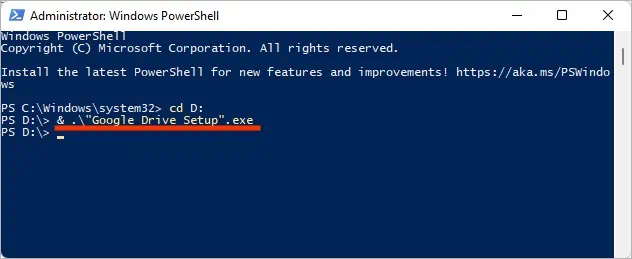
Start-Process is a more advanced and powerful cmdlet where you may specify multiple parameters. Thus, it can run several executable files at once.
Start-Process -FilePath “”
Here, we are using the Path parameter tospecify the file pathof the executable file. Along with the above parameter, some of the commonly used parameters with syntax are listed below.
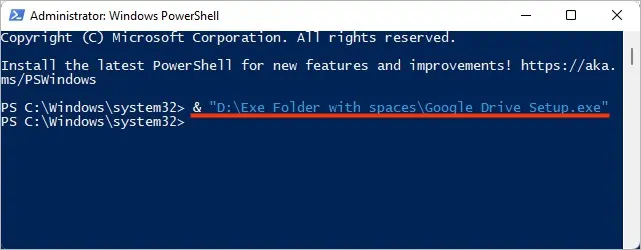
Start-Process -FilePath “<FilePath<file-name>.exe” -Wait
This command tells PowerShell to wait until the whole process finishes executing and then takes other inputs if any.
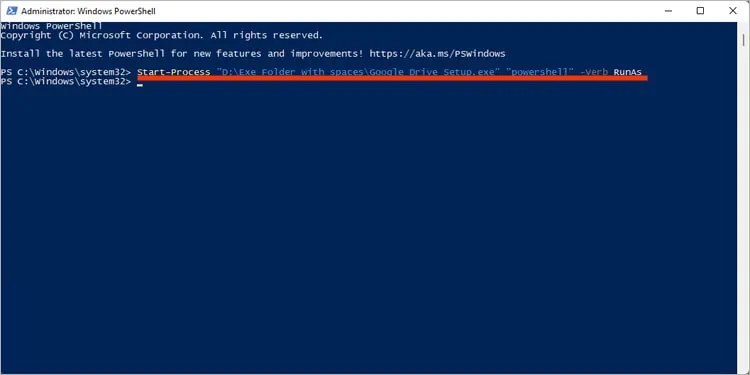
Start-Process -FilePath “powershell” -Verb RunAs
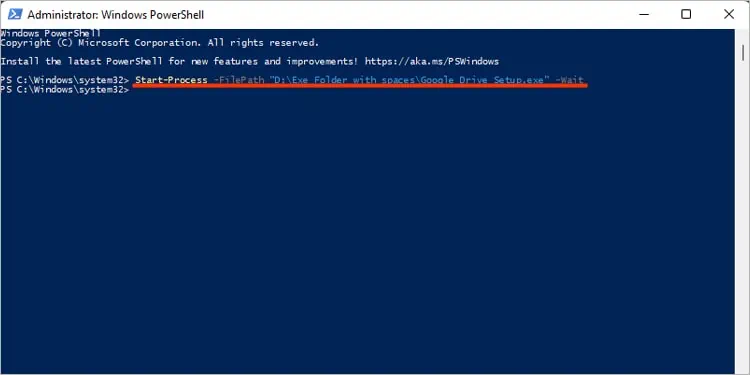
The above command launches PowerShell as administrator. Instead of the RunAs verb, you may also use Open and RunAsUser verbs for the.exefiles.