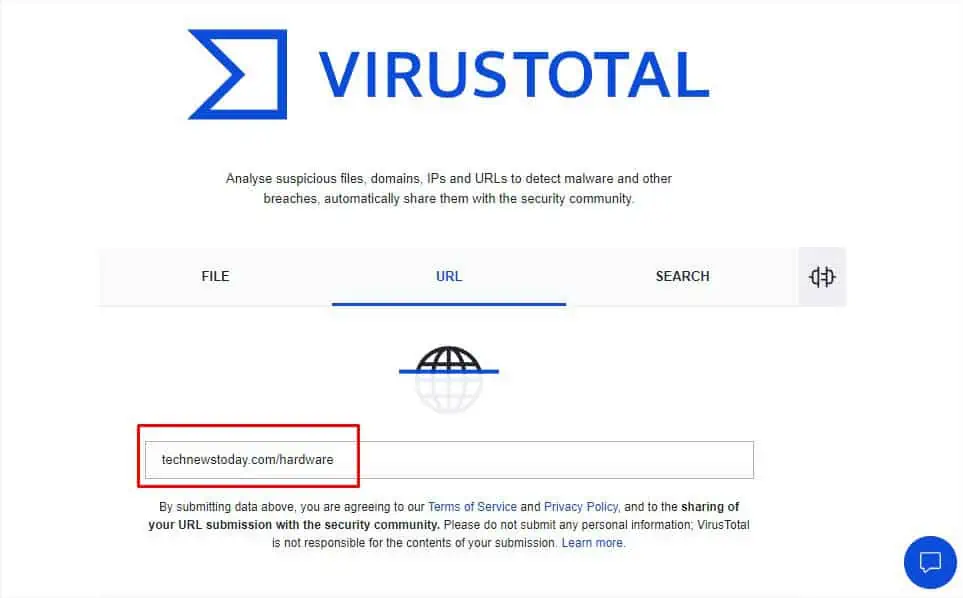
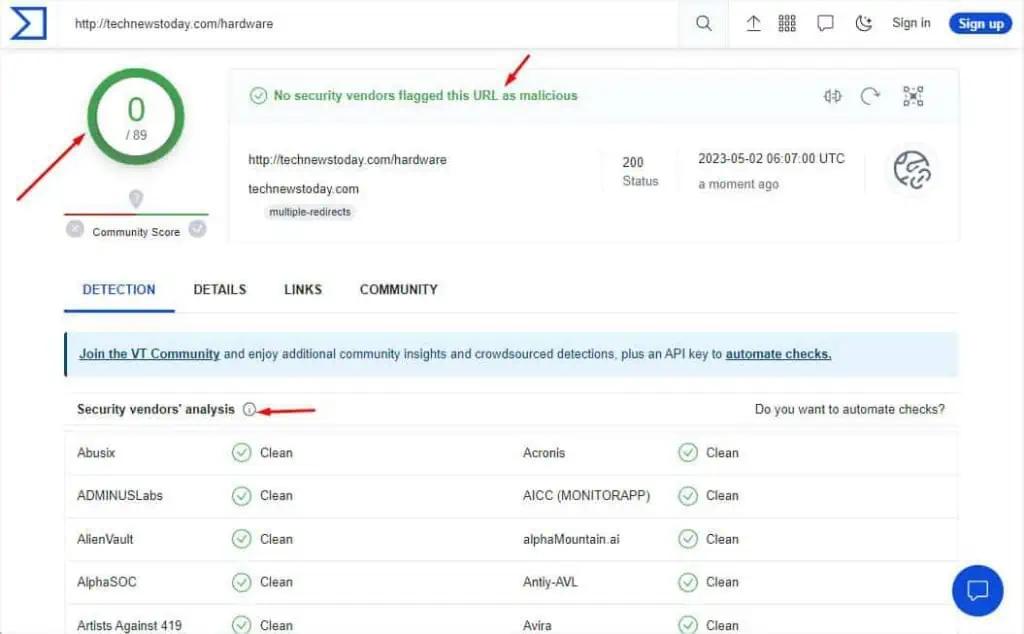
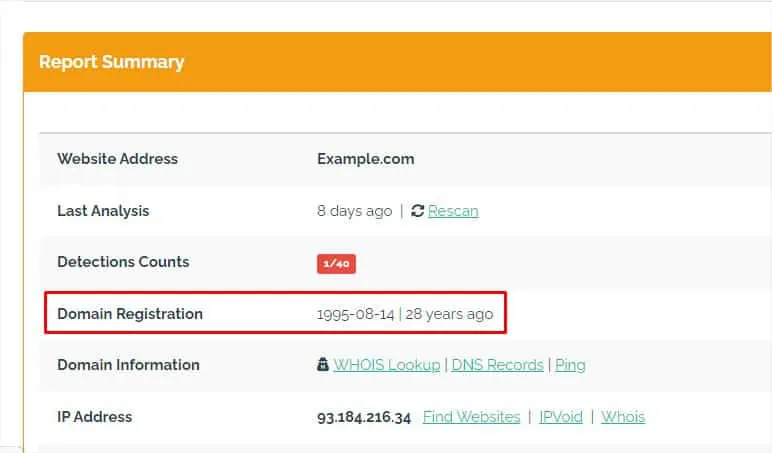
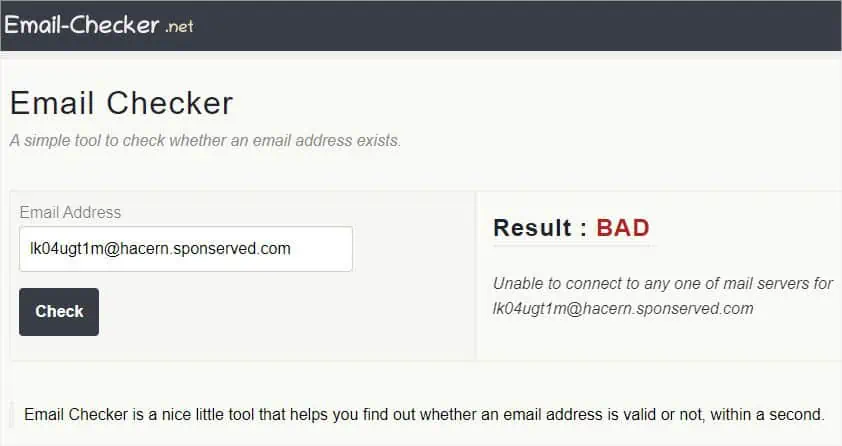
In this modern internet age, cyber crimes are reportedly increasing daily. You’ve probably got links in your inbox claiming you’ve won a prize or asking you to change your password! These are all different forms ofphishing attacksthat you should avoid.
No matter who sent this to you and how legitimate they appear, you should think twice before clicking on them. These suspicious links might trigger an automatic malware installation on your device, steal your data(which could be login credentials and banking information), or evenhack into your account.
The first-hand rule is toavoid the URL that you do not find trustworthy. However, there are different ways to determine whether the link is safe or fraudulent. Without further ado, let’s jump right into them.
Manual URL Inspection
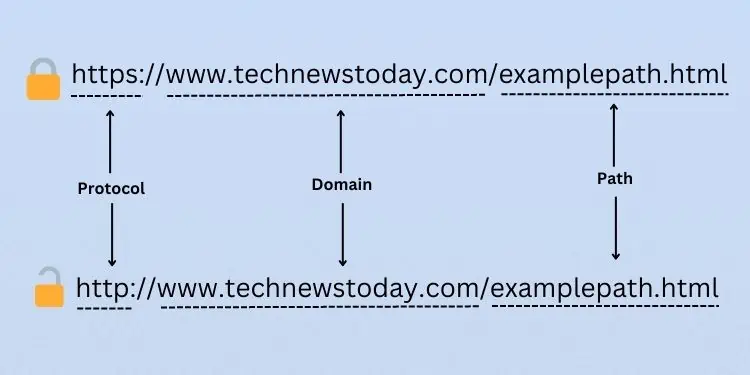
The most basic method to validate the link is through manual link/URL inspection. In technical terms, a URL can be broken down into several parts. For your simple understanding, these are the three basic components—protocol, domain, and path.
Let’s begin with Protocol. If alink contains ‘HTTP’ instead of ‘HTTPS’, it’s the first sign indicating the site is unsafe. HTTPS is the secured version of the former and incorporates SSL/TLS certificates that encrypt your information, thus adding an extra layer of security.
However, HTTPS isn’t the only thing to consider on a link. With improvements in technology, most attackers are already utilizing SSL certificates, making the links appear more authentic. In fact, some evenmimic the original domainto fool the users (URL spoofing). Others adopt this strategy to attack those netizens who may type the URL incorrectly (URL hijacking/typosquatting).
For example, a phisher might mimic the originalgoogle.comdomain asgoo-gle.com. Note that the two might look similar but the ‘-’ sign changes the context. This way, you may determine that the spoofed link is not safe.
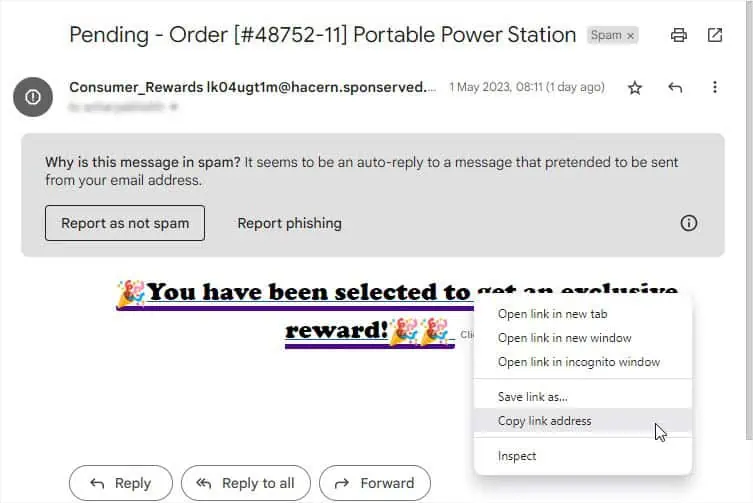
The third and most important part of an URL is the Path. you may easilyexamine the exact locationthe URL is trying to take you to. That’s the reason some attackers have started shortening the URLs using Bitly or similar tools. This helps hide the website’s file paths making it impossible to know whether it’s malicious. In such cases, manual inspection might not be the best option.
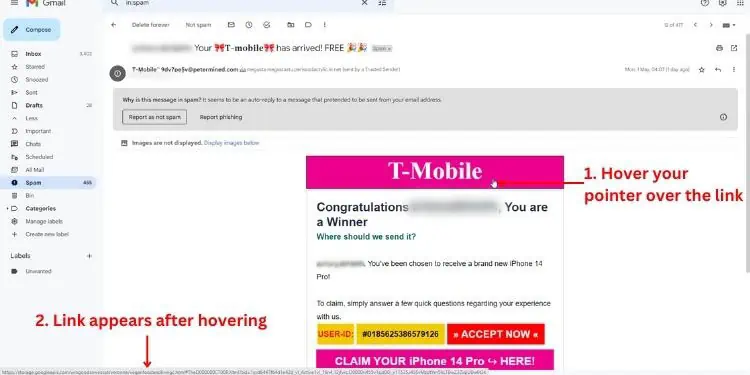
If you’re on a web browser, you might have noticed that different articles contain tons of linked phrases (and even images) directing you somewhere. To check the URL, you may simplyhover over the linked phrase,and you’ll likely get it from the bottom-left corner of the window.
Using Site Operator in Search Engine
If you find the manual inspection method too difficult to understand, you do not need to scratch your head! It’s definitely not the only way to detect the link’s integrity.
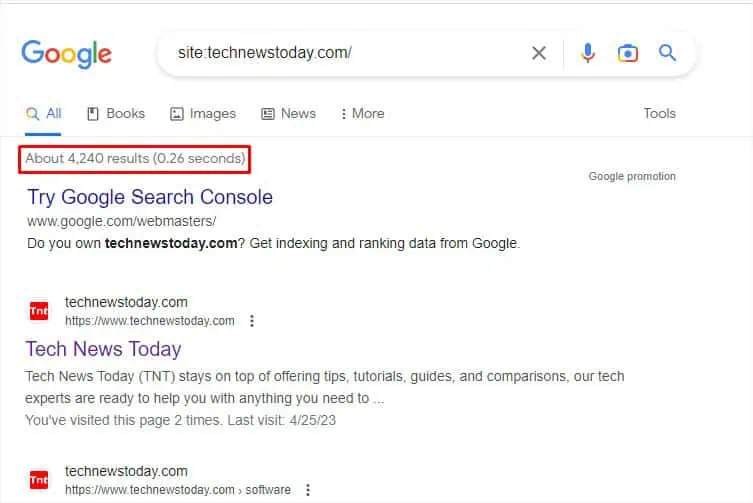
One of the many methods is checking the search results on a preferable search engine. All you have to do is utilize the ‘site’ operator and enter the site’s name. If you get a large number of results, you may confirm that the link is probably safe.
Note:This technique might help validate the site but is not handy to get accurate results about a specified link/URL.
Use a URL Checker Tool