Whenever you try copying or moving a file to a folder when your current user account or computer does not have the write permissions, you will encounter the Destination Folder Access Denied error. It can happen on a local, external, or even a network shared drive/folder.
Apart from the usual write permissions of a folder, some group policy settings can also impose write restrictions on removable storage, resulting in this error.
Provide Permissions for a User Account
The NTFS drives (local or external) in Windows have a security feature called Access Control Lists (ACLs), which determines the owner of a file/folder and the user permissions for the file/folder.
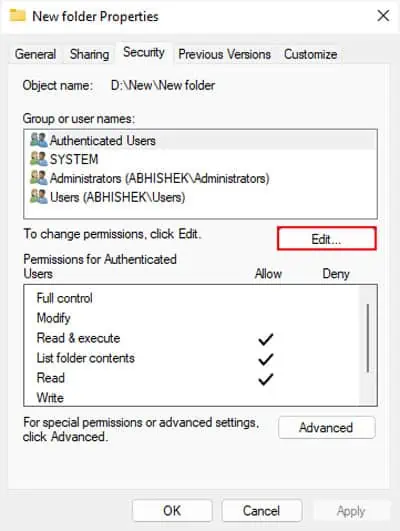
The write permissions of a folder specify whether a user account or group can copy/move an item into the folder or modify its contents. If the current user does not have such permission, you will get this error if you attempt to write to the folder.
You need to change the permissions for the user account through an administrator account to resolve the issue.
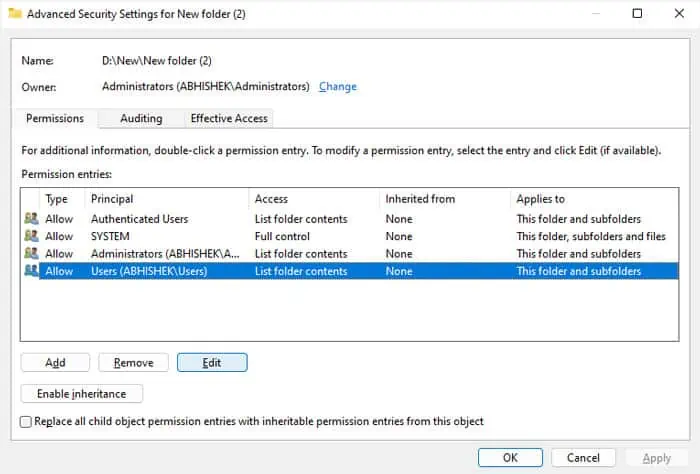
Here, we are only providing full access to theUsersgroup (which includes all user accounts) or onlyyour user account. But if you need to provide access for other user groups as well (for instance network groups), you need to give full permissions to the group,Everyone.
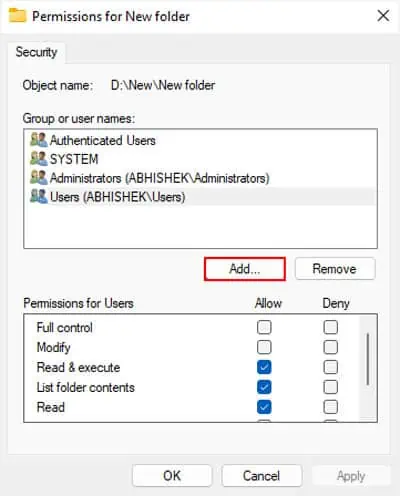
For root directory inside external drives, it’s best to selectEveryoneinstead of just Users or an user account.
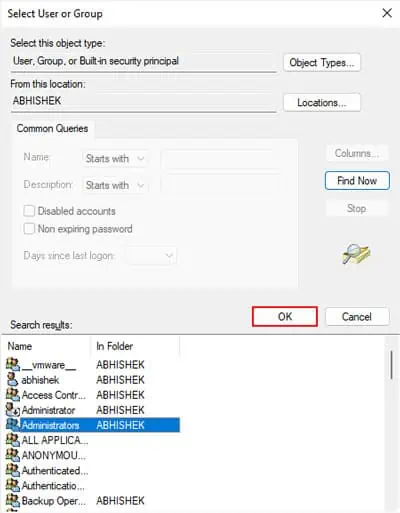
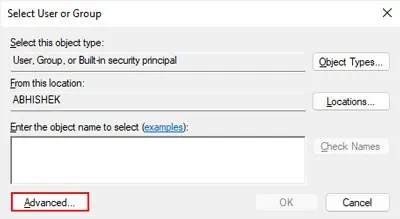
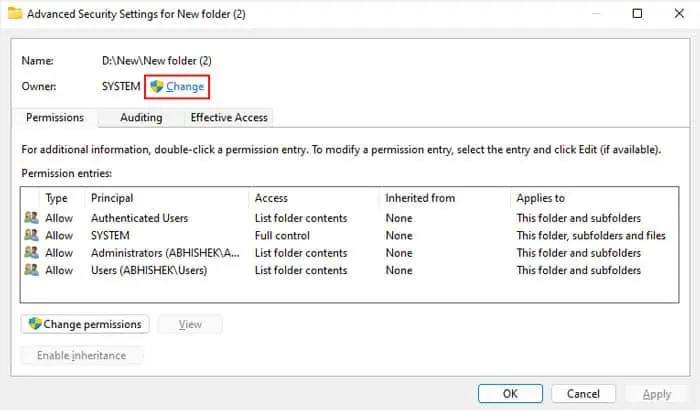
First, log in with an admin account. Then, you need to check whether the admin account or Administrators user group (that includes all admin accounts) is the current owner.
If one of the aboveis the current owner, the Add icon or the permission checkboxes are not grayed out. So you may directly edit the permission settings.
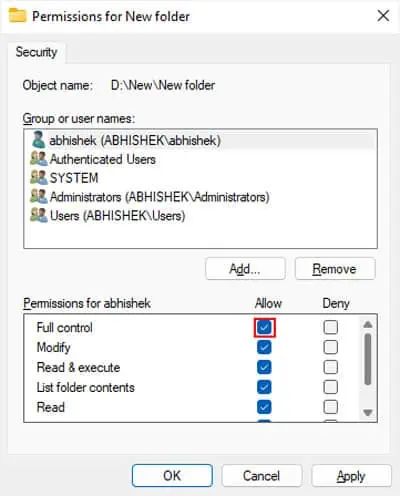
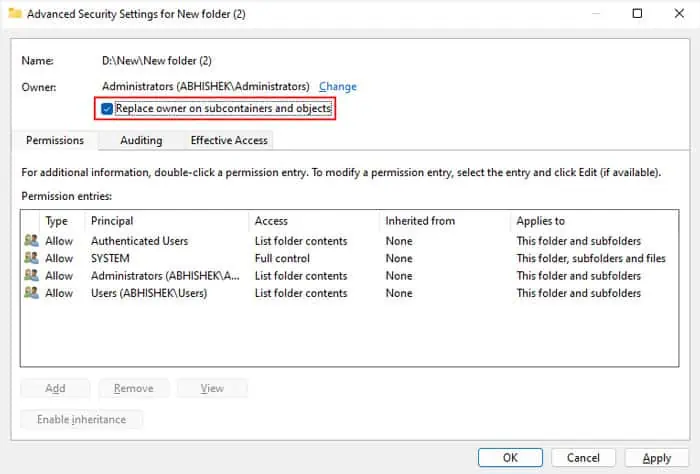
If the icons are grayed out, the current owner issome other group or account. So, you need to change the owner to the admin account or Administrators first and then change the permissions.
Provide Permissions for User Account using Command Prompt
you may also perform the above processusing Command Prompt. It may be easier than the graphical method above if you are familiar with using command-line interfaces.
Also, it does the same task as the graphical method. So you may skip it if you have already performed the above solution.
Provide Permissions for Network Share