Port 22: Connection Refused is a common SSH error that generally happens because users attempt to connect to the wrong port.
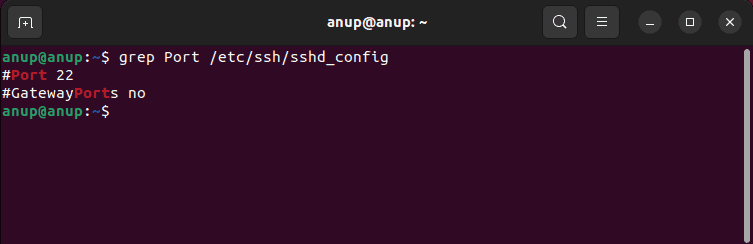
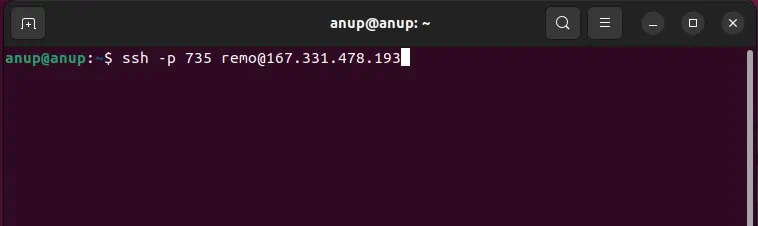
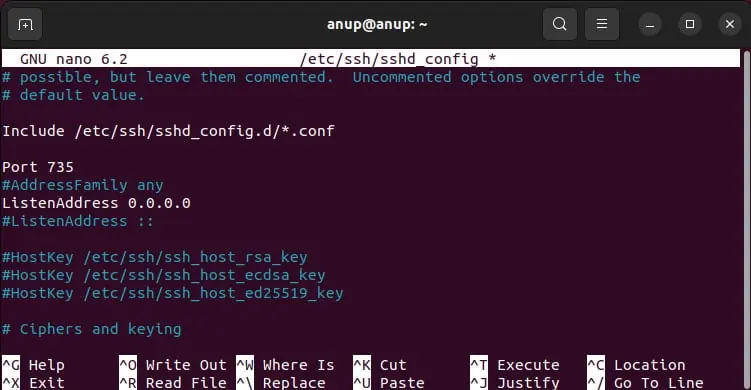
The default SSH port is 22, but it’s generally changed to something else due to security concerns. As such, when users attempt to connect to port 22 (by default), they inevitably encounter this error.
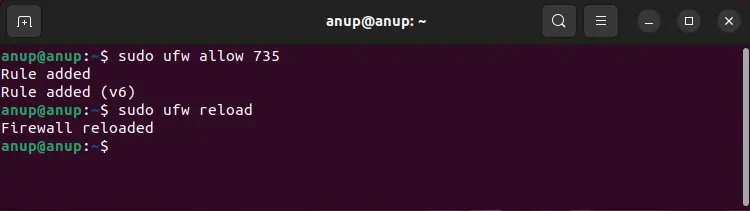
In addition to this, reasons like the firewall blocking the SSH port or the SSH service being down also usually lead to this error. We’ve detailed more reasons, as well as steps to deal with each one in the sections below.
How to Fix Port 22: Connection Refused Error
Before you start troubleshooting, we recommend rebooting your router, as that could be all that’s needed to resolve the issue. Additionally, you should perform a ping test to confirm that this is actually an SSH issue rather than ageneral internet issue. If there’s packet loss, you’d better off fixing that first.
Also, this error is, for the most part, a server-end issue. As such, the first two fixes are applicable on the client end, but there’s not much you may do from the client system. Your best bet will be to try out the server-end fixes.
Verify Login Credentials
It’s easy to miss, but users sometimes enter incorrect credentials on the client end when attempting to connect to the SSH server. Try reconnecting with the correct credentials if this is the case before moving on to the other fixes.
The second possible issue on the client end is that the system isn’t resolving the hostname, leading to this error. you may utilize the Public IP of the SSH server instead of the domain name to confirm this.
If there does indeed seem to bea DNS issue, you couldtry flushing the DNS cachewith the following commands:sudo systemd-resolve –flush-cachessudo resolvectl flush-caches
If that doesn’t help, you shouldchange your DNS servers.Here are the steps to do so:
If on a private network, you could also contact your system admin to ensure that the SSH server’s DNS entry is correct.
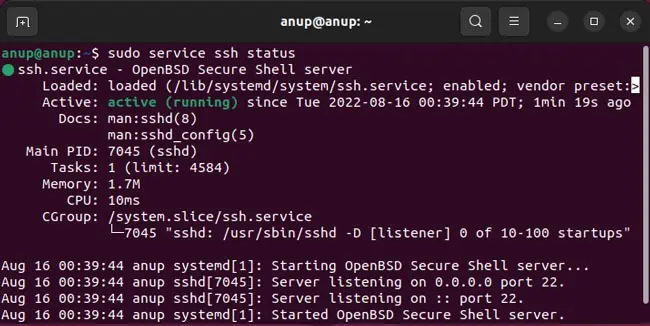
Ensure SSH is Installed
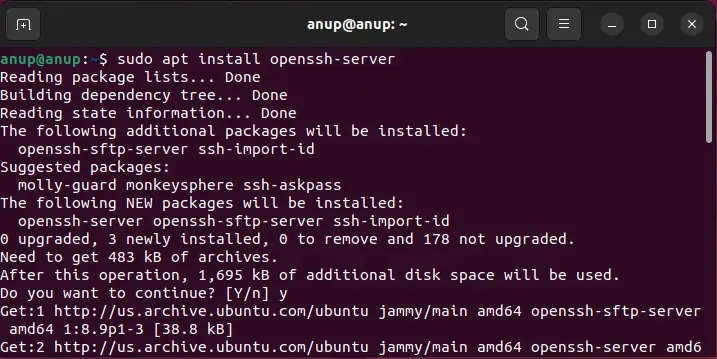
This might seem like a no-brainer, but users often encounter SSH issues on fresh installations as they forget that SSH doesn’t come preinstalled.
Toinstall the OpenSSH server application and related fileson Debian-based distros, utilize the following command:sudo apt install openssh-server