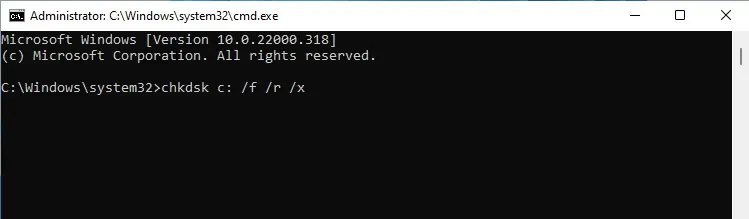
Thermdircommand is used to remove empty directories. If you attempt to remove a non-empty directory with this command, you’ll encounter theRmdir Directory Not Emptyerror.
That much is intended behavior, but some users have reported cases where they faced this error despite usingrmdiron an empty directory. This happens due to reasons like file system errors or broken symbolic links.
We’ve detailed various ways to solve or work around this error on both Linux and Windows systems in the sections below.
Fix Rmdir Directory Not Empty Error on Linux
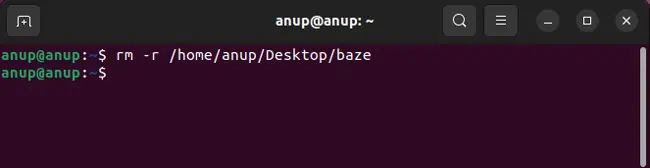
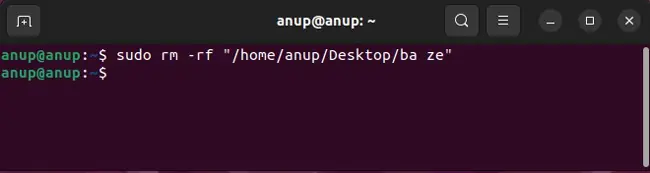
The easiest fix is to use thermcommand instead ofrmdir. If this workaround doesn’t appeal to you, or the rm command doesn’t work either, the rest of the solutions will be helpful.
The base syntax for the rm command isrm . The-dflag removes the directory if it’s empty. But in the case of non-empty directories, you may utilize the-rflag to recursively delete the specified directory and its contents.
Finally, ensure youdon’t usesudo rm -rf /as this would cause the contents of the root directory, i.e., every mounted filesystem, to be deleted.
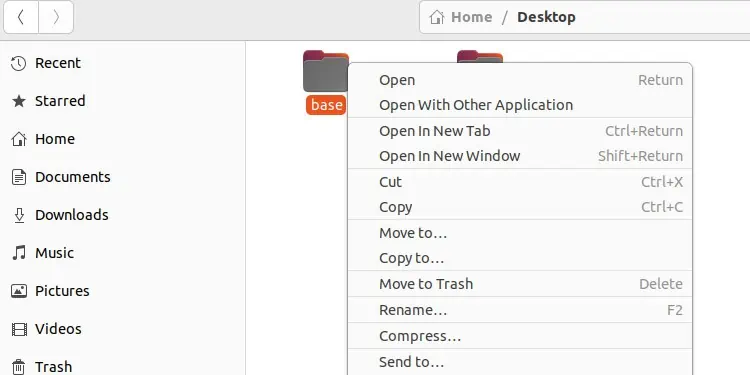
When things don’t work in the GUI, we turn to the command line. As unusual as this may sound, things are the opposite in this case. Numerous users have reported that deleting the folder via the File Browser worked for them. It’s worth trying this before checking out the other solutions.
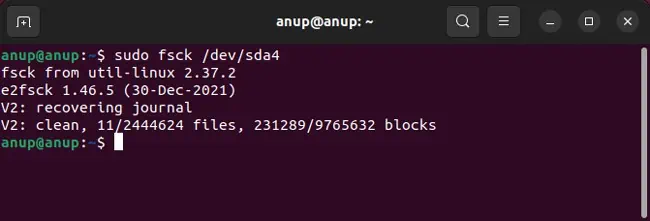
File system errors are a common reason for file deletion and similar issues. As such, using thefsck(File System Consistency Check) utility can be helpful. Here are the necessary steps for this:
Delete from Fileserver
There have been cases where the directory couldn’t be deleted because it was part of a filesystem mounted with CIFS (Samba). As there was a file that was a broken symbolic link, ls failed to mention it.
Over CIFS, you wouldn’t be able to see this and thus could be mistakenly assuming that the directory is empty. In such cases, you would need to delete the file directly from the fileserver.
Users have reported cases where the directory was open in a node.js app or where a node server was periodically accessing the files in the directory, causing minor meta files to exist inside the directory constantly.
In such cases, shutting down the application or server that’s accessing the directory at the moment would resolve the issue.
Fix Rmdir Directory Not Empty on Windows