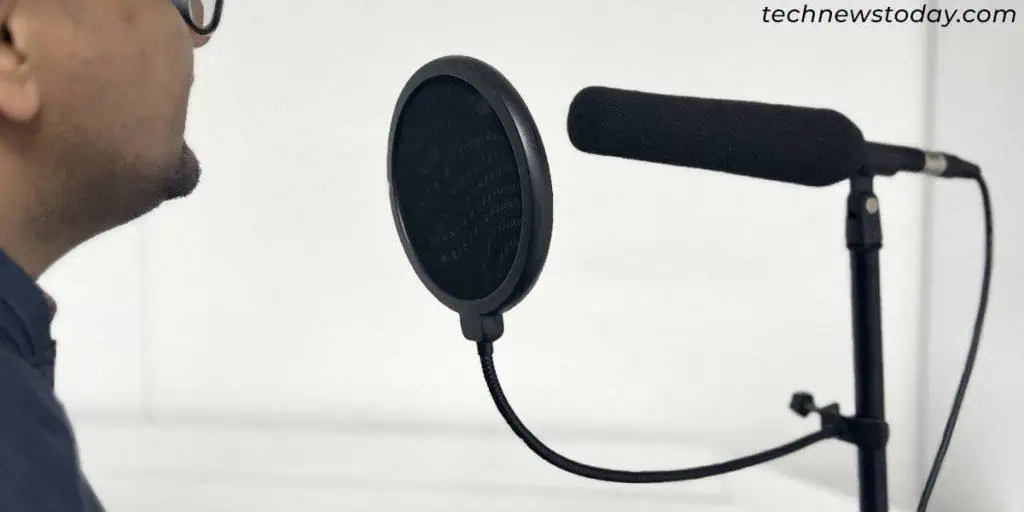
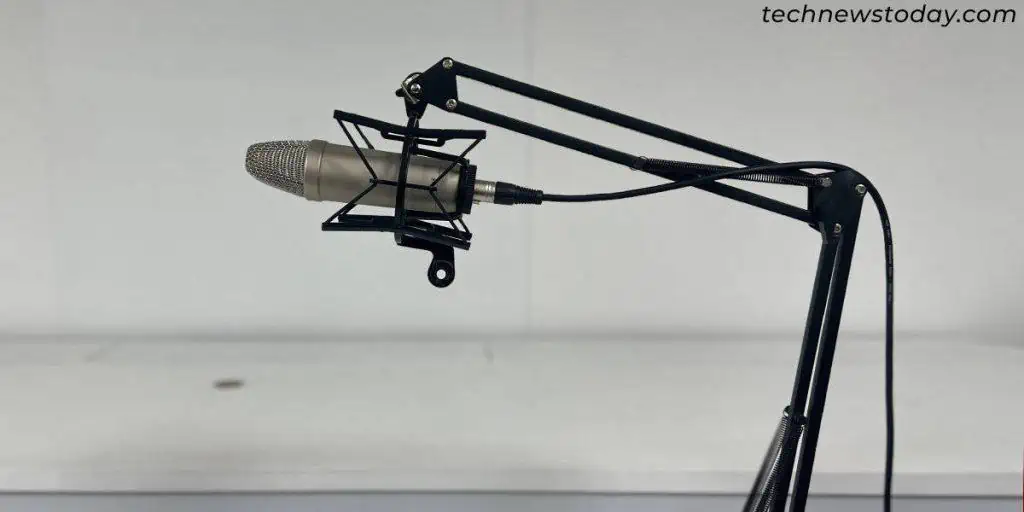
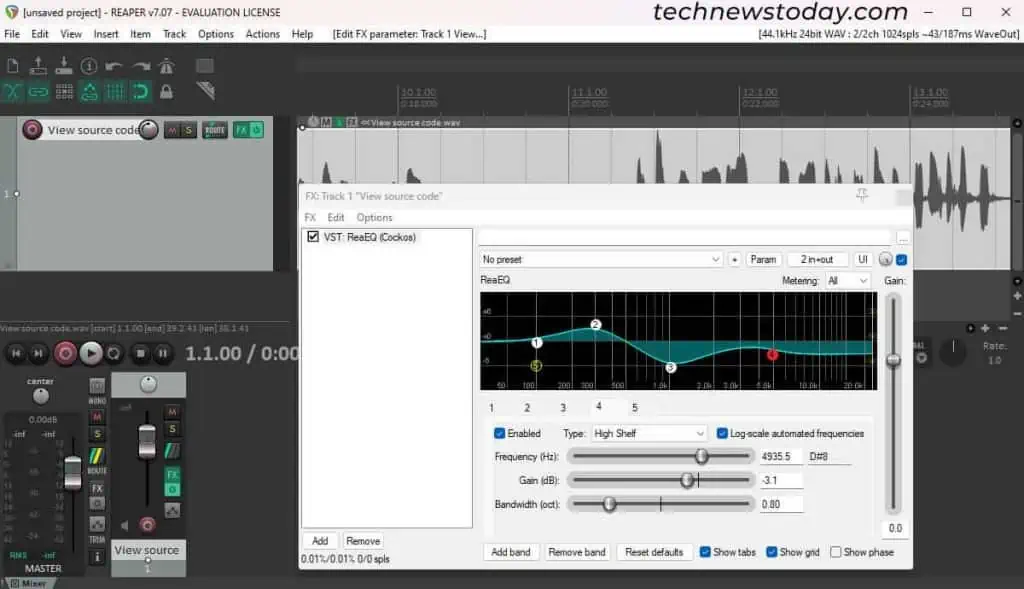
You don’t need to upgrade to a more expensive mic to sound better. With theproper acoustic treatment, tools like apop filter, a boom arm,and my expert tips, you’ll be able to create a professional recording at home in no time.
These tips will cover everything from how toposition your microphoneto usingtools like equalizer and compressorfor the final mixing.
Record in a Quiet Room with Proper Acoustics
You obviously need a quiet room that doesn’t get much disturbance from the outside. But you also have to treat it for a proper acoustic environment.

As the subject of Acoustic Treatment is very vague, I’ll just talk about the basics. But if you want to learn more, you’ll find tons of resources on the internet.
The walls and corners of the room reflect your voice to the microphone. Since there’s a delay between your original sound and the sound from the reflections, the echoes will mess up your recording.
So, you’ll be using sound absorbers or diffusers to restrict echo and reverberation in your recording. Here’s what you need to know:
It’s also best to use directional mics to eliminate high-frequency sounds like keyboard and mic clicks.
However, these mics will capture low-frequency noises from all directions anyway. So you’ll have to rely on your room acoustics, and the post-processing to account for them.
Understand the Type of Your Mic
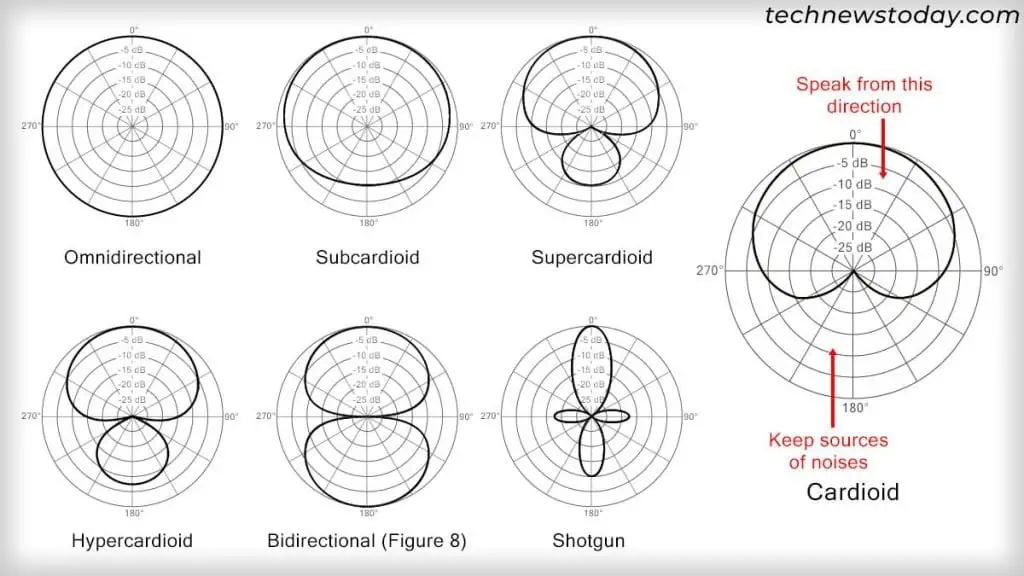
Different types of mics are suited for different positioning while recording. One of the most important aspects you need to pay attention to is thepolar pattern (directivity)of your microphone.
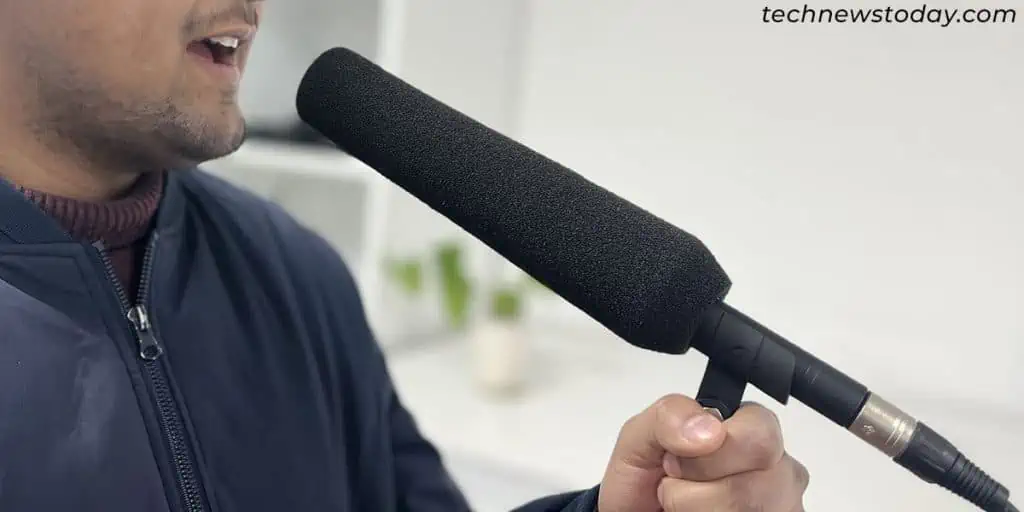

This pattern describes the directions from where the mic picks up the sound. Some common examples are:
You should always speak or record from the proper side. Also, ensure to keep all unmanageable sources of background noises on the suppressed side.
Other than the polar pattern, different mics havedifferent address types. Top-address mics are more sensitive to the direction they are pointed at, and side-address mics are more sensitive to the sound from the sides.
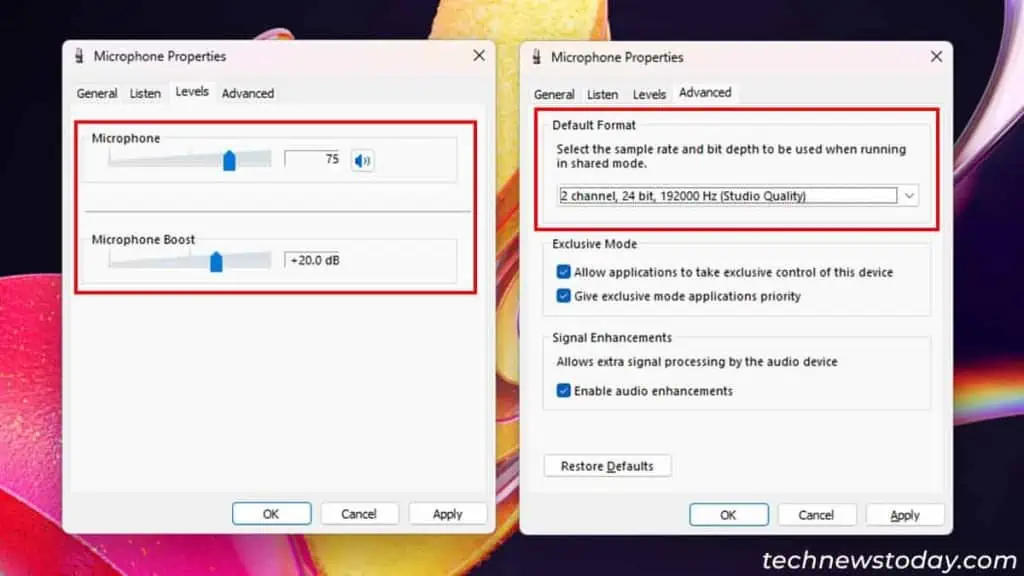
you may find out the polar pattern and address type of mic from its official source. If not, test out your microphone by recording at different orientations and directions accordingly.