Whenever you try formatting a disk or a volume, one of the choices you get is the File system on the drive. On Windows, you’ll get a choice between NTFS, FAT32, and exFAT.
FAT32 and exFAT both represent FAT file systems. NTFS is Microsoft’s proprietary file system developed to overcome all the limitations of the FAT32 file system. Although NTFS superseded FAT32 in the 1990s, the latter is still used a lot even today.
Both file systems differ in properties and working mechanisms. Let’s find out in detail.
Microsoft introduced FAT32 along with Windows 95 in 1996. It is the last of the unextended FAT file systems after FAT12 and FAT16 and was used for all storage disks before the development of NTFS. Now, it is only used in small solid-state storage devices likeflash drives.
All FAT file systems use an index table called File Allocation Table (hence, the name) to determine the location of all files stored in the drive as well as the available storage space. A FAT volume, including FAT32, actually contains the following components:
The system creates a File Allocation Table for a drive when formatting it to a FAT filesystem. FAT32 uses a 32-bit FAT entry, and it classifies each cluster in the volume as:
It also includes other information like thenumber of the next cluster associated with the fileand reserved areas on a disk. The drive also stores a backup of the table for recovery purposes.
Accessing and Storing File in FAT32
The Root Folder only contains information about the starting cluster of a file. So whenever you try accessing a file, your system needs to look up this table to keep checking the numbers of the successive clusters until it reaches the last cluster of the file.
The FAT32 file system regards the other folders and sub-folders as special files with their respective path entries. This way, it can use a similar process to access the files within them by using the data inside the components, other folders and files and the FAT.
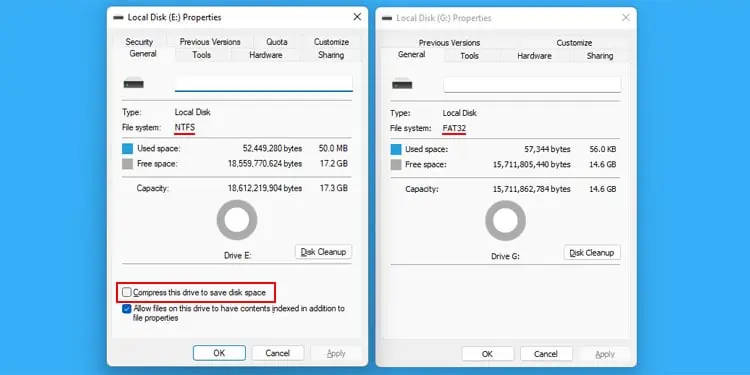
While storing a file on a FAT32 drive, the file system searches for an unused cluster and saves the file in that cluster. If the cluster does not have enough space, it will search for other clusters to hold the remaining data of the file. It will also update the cluster information in the File Allocation Table while storing the data.
Microsoft released the first version of NTFS as the disk file system for Windows NT 3.1 in 1993. Since then, it has long succeeded FAT as the default file system for internal drives.
Like FAT32, the New Technology File System (NTFS) also uses an index table, Master File Table (MFT), to determine the file locations and available storage areas. The components of an NTFS drive include the following:
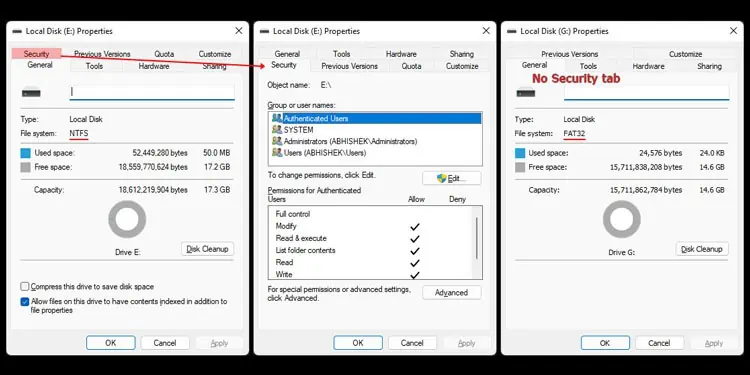
Unlike the FAT, MFT also stores a lot of information regarding file attributes, such as security descriptors and log files, which helps your system maintain all the advanced features that NTFS drives provide.
Accessing and Storing File in NTFS