All the resources or web servers on the internet have unique addresses assigned to them, which are the IP addresses. The Domain Name System (DNS) is basically a phonebook for the internet that translates or resolves the domain name or URL you type on web browsers to these IP addresses so that you may access the resources.
Normally, your ISP automatically designates theDNS serversyou need for the domain name resolution. However, these servers may come with certain restrictions. So, you may want to change the DNS for faster internet browsing as well as to access more resources on the internet.
Using random DNS servers can invite various DNS problems. These issues range from less severe ones like high latency to major attacks like DNS cache poisoning, Denial of Service (DOS), and so on.
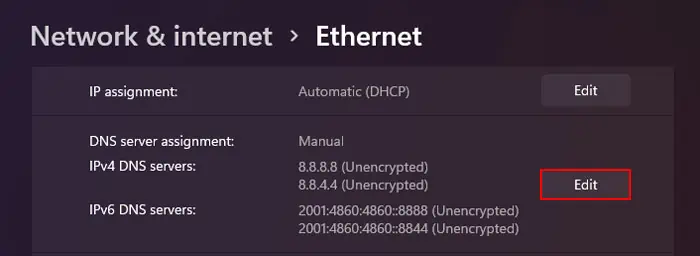
If you don’t have an appropriate DNS server in mind, we recommend using public DNS servers as manual DNS addresses. Many public DNS are available for your use, such as:
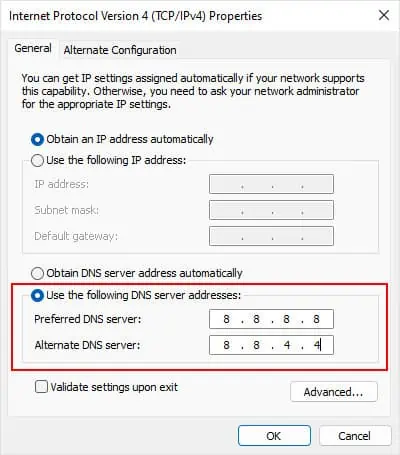
you may utilize the first address in the Preferred DNS address and the second one under Alternate DNS Addresses.
Change DNS Server on Windows
There are many methods to set up or change the DNS server on Windows. you may use all of them to change the DNS address for the IPv4 address, or the IPv6 address, or both depending on your need.
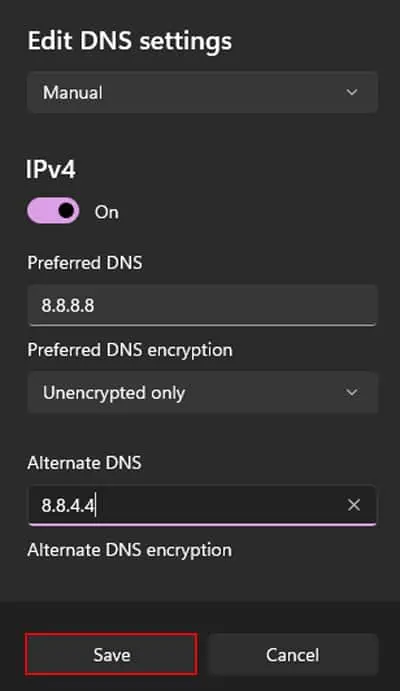
If you don’t know which one to change, go for IPv4, as it is the default internet protocol for almost all web servers.
Through Windows Settings
Windows Settings is the default application you may use to change all your system settings, including the manual DNS server address. It also allows you to easily encrypt your DNS for more security.
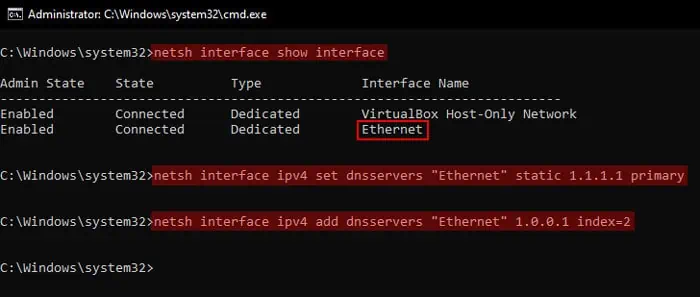
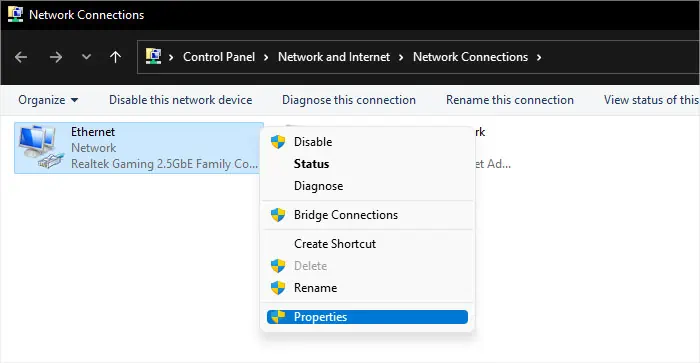
you may also change all relevant network settings, including the DNS address, using the Command Prompt.
It is also possible to change the DNS server address for both IPv4 and IPv6using the Command Prompt.
However, the command to set up the primary (or preferred) and the alternate DNS server addresses are somewhat different. So go through the following steps carefully before carrying them out.
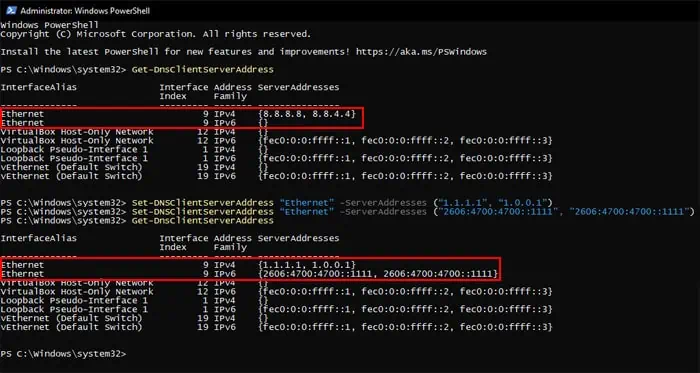
you may also utilize the Set-DNSClientServerAddress cmdlet on PowerShell to change the DNS server address.
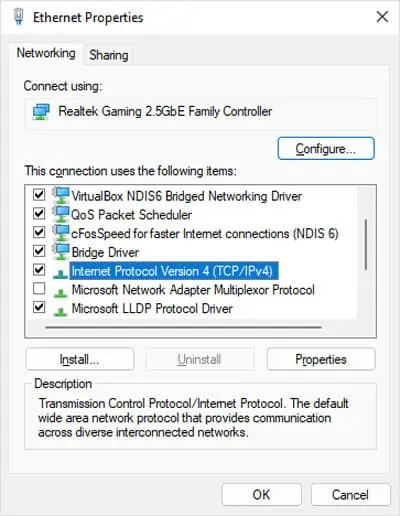
you may actually utilize the same cmdlet with the same attributes for both IPv4 and IPv6. Your system will automatically change the setting for the relevant protocol depending on the address.