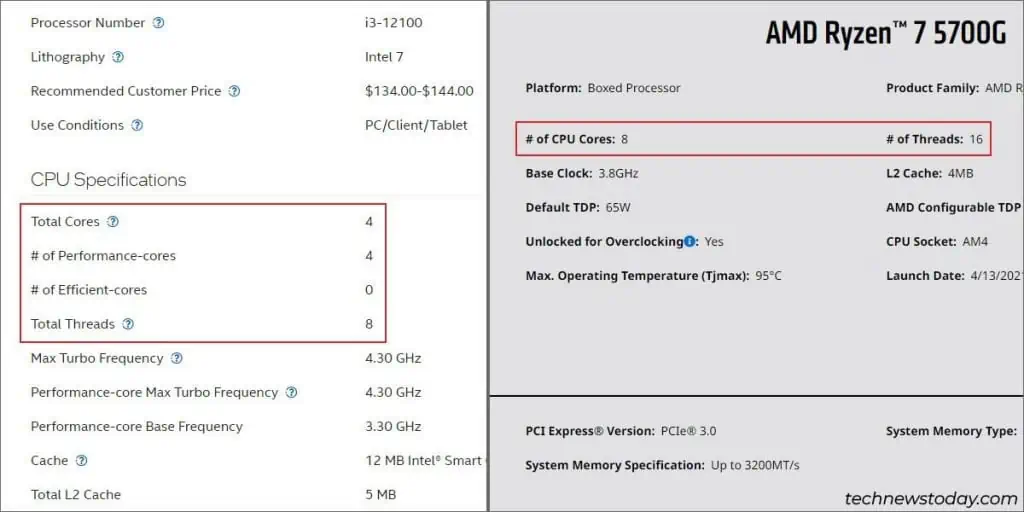
Intel and AMD providespec sheetsthat outline how many cores and threads a processor has among various other details.
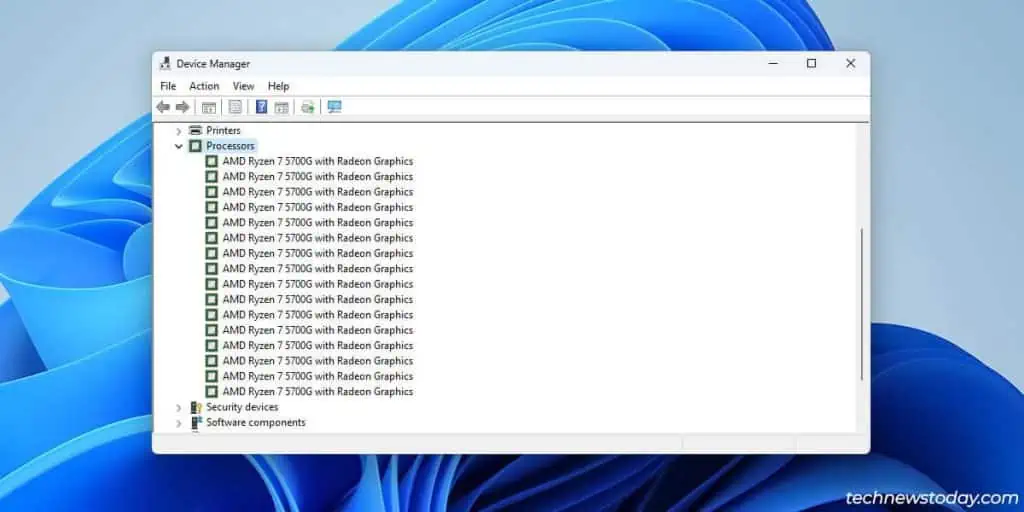
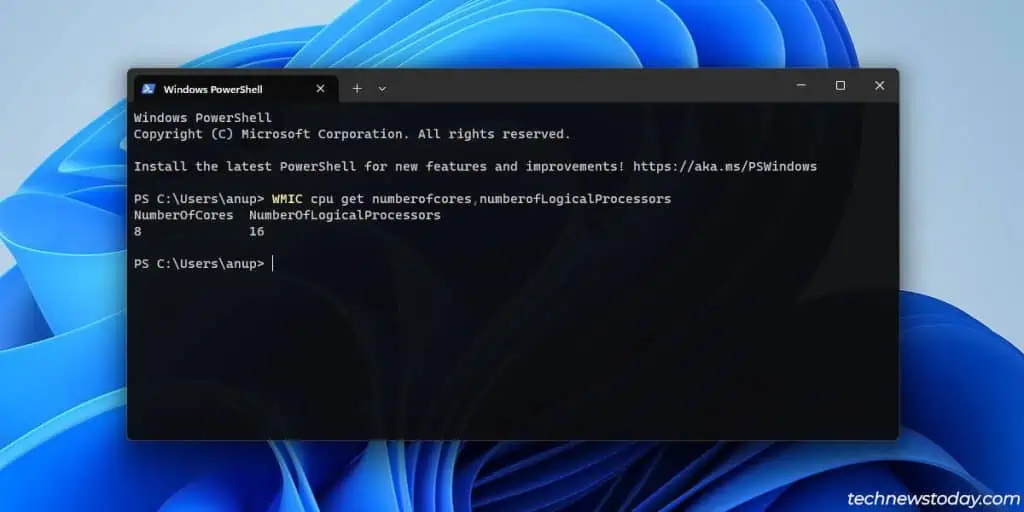
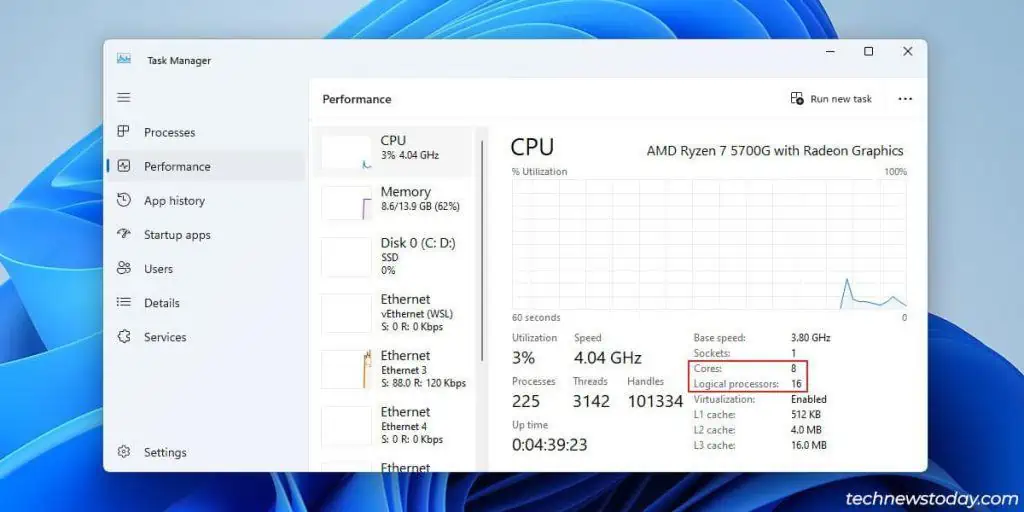
you may get the same info in Windows with programs like theTask ManagerorCPU-Z.
The main difference between these methods is that spec sheets utilize the termThreads, while some Windows apps sayLogical Processorsinstead.
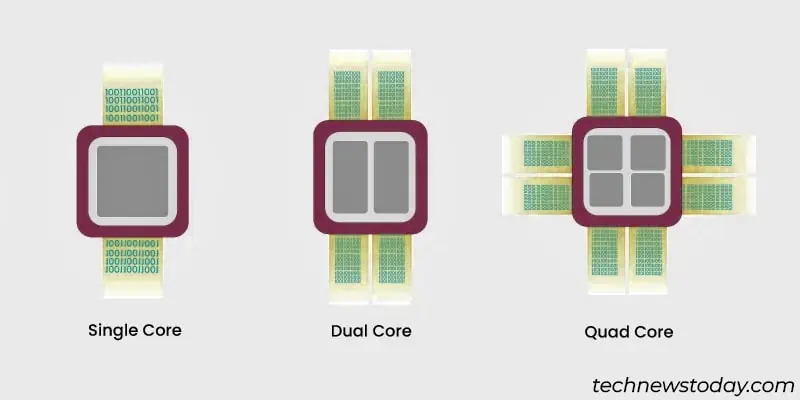
This can be confusing. So, let’s start by understanding what cores, threads, and logical processors are.
Cores, Logical Processors & Threads
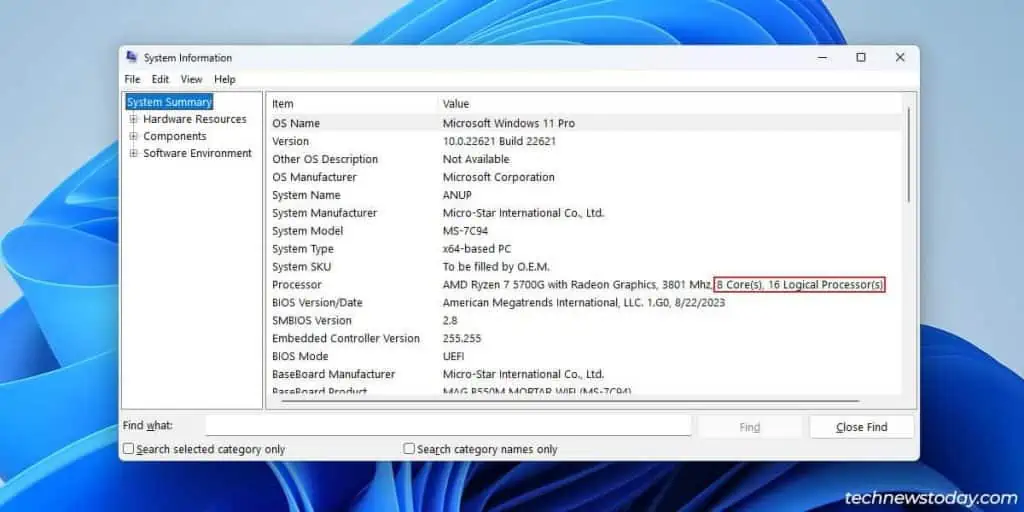
Physicalcoresare actual processors installed on the integrated circuit die. Modern CPUs are multi-core (e.g.,my Ryzen 7 5700Ghas8physical cores).
Athreadis a set of instructions that programs send to the CPU.
One core can only process/execute one thread at a time. To deal with this limitation, modern CPUs use a technique calledHyperthreading. This splits the physical cores into two or more virtualized cores.
For instance, my Ryzen 5700G’s 8 physical cores are split into16 logical cores. This means my system can parallelly process up to16 threadsat a time.
This is why CPUs are labelled in formats like8 Cores 16 Threads, and why the termsThreadsandLogical Processorsare used interchangeably.
CPUs use various other advanced technologies likeMultithreading,scheduling, etc. These enable modern systems to processthousandsof threads near-simultaneously.
Finally,how many cores you needandwhether your CPU is powerfulenough entirelydepends on your workload. 4-6 cores will be enough for active workloads like gaming. Passive workloads like CPU or GPU rendering will benefit from higher core counts.
Although all of this was a simplified explanation, you should be better equipped to check the CPU cores/threads and determine whether they’re enough now.
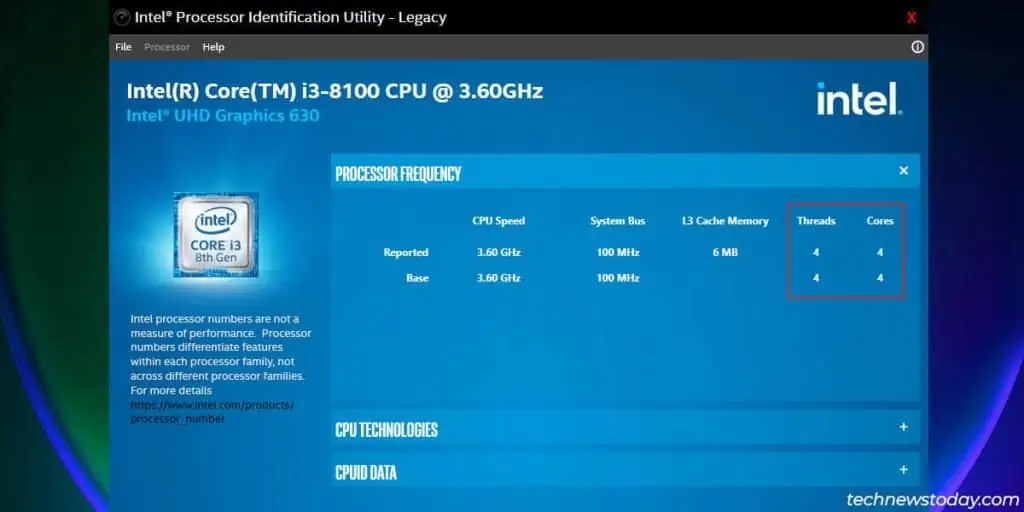
Check the CPU Spec Sheet
If you access the CPU specs page for yourIntelorAMD processor, you’ll find the number of CPU cores and threads along with other specs.