TPM used to be installed as a dedicated chip on motherboards. But since TPM 2.0, it’s more commonly implemented via a board’s chipset.
This means that even without a discrete TPM chip on your board, you may still enable TPM 2.0 from the BIOS.
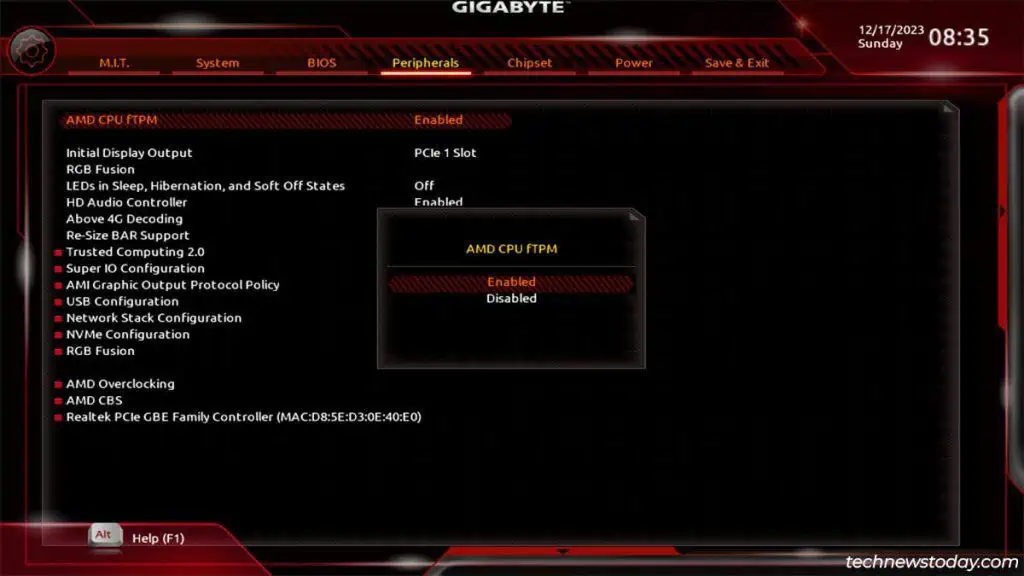
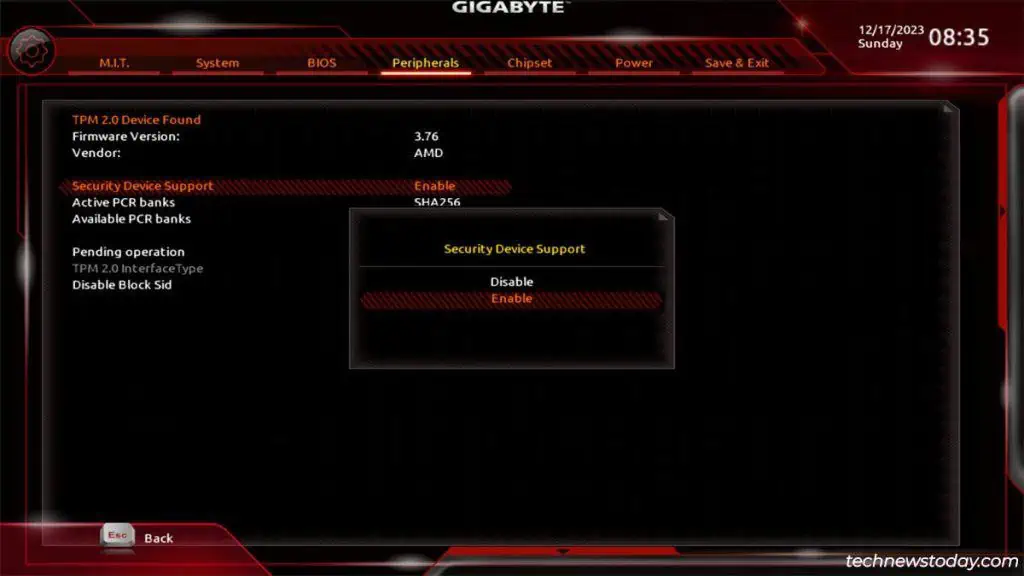
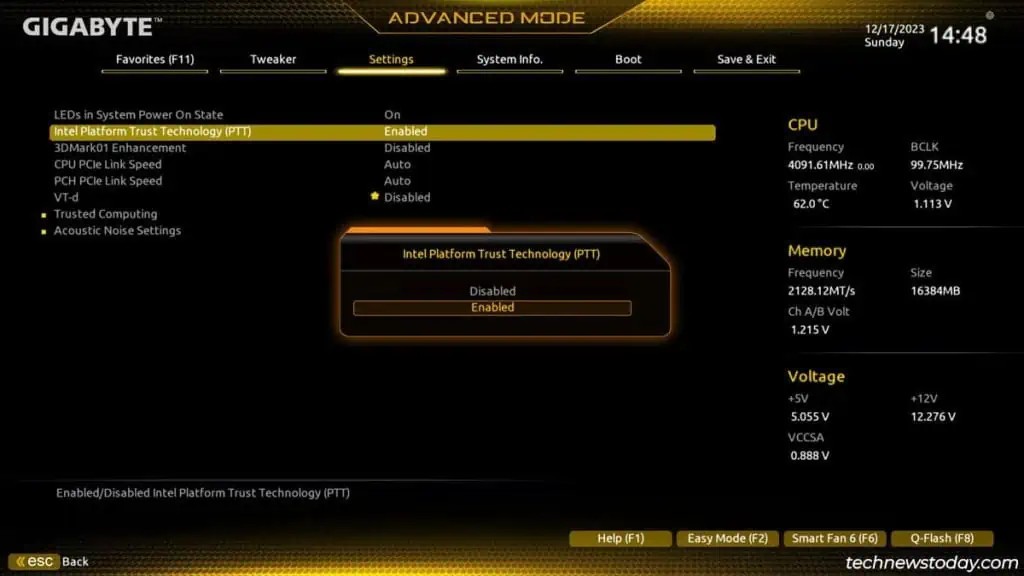
Specifically, you’ll need toenable thefTPM(AMD),PTT(Intel), andSecurity Device Supportsettings in the BIOS.

But before you do this, take a minute to understand what TPM is and why you may want to enable it.
What is TPM? Should You Enable It?
TPM (Trusted Platform Module) is a technology that improves the security of your system in various ways. Mainly,
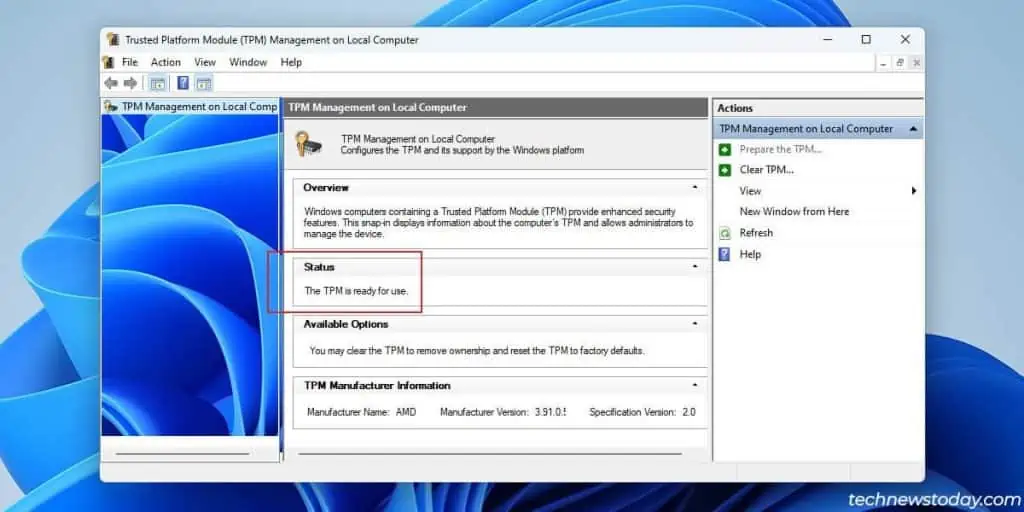
In the current context, enabling TPM 2.0 is also a requirement forinstalling Windows 11and playing Valorant.
If you need to enable TPM 2.0 for these reasons or simply want the security benefits, start by getting to your system’s BIOS UI.
Access the BIOS Setup Utility
Turn on your PC and repeatedlypress the BIOS key(Delon most systems). The PC should boot to theBIOS/UEFI.
Ifthis method doesn’t work, you may also use alternative methods likeWinREto get to the firmware interface. This guide onentering the BIOScovers such methods in detail.
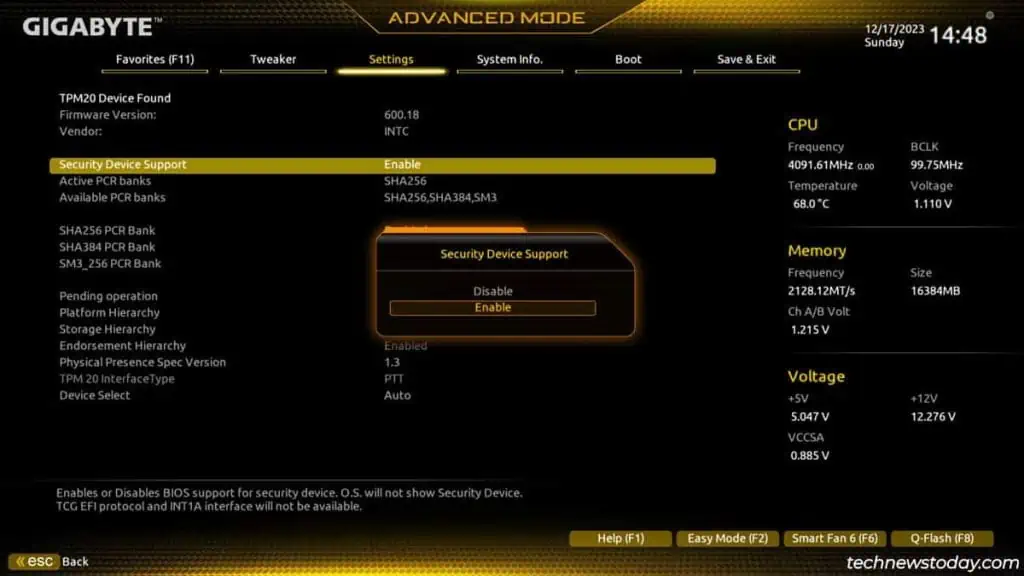
Enable TPM in the BIOS
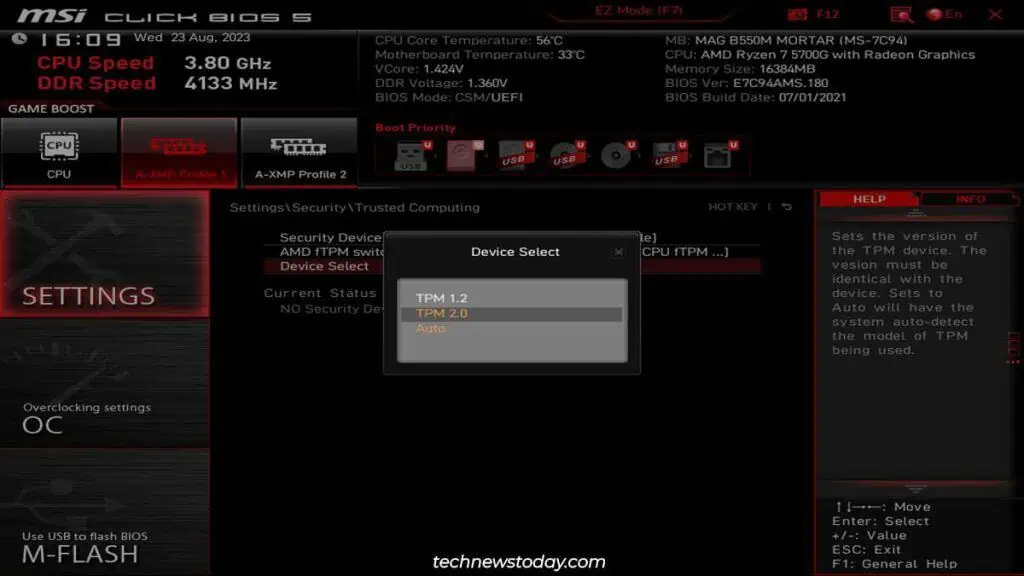
What we’re trying to set up is firmware-based TPM. Intel calls it thePlatform Trust Technology (PTT)while AMD calls itfirmware-TPM (fTPM).
To enable AMD’s fTPM,
Besides setting the TPM version, there’s not much else to do here. Some boards let you set up advanced settings likePCR banksandPlatform Hierarchybut these arebest left to default.