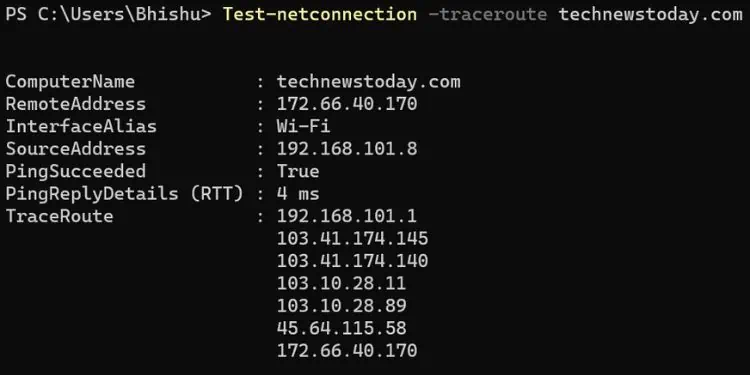
When troubleshooting network-related problems, running a traceroute command can help detect where (in the route) the connection has become slow or unresponsive. It works by sending ICMP echo packets to the destination andtracking every single hop(usually router/gateway) on its way.
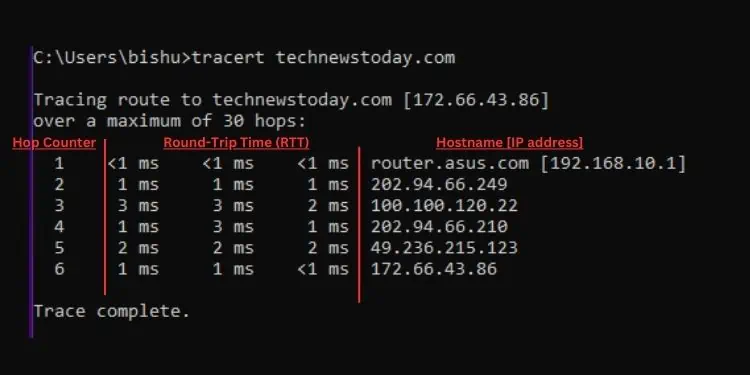
After executing thetracertcommand on Windows, the round-trip time of every packet along with the hop’s IP address/hostname is displayed. Analyzing this output, you may now get a general idea of which hop could be facing the trouble.
In this article, I will guide you on how to properly utilize the Traceroute command on Windows.
Basics to Traceroute Command
Most of us haveused the ping commandto test the reachability of our devices on the network. While this is an effective utility to detect possible network anomalies, it’s limited to telling the user whether the specified destination is reachable.
Like Ping, the Traceroute or Tracert command also runs on the third layer of the OSI model. It sends ICMP request packets to the destination host. The main difference is that it doesn’t just specify whether the server can be reached but also displays the exact route.
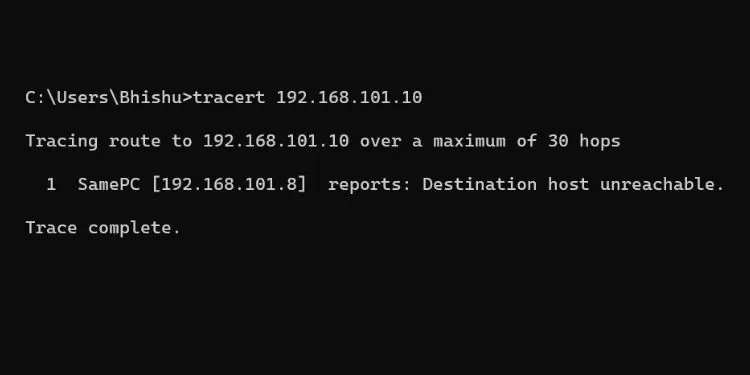
Traceroute usesTime-To-Live (TTL)values which decrease (by 1) every time the packets reach a hop. When the value is 0, that router/gateway responds with an ICMP reply packet.
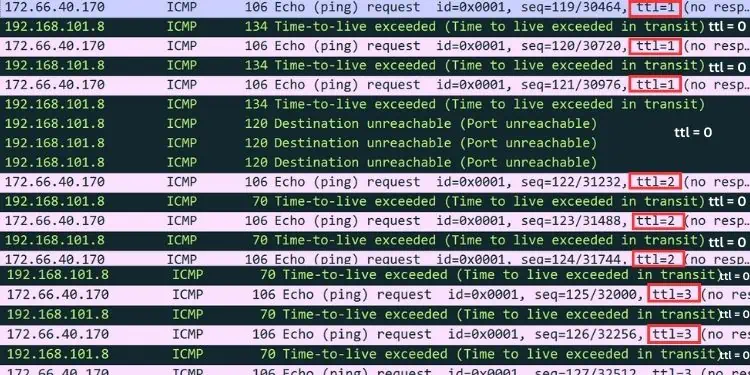
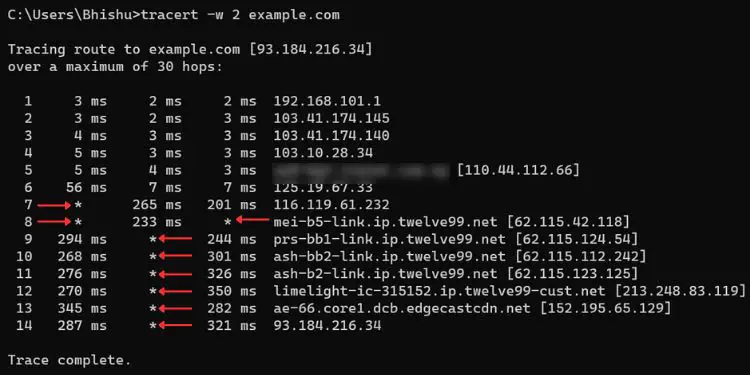
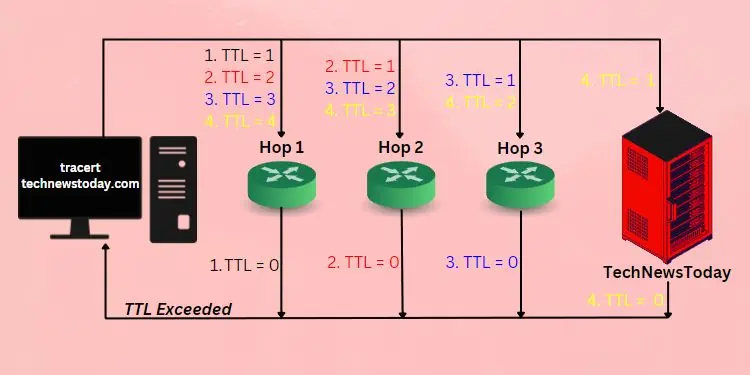
Let’s understand this with a simple example. Suppose you’re trying to track the route of our site, TechNewsToday. Once you execute the Traceroute command,three ICMP packetsfrom your device are forwarded to our server withTTL = 1.
Once it reaches the first hop, the TTL value decreases by 1 (nowTTL = 0) and replies with a “TTL exceeded” message. Then, your device displays theround-trip time (in ms)of every packet along with thehop’s IP/hostname.
With the notedIP address, it resends the ICMP packets withTTL = 2. Again, the value is decreased by 1 (nowTTL = 1) and the packets are forwarded to the destination server.
After the request message hits the second hop, the value is again decreased by 1 (nowTTL = 0). As earlier, this router replies to your source device with the “TTL exceeded” message. The process repeats until the final destination is reached. On its way, it keeps on displaying the round-trip time and IP of each hop.
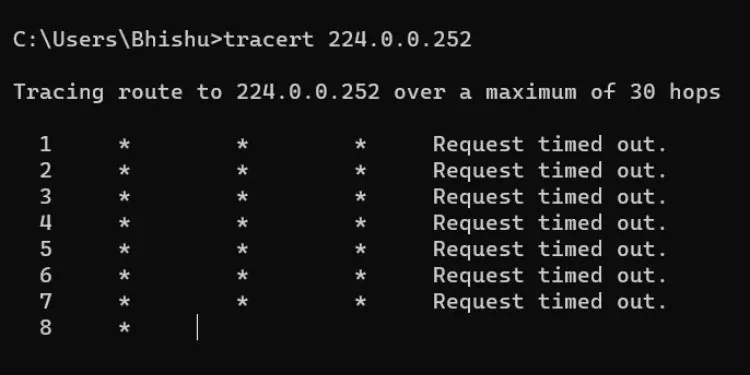
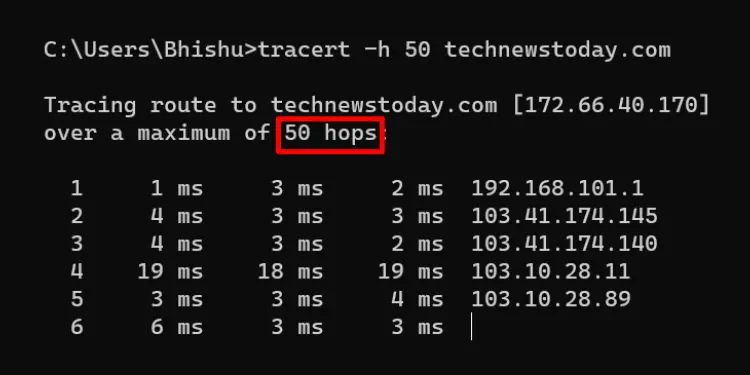
In Windows, thedefault maximum number of hopsthe packets can travel is30. Thus, once the hop counter reaches the limit, the packets are dropped and the final route can’t be found. But you do not need to worry as it’s possible to increase this number using a dedicated parameter, which I will discuss later.
How to Run Traceroute Command?
To determine the route of the ICMP request packets from your source device to the destination, you need to execute thetracertcommand. The syntax is the same for bothCommand Prompt and Powershell.
Syntax:tracert