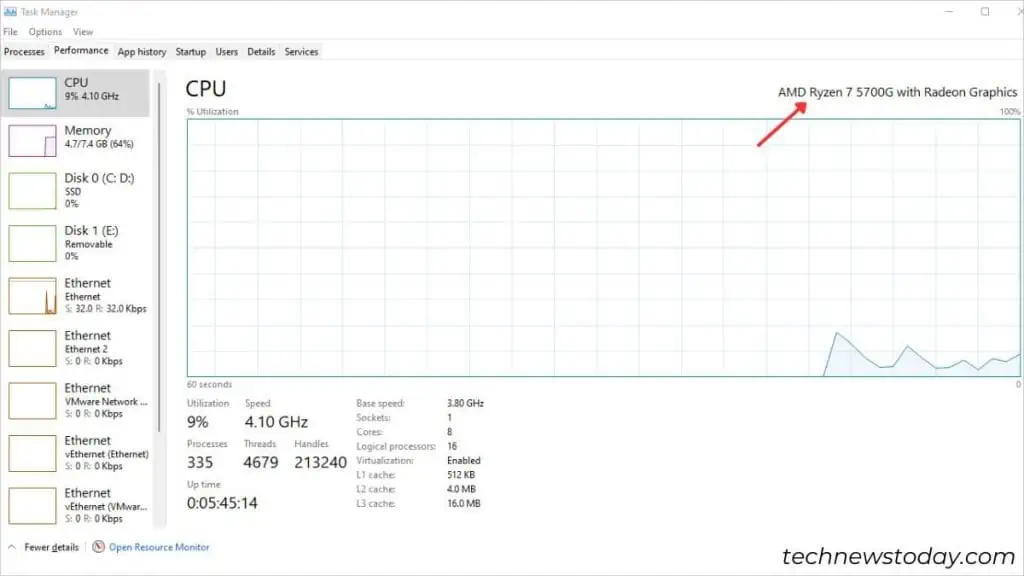
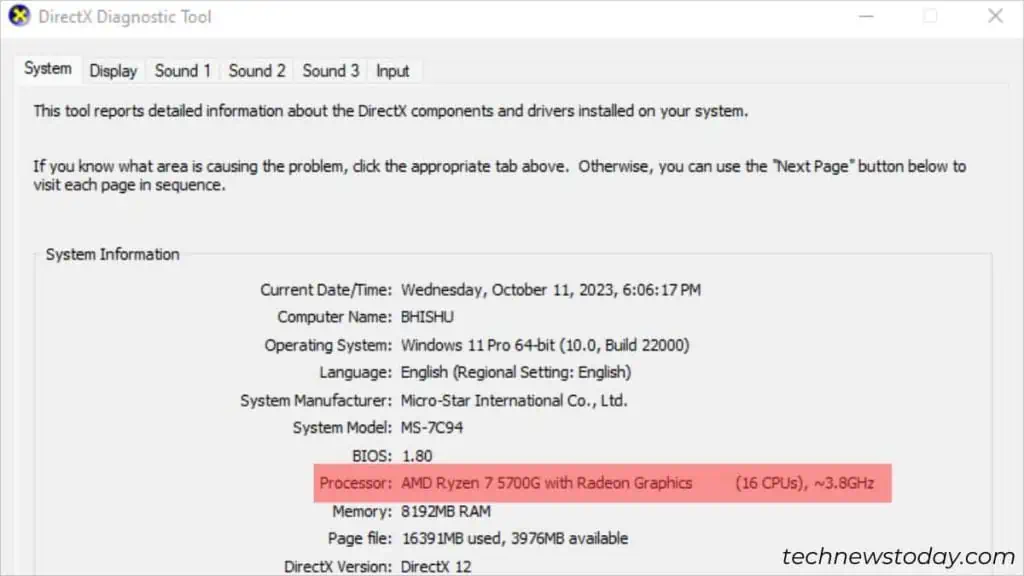
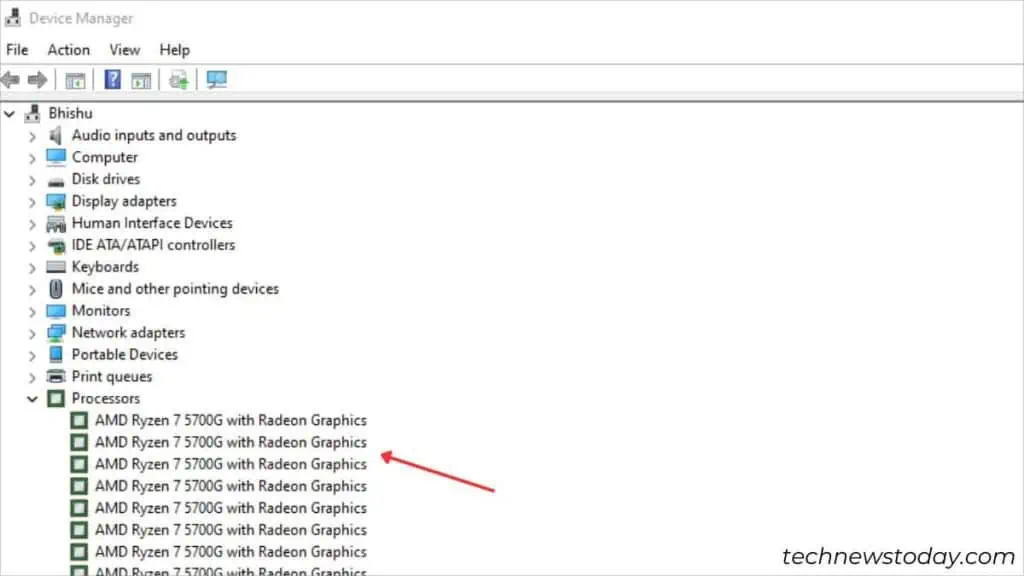
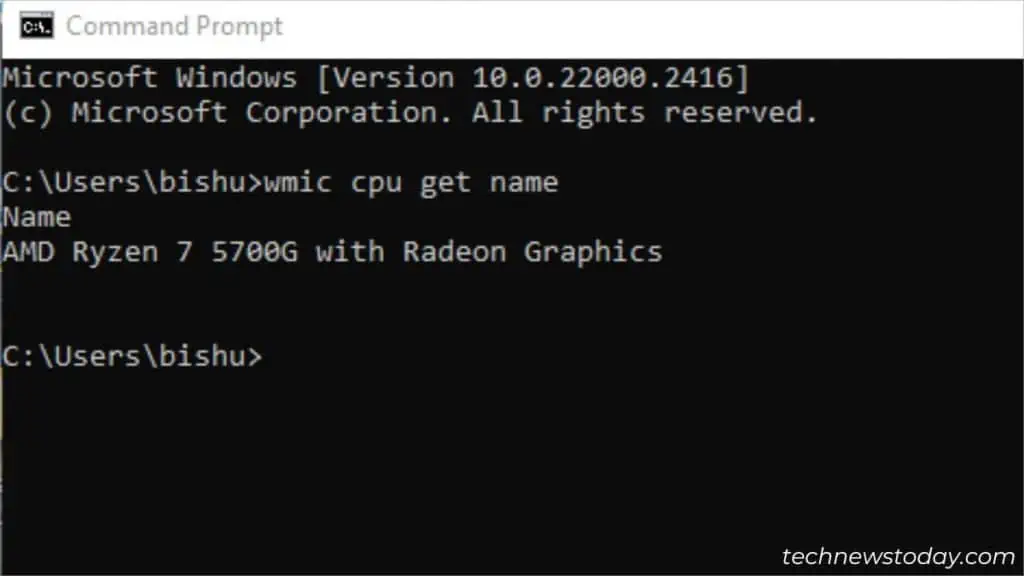
To check what CPU your computer is using, there are several built-in or OEM-based utilities available.
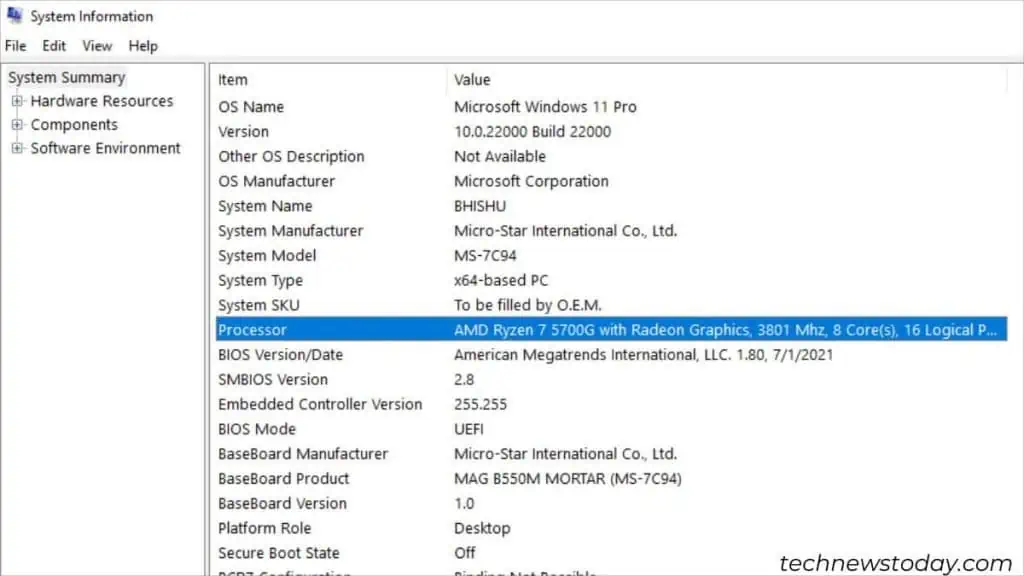
The simplest way is to access the System Information utility. Just type “system” in the Start menu and select “System Information“. This will display your CPU name, speed, cores, and other specifications.
As a hardware enthusiast, I prefer usingCPU-Z. It provides the name, codename, and other specifications in much greater detail.
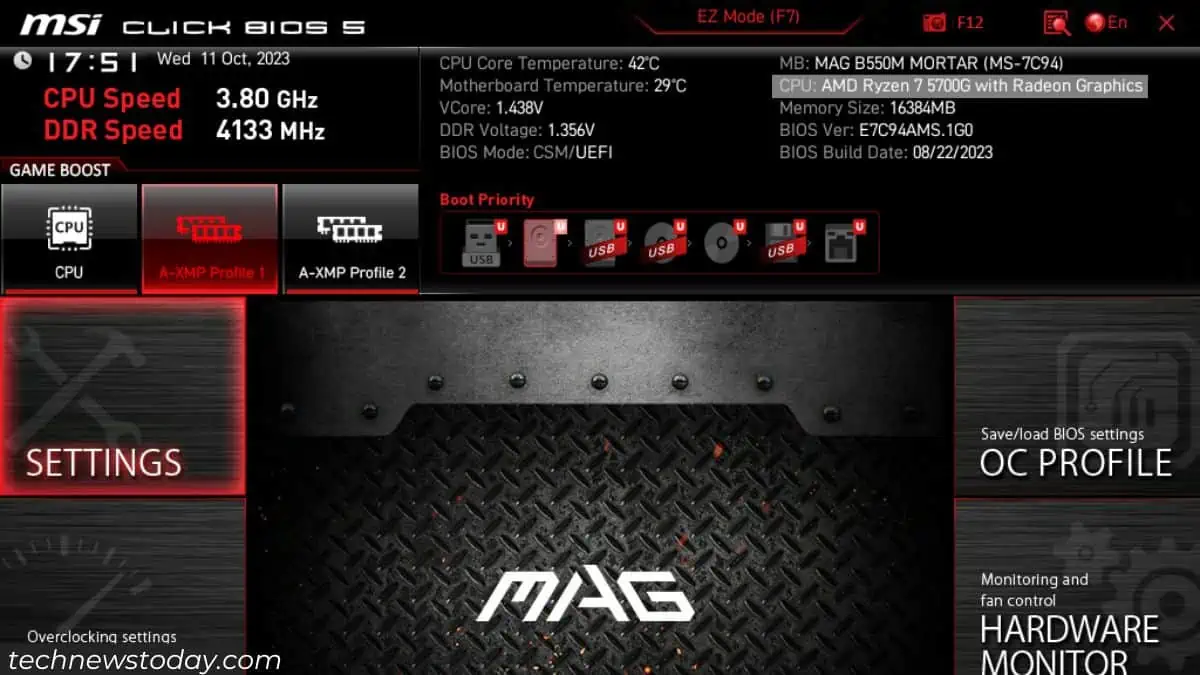
For cases when theOS isn’t booting up, I like to check this directly from theBIOS/UEFI utility.
Without further delay, let’s jump into the different ways to find out the CPU details.
Whether running a Legacy or UEFI BIOS, you may quickly retrieve yourPC specificationshere. Especially, if you’re keen to know your CPU details for troubleshootingNO BOOTissues.
Toenter the BIOS utility, the standard keys areDel and F2. The best approach would be repeatedly pressing or holding the appropriate one when yourPC is performing POST.
The exact field to check the CPU information can vary dependingwhat motherboard you rock. Below is the general idea on both Easy and Advanced modes:
For instance, inMSI CLICK BIOS5, I can monitor all my hardware from thetopmost sectionas demonstrated below.
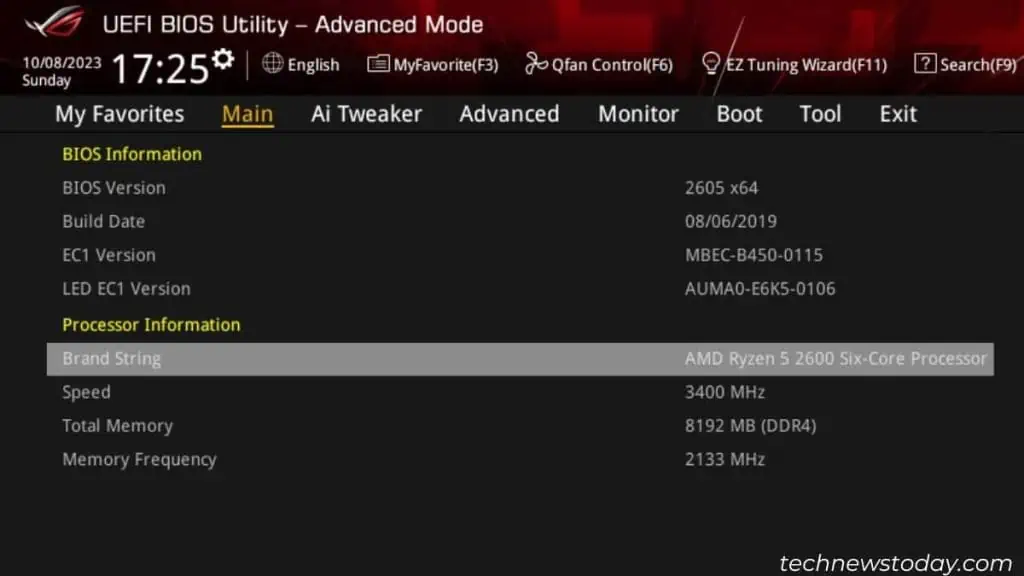
In theASUS UEFI Utility’s Advanced mode, the CPU information is indicated in theBrand Stringfield.
Use OS-based GUI Utilities
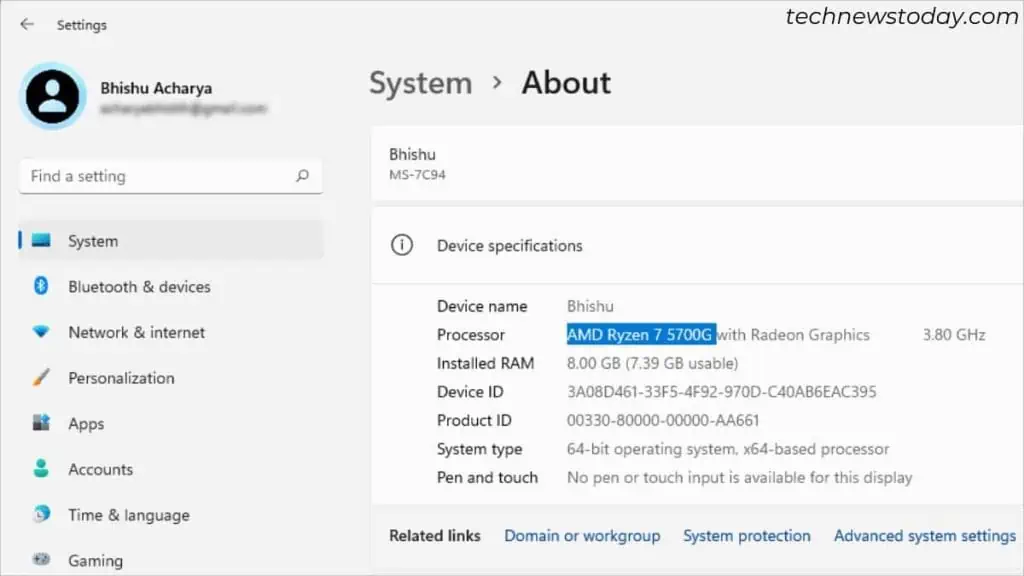
If you’re already in the OS environment, you may try different Windows-based utilities to check CPU details. Here are a few ones that I recommend:
For MAC Users:Press theAppleicon and selectAbout this Mac. Check theProcessorfield that lists the exact model, speed, and cores.
Execute Dedicated Commands
GUI methods are simple and straightforward. But it still requires you to navigate to different sections just to get a single CPU detail. If you opt for a Command Line Interface, the task comes down to executing a single command.