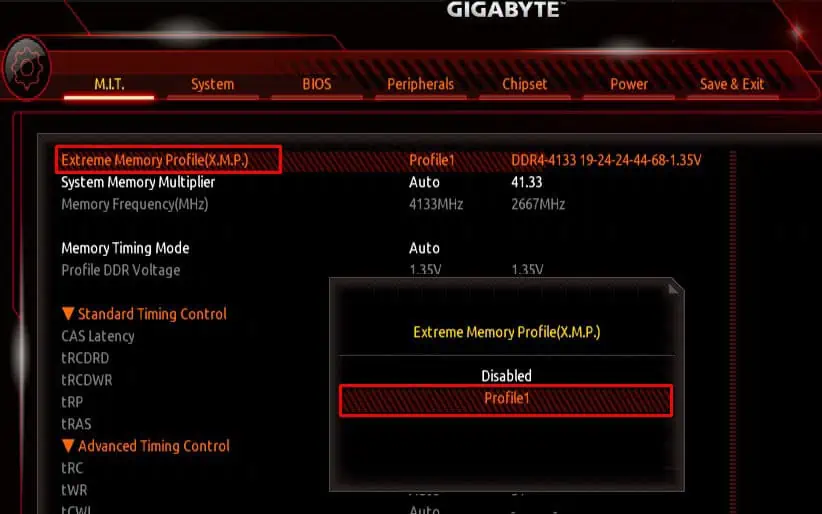
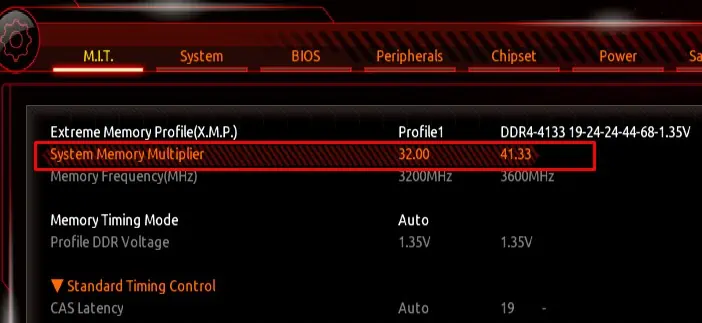
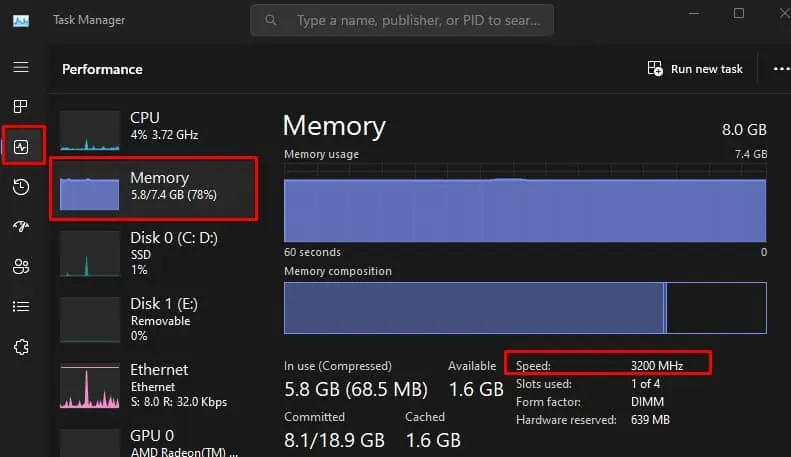
The advertised RAM speed is the maximum speed supported by that particular RAM stick. However, by default, your system will not run at this speed. To make use of it, you need to enable memory profiles.
In some cases, the RAM stick still might not run at its full speed even after you enable memory profiles. If you have a CPU or motherboard that supports lower RAM speed, it will restrict the RAM from reaching its advertised speed.
Check CPU and Motherboard User Manual
Before we begin, it’s best tocheck the maximum RAM speedsupported by your system’s motherboard and CPU.
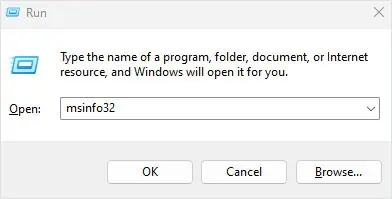
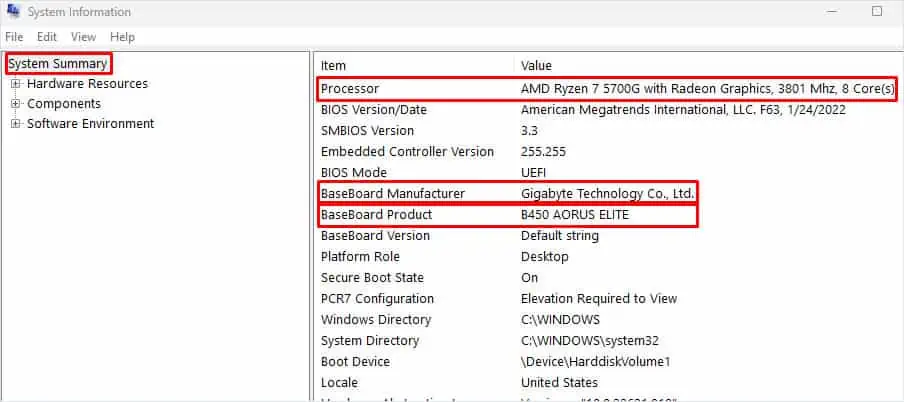
So let’s start by finding out the CPU and motherboard model in your system.
After finding the motherboard and the CPU model, visit the motherboard manufacturer’s official website and search for your motherboard’s specification list or user manual. In that, find out the RAM speed supported by your motherboard. Also, verify if there is support for XMP, EOCP,or DOCP.
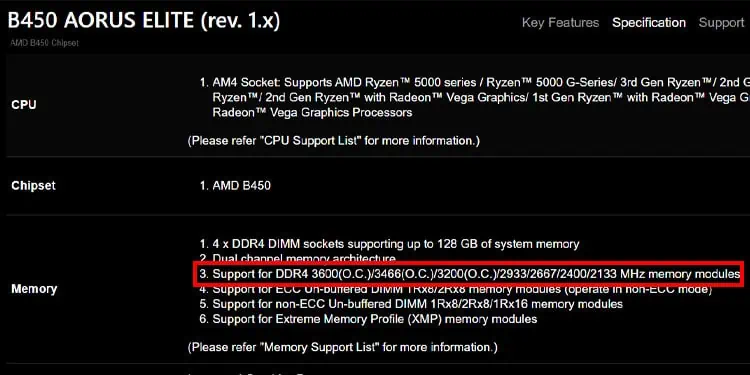
For instance, the B450 Aorus Elite motherboard offers a maximum frequency of 3600 MHz (on overclocking) and supports XMP.
After that, visit your CPU manufacturer’s website and check the CPU specification or user manual for your processor to determine the maximum RAM speed supported by your processor.
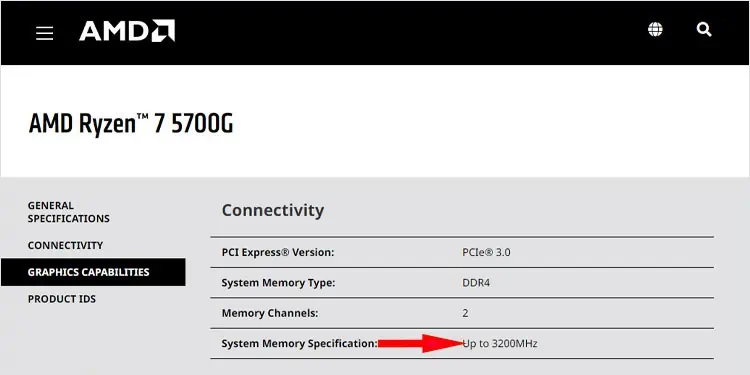
For instance, AMD Ryzen 7 5700G supports a maximum RAM speed of 3200 MHz.
Choose Suitable RAM Speed for Your PC
Now that you know the Maximum RAM speed for both the motherboard and the processor, it’s time to set the RAM speed.
In my case, my motherboard and CPU support a maximum RAM speed of 3600 and 3200 MHz, respectively. So it’s best to stick to the RAM speed of 3200 MHz, although my RAM supports 4133MHz.
Your system might be able to handle slightly higher values than the recommended amount, but there is a chance of system instability.
This may result in a random system crash, higher system temperature, or even aBlue Screen of Death (BSOD) error.
Enable Extreme Memory Profile