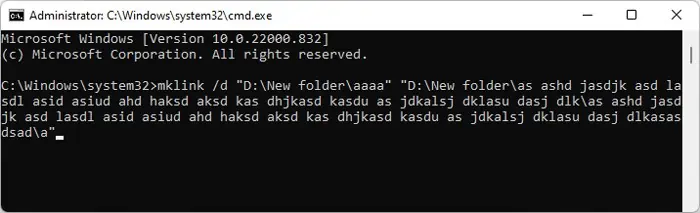
Windows has a limitation of 255-260 characters for the path length of a folder. If while transferring a folder, the new path length of the folder or any subfolder were to exceed this number, Windows does not allow transferring the files at all. Instead, it’ll give you the “Destination Path Too Long” error message.
The full path includes the drive letter, colon, name components together with backslashes as well as a terminating null character. For instance,C:\Windowsis the full path of the Windows folder and it’s path length is 11.
People often encounter this issue while moving or copying saved web pages where the supporting files have very long names. They are not able to transfer some files which causes issues while viewing the web document.
In such cases, there are a few things you may do to avoid or resolve this issue, which we provide in this guide.
How to Fix Destination Path Too Long Error
There are a few ways to resolve the Destination Path Too Long Error whiletransferring a file on Windows. Go through the possible solutions we have mentioned below and apply one according to your preference.
The first thing you should do is rename the folders with long names along the destination path. You should also change all long names in the source folder and it’s subsequent files and subfolders. Since Windows has a maximum limit of 256 for a path, ensure the directory length (after copying/moving) of any folder or subfolder does not exceed this number.
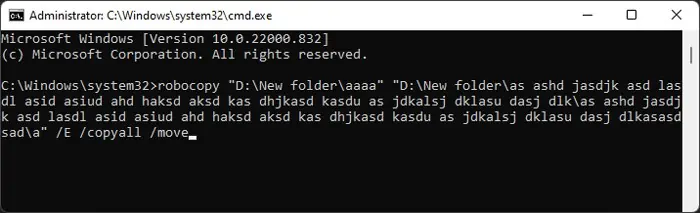
Use Command-line Interface to Move/Copy Files
It is possible to utilize the robocopy utility to move or copy your files and folders while disregarding the maximum path limit.
However, robocopy is not exactly a tool intended to copy or move but synchronize two folders. So it actually transfers the contents of the source folder to the destination folder instead of transferring the source folder itself.
Here’s how you may use this CLI tool to avoid the “Destination Path Too Long” error:
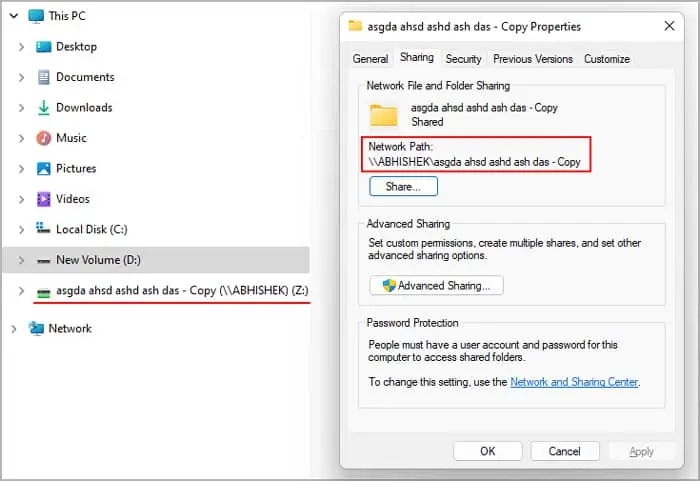
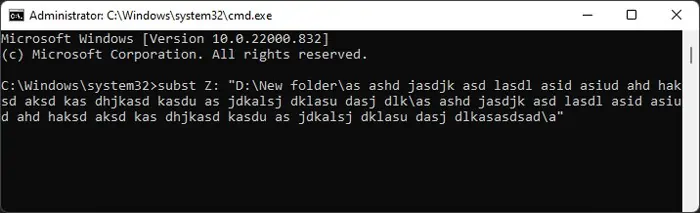
Another way to resolve this issue is to substitute a long part of the path with a shorter path. In this process, you link the destination folder’s path to a new drive or another location. So, when you add files/folders to the new location, your system will update the previous location as well.
If the new path is shorter than the max path limit, this method bypasses the above error. However, if the folder you are copying itself contains subfolders with long names (more than the limit), this method may not work.
There are mainly three ways to substitute the path on a Windows OS using built-in tools. you may pick any one of them.