Both GDDR6 and GDDR6X are the graphics synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) on a Graphics Cards. you may also call them a synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SGRAM).
If you take off the heat sink on the graphics card, you may see the graphics processor (GPU) surrounded by many black rectangular chips. These are the SGRAMs on the GPU and they work as the RAM for the GPU.
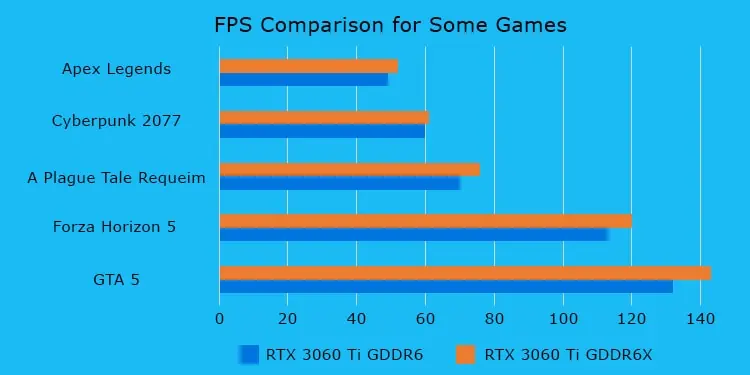
Micron and NVIDIA joined forces to create GDDR6X, providing faster data transfer for high-end GPUs with over 6000 cores. However, now that NVIDIA has started using this component in lower-core GPU, such as the RTX 3060 Ti, it is worth knowing the differences between the two. This way you could make a better decision on which graphics card to buy.
What’s Different in GDDR6X?
There are not many distinctions between GDDR6 and GDDR6x. The fundamental difference comes from the encoding technology implemented in the devices. All other dissimilarities are simply a byproduct of this parameter.
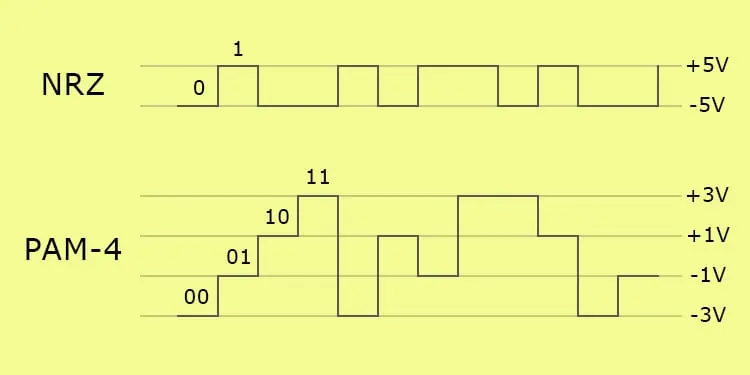
Before transferring data, the VRAM needs to encode it to prevent data loss. Unlike GDDR6, which uses NRZ (Non-Return to Zero), GDDR6 uses PAM-4 (Pulse Amplitude Modulation-4).
NRZ modulates data on two signal levels, high and low, represented by a positive and a negative or zero voltage respectively. So it can transfer one of two power levels at a time. Consequently, it means it can only transfer one Binary digit (bit) of data per clock pulse, either 0 or 1.
PAM-4 on the other hand enables devices to send one of four power levels at a single time by modulating data on four signal levels. So it can send two bits at a time, 00, 01, 10, and 11.
Bandwidth and Performance
The difference in encoding may not seem that important but in actuality, it determines the data transfer rate of the SGRAM. This is because the device transmits encoded data rather than raw data.
The GDDR6 SGRAM provides a per-pin bandwidth that maxes out at 16 Gigatransfers per second (GT/s). PAM-4 encoding raises this value to 19-21 GT/s bandwidth increasing the bandwidth by over 40%.
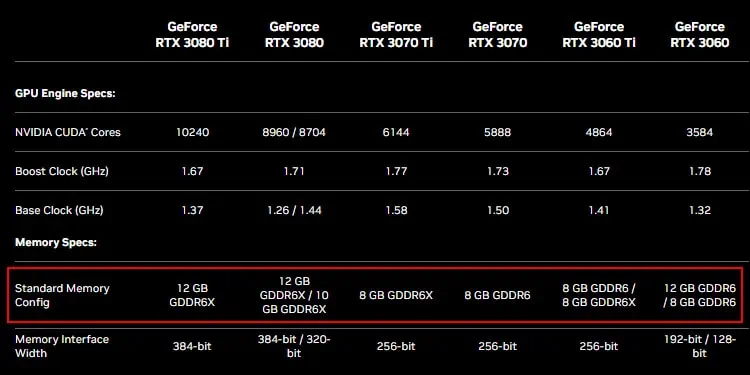
Now, to how this actually affects GPU performance, we need to first look at how these graphics SGRAMs work. These components store the graphic textures, frames, and shaders before sending them to the GPU cores for rendering. So, higher bandwidth always helps in faster rendering andincreases frame rate.
However, this remains true only as long as the SGRAM contains data that it can push to the cores. If it doesn’t buffer enough data necessary for the whole rendering due to a lower SGRAM capacity or other reasons, you will still experience lags or stutters.
All the factors of the GPU, including the SGRAM collectively impact performance. But there’s no denying that if all the other factors are the same, GDDR6X provides better performance than GDDR6.