You may be trying to write a script that requires user input to complete, or sometimes the script requires a delay to let another process finish executing first.
The most used command for purposes like this is theStart-Sleepcmdlet. Since PowerShell also supports CMD commands, you may also use thePauseandTimeoutcommands.
In this article, we’ve explained the usage of these and more commands to pause in Powershell.
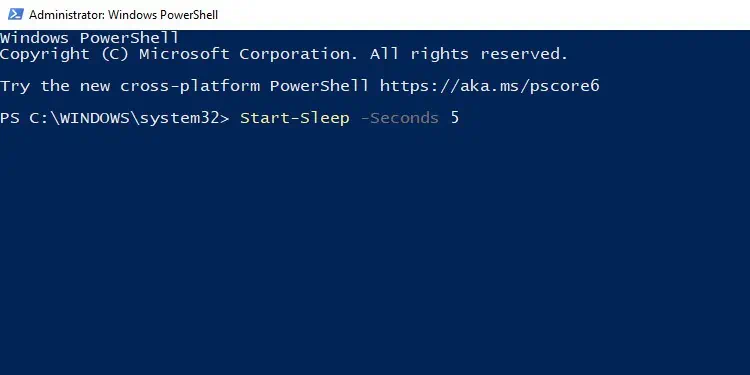
How to Pause PowerShell
you may utilize the following methods to pause in PowerShell. As we’ve included both native and non-native methods, you can use them as appropriate.
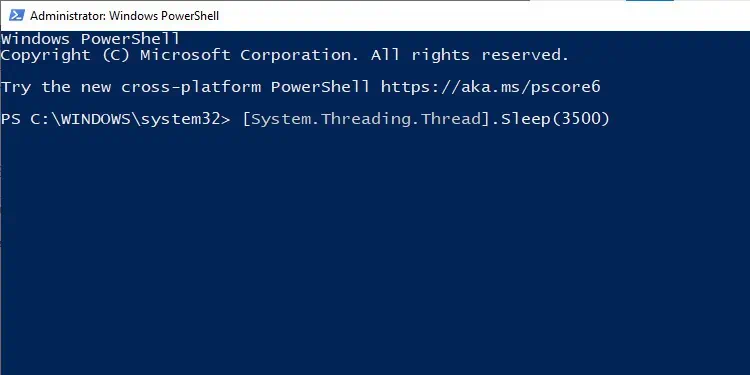
The purpose of theStart-Sleepthe cmdlet is to suspend the activity in a script or session for a specified amount of time. you may use it with the-Secondsand-Millisecondsparameters, as shown in the examples below.
To suspend the activity for 5 secondsStart-Sleep -Seconds 5
To suspend the activity for 200 millisecondsStart-Sleep -Milliseconds 200
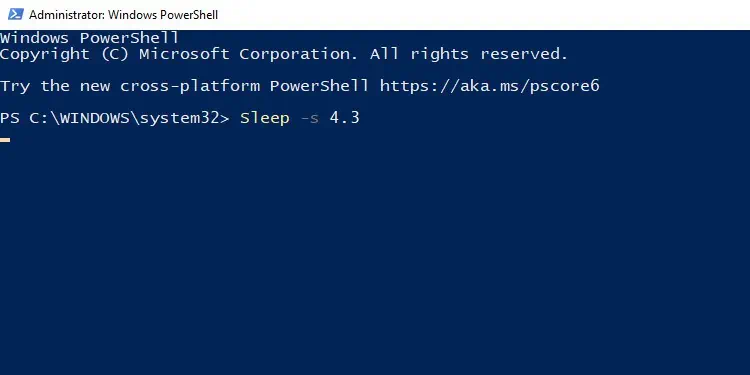
To suspend the activity for 4.3 seconds, you may use any of the following:Start-Sleep -Seconds 4.3Start-Sleep -Milliseconds 4300Start-Sleep -Seconds 4 -Milliseconds 300
you may also make use of built-in PowerShell aliases. You can use sleep and -s in place ofStart-Sleepand-Secondsrespectively. So, the previous command can be written as:Sleep -s 4.3
Finally, you may press CTRL + C to break out ofStart-Sleep.
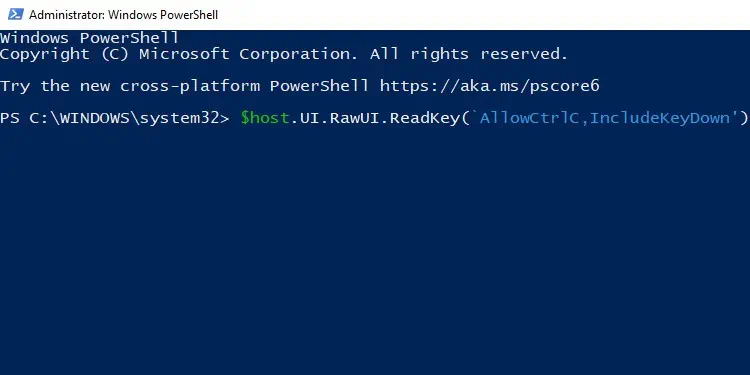
The purpose of theRead-Hostcmdlet is to read some input from the console, and in doing so, it pauses the script. It’s normally used to prompt the user to enter data such as passwords, usernames, etc.
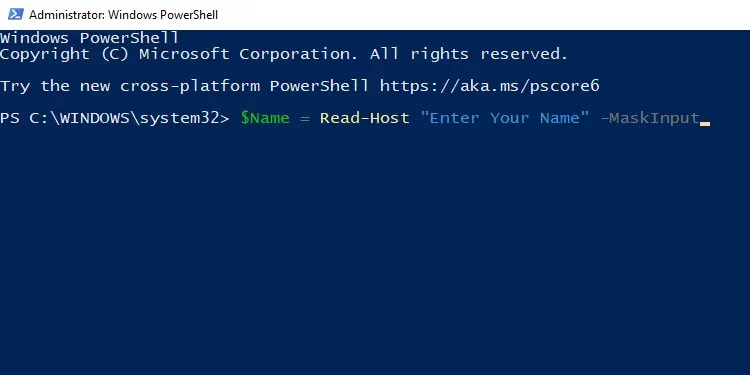
For instance, the command below prompts the user to enter their name, and the input is saved in the “$Name variable.”$Name = Read-Host “Enter Your Name”
If you use this to prompt the user for their password, you may want to add the-AsSecureStringor-MaskInputparameters at the end to display asterisks in place of the password.
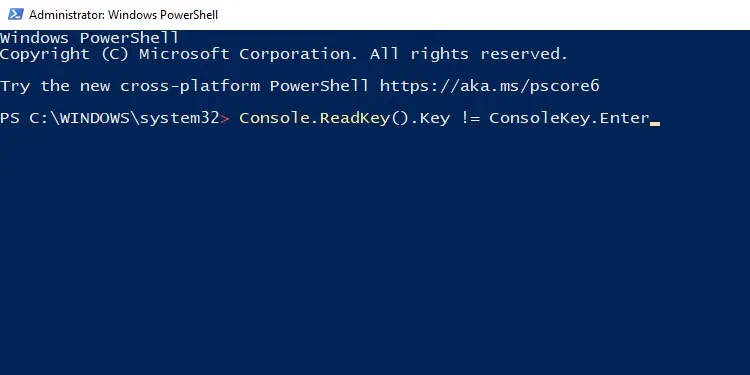
TheConsole.ReadKey()method is often used to pause program execution until the user presses a key. For instance, if you’re trying to pause the program until the user presses Enter, you would use it as such:Console.ReadKey().Key != ConsoleKey.Enter