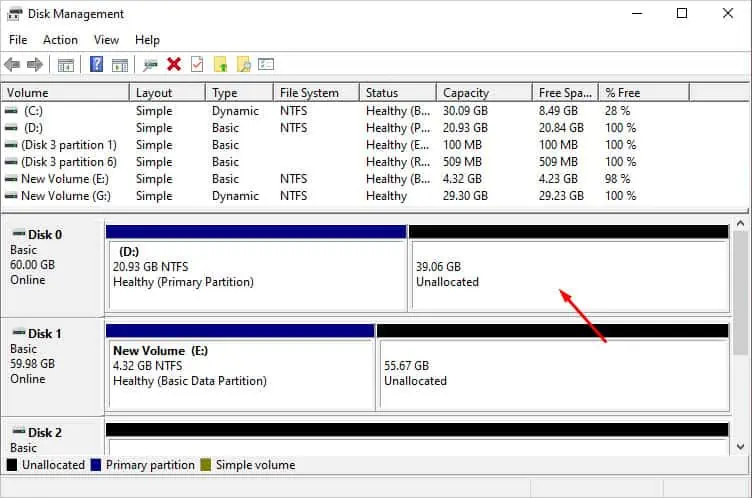
Mechanical hard drives work best on small chunks of data. If all files, including system and personal, are kept in the same partition, the drive takes up more time to operate, and alongside comes the risk of data loss.
Keeping these things in mind, partitioning your hard drive can help achievebetter data organizationandimproved performance. Also, this is beneficial if you plan torun two operating systemson a single hard drive or create a local backup for future recovery.
In Windows, you may partition a hard drive using the built-in utilities—Disk ManagementandDiskpart. But before moving ahead with the necessary steps, ensure you’re logged into the system as an administrator. Also, there needs to be unallocated free space or enough free space (in an extended partition).
Basics to Hard Drive Partitioning
The term ‘hard drive partitioning’ refers to thecreation of multiple volumes(logical drives) within the same storage disk. This way, the operating system treats each of the sectors as individual drives.
It can be compared to partitioning a house into different rooms for better organization. For every partition, there’s a unique letter that offers better navigation to both the user and the OS.
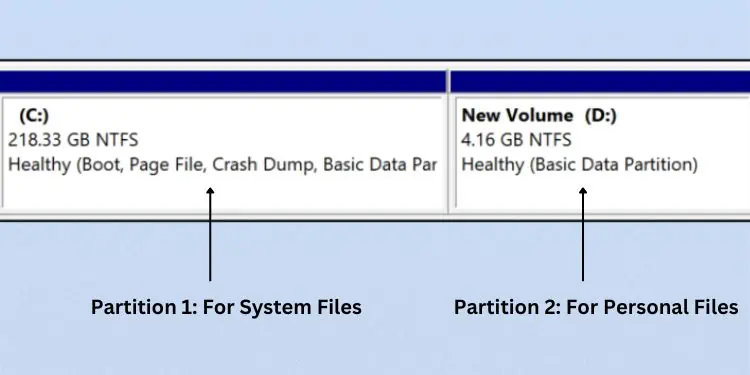
The main purpose of hard drive partitioning is toseparate different forms of datain individual drives. In fact, it’s always recommended to keep Windows files in one partition and personal data in another.
This way, even if your system fails, you canreinstall Windowswithout affectingyour personal files. However, this won’t be useful in case of physical drive failures.
Additionally, you may format each of the partitions indifferent file systemswithout affecting the others. For example, you can install two operating systems on different partitions that use different file systems.
Whenever youinstall a new hard drive, it either comes with one partition or unallocated space. In the latter case, you need to initialize the drive, create at least one primary partition, and assign a letter to use it.
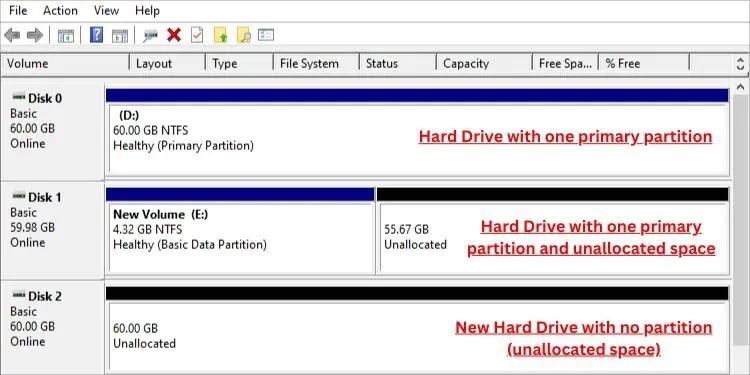
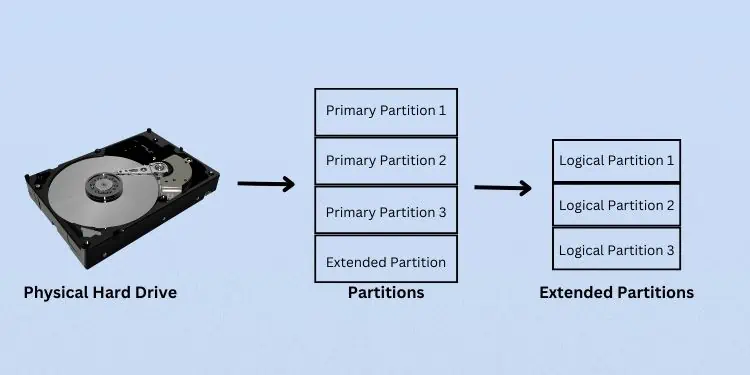
Well, there must be at least oneactive primary partitionwhich is where the OS files reside. Apart from that, you may createthree otherprimary partitions for MBR drives.
Also, you may have a total of three primary partitions andone extended partition. You may further create logical drives (small-sized volumes) for this extended partition.
Talking aboutGPT drives, you may create up to128 partitions.

While the above is for basic disks that use a partition table to keep track of all partitions, the partitioning on dynamic disks works a bit differently. Here, you may create only one primary partition, also called anLDM partition.
It restricts the creation of extended partitions. you may follow our other guide that discusses their differences in detail.